Computational modeling of an early evolutionary stage of
... Computational modeling of an early evolutionary stage of the nervous system ...
... Computational modeling of an early evolutionary stage of the nervous system ...
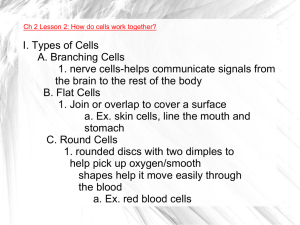
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
... C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
... C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
therapeutic approaches and perspective
... repairing or chimeraplast, using a synthetic blend of DNA and the related RNA, which tricks the patient's own cells to repair the mutation. The chimeraplasts match the patients' own DNA except for where the mutation occurs, attach to the DNA, and then activate DNA repair mechanisms. ...
... repairing or chimeraplast, using a synthetic blend of DNA and the related RNA, which tricks the patient's own cells to repair the mutation. The chimeraplasts match the patients' own DNA except for where the mutation occurs, attach to the DNA, and then activate DNA repair mechanisms. ...
Front matter
... pluripotent and are derived from an early embryo in the blastocyst stage. Many consider this type of stem cell research unethical because of the moral debate over the status of the embryo. Researchers believe these cells hold great potential for disease treatment, but embryonic stem cells have not y ...
... pluripotent and are derived from an early embryo in the blastocyst stage. Many consider this type of stem cell research unethical because of the moral debate over the status of the embryo. Researchers believe these cells hold great potential for disease treatment, but embryonic stem cells have not y ...
Unit 5 Cellular & Organismal Reproduction
... • Each chromosome has a homologue, or a chromosome that carries the same type of information as another chromosome • The chromosomes may have different versions of the genes but the genes code for the same type of information ...
... • Each chromosome has a homologue, or a chromosome that carries the same type of information as another chromosome • The chromosomes may have different versions of the genes but the genes code for the same type of information ...
AP Bio Chapter 47 – Animal Development Review Guide
... In non–amniotic species, unevenly distributed cytoplasmic determinants in the egg cell are important in establishing the body axes and in setting up differences between the blastomeres resulting from cleavage of the zygote. Cells that receive different cytoplasmic determinants undergo different fate ...
... In non–amniotic species, unevenly distributed cytoplasmic determinants in the egg cell are important in establishing the body axes and in setting up differences between the blastomeres resulting from cleavage of the zygote. Cells that receive different cytoplasmic determinants undergo different fate ...
Cell Specialization and Organization
... Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perfo ...
... Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perfo ...
what know about protists cells and human body
... the intestinal tract removes solid wastes, the skin and lungs aid in the transfer of thermal energy from the body. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are needed or produced, responding to changing demands. The human body has a set of systems, which ...
... the intestinal tract removes solid wastes, the skin and lungs aid in the transfer of thermal energy from the body. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are needed or produced, responding to changing demands. The human body has a set of systems, which ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... cells • 1855 Virchow proposed that all new cells come from cells that already exist. ...
... cells • 1855 Virchow proposed that all new cells come from cells that already exist. ...
CELL SPECIALIZATION - Biology with Miss Amy
... When a cell is modified from the general structure – parts removed or added. The specialized cell now performs one major task that will contribute to the ...
... When a cell is modified from the general structure – parts removed or added. The specialized cell now performs one major task that will contribute to the ...
CELLS
... 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? ...
... 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? ...
Unit 03 - fixurscore
... 4. Guard cell (stomata): Allows O2 and CO2 to pass in and out the leaf. They can change their shape thus can open and close their holes. 5. Red blood cells: It transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues. It has no nucleus, t has hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface are ...
... 4. Guard cell (stomata): Allows O2 and CO2 to pass in and out the leaf. They can change their shape thus can open and close their holes. 5. Red blood cells: It transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues. It has no nucleus, t has hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface are ...
UNIT 1 LESSON 4 Specialised cells
... the cell membrane which holds the contents of the egg together, the nucleus which is fertilised by the male sperm to form a new chicken (if it is visible), the albumen (egg white) which forms the cytoplasm. The ova is a specialised cell having its own food store in the yolk which is designed to prov ...
... the cell membrane which holds the contents of the egg together, the nucleus which is fertilised by the male sperm to form a new chicken (if it is visible), the albumen (egg white) which forms the cytoplasm. The ova is a specialised cell having its own food store in the yolk which is designed to prov ...
Respiratory System
... Correct CH & Collect Clean out notes OBJ How the respiratory system cleans the air before it reaches the lungs Understand Organs=tissues=cells What are the parts of a cell ...
... Correct CH & Collect Clean out notes OBJ How the respiratory system cleans the air before it reaches the lungs Understand Organs=tissues=cells What are the parts of a cell ...
Cillia and flagella
... Cilia and flagella Cilium , flagellum are projections of cells that can move both in an undulating fashion like a whip or stiffly like an oar .cilia are short (2-10 µm ) while flagella are longer (usually no more than 200 µm).Ciliated cells are critical to our respiratory health and to the ability t ...
... Cilia and flagella Cilium , flagellum are projections of cells that can move both in an undulating fashion like a whip or stiffly like an oar .cilia are short (2-10 µm ) while flagella are longer (usually no more than 200 µm).Ciliated cells are critical to our respiratory health and to the ability t ...
levels of organization directed reading
... into five categories: cells, tissues, organs, systems, organism. When we are organizing these parts, you can consider them as levels or parts of a whole. Organisms are made of multiple systems; each system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissue ...
... into five categories: cells, tissues, organs, systems, organism. When we are organizing these parts, you can consider them as levels or parts of a whole. Organisms are made of multiple systems; each system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissue ...
I`m Bigger Than You
... I’m Bigger Than You An organ, such as the heart, is made up of groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The heart is a pump that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is primarily made up of muscle tissue, but also contains connective and nerve tissue. Howeve ...
... I’m Bigger Than You An organ, such as the heart, is made up of groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The heart is a pump that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is primarily made up of muscle tissue, but also contains connective and nerve tissue. Howeve ...
Carcinogenesis – The Development of Cancer
... The cells of the cancer, at least at its beginning, must have been derived from a single cell that went wrong. The cell must have independent ability to divide continuously and out of control. The cell must be able to separate from its neighbouring cells and move to a new location where a new mass o ...
... The cells of the cancer, at least at its beginning, must have been derived from a single cell that went wrong. The cell must have independent ability to divide continuously and out of control. The cell must be able to separate from its neighbouring cells and move to a new location where a new mass o ...
found in all eukaryotes
... Mitochondria have their own nuclei and can reproduce like in muscle tissue. ...
... Mitochondria have their own nuclei and can reproduce like in muscle tissue. ...
Cellular organisation
... Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialise throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. ...
... Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialise throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. ...
I am a sperm cell
... Function: A PHLOEM cell transports food and nutrients from the leaves to storage organs and growing parts of the plant. A PHLOEM cell moves food and nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant, because the food is being made in the leaves by photosynthesis and stored in other parts of the ...
... Function: A PHLOEM cell transports food and nutrients from the leaves to storage organs and growing parts of the plant. A PHLOEM cell moves food and nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant, because the food is being made in the leaves by photosynthesis and stored in other parts of the ...
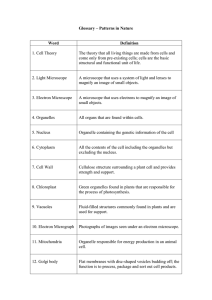
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... A group of organs working together to perform a similar function. ...
... A group of organs working together to perform a similar function. ...
kakamega south cemtral districts mock examination
... a) Meiosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form four haploid daughter cells; while mitosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form two diploid daughter cells; b) Lead to formation of haploid gamete cells who through fussion maintains the ...
... a) Meiosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form four haploid daughter cells; while mitosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form two diploid daughter cells; b) Lead to formation of haploid gamete cells who through fussion maintains the ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.