ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 38
... Free-living flatworms belong to the class Turbellaria. The classes Monogenea, Trematoda and Cestoda are all parasitic. All these groups lack circulatory or respiratory systems, relying instead on diffusion over the body surface (aided by their flat shape to increase the SA:V ratio) and, in the case ...
... Free-living flatworms belong to the class Turbellaria. The classes Monogenea, Trematoda and Cestoda are all parasitic. All these groups lack circulatory or respiratory systems, relying instead on diffusion over the body surface (aided by their flat shape to increase the SA:V ratio) and, in the case ...
Cells Study Guide
... Levels of Organization (CTOS) o Organelle – small structures found inside of cells that perform life processes for cells (i.e. nucleus, mitochondria) o Cell – the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life o Tissue – a group of cells with the same function o Organ – a group ...
... Levels of Organization (CTOS) o Organelle – small structures found inside of cells that perform life processes for cells (i.e. nucleus, mitochondria) o Cell – the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life o Tissue – a group of cells with the same function o Organ – a group ...
Cells Study Guide
... Levels of Organization (CTOS) for living things made of many cells o Organelle – small structures found inside of cells that perform life processes for cells (i.e. nucleus, mitochondria) o Cell – the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life (i.e. red blood cell, brain cell ...
... Levels of Organization (CTOS) for living things made of many cells o Organelle – small structures found inside of cells that perform life processes for cells (i.e. nucleus, mitochondria) o Cell – the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life (i.e. red blood cell, brain cell ...
Cells
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
7.2 Many organisms, including humans, have specialized organ
... the organism alive. Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 3. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and gr ...
... the organism alive. Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 3. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and gr ...
Trott Lecture 3 PPT
... •Wipe area before/after work and if spills occurring during work with 70% ethanol •Work quickly to minimize exposure ...
... •Wipe area before/after work and if spills occurring during work with 70% ethanol •Work quickly to minimize exposure ...
DNA damage (Comet Assay) as biomarker of Cd exposure in
... Copper oxide (CuO) is one of the most widely used nanoparticle applications in consumer products. They are extensively used in microelectronics, cosmetics and catalysts. In the present study, the DNA damaging potential of CuO-NPs in the marine eastern mussel Mytilus trossulus was evaluated and compa ...
... Copper oxide (CuO) is one of the most widely used nanoparticle applications in consumer products. They are extensively used in microelectronics, cosmetics and catalysts. In the present study, the DNA damaging potential of CuO-NPs in the marine eastern mussel Mytilus trossulus was evaluated and compa ...
Test Study Guide-cell processes_ homeostasis2
... Date(s): Red Day: Monday, February 9 or Black Day: Tuesday, February 10 Cells and Heredity Text Lesson 5: Homeostasis and Cell Processes-pages 50-61 SHORT ANSWER: Know the four things that cells need to maintain homeostasis: obtain and use energy, make new cells, exchange materials, and eliminate ...
... Date(s): Red Day: Monday, February 9 or Black Day: Tuesday, February 10 Cells and Heredity Text Lesson 5: Homeostasis and Cell Processes-pages 50-61 SHORT ANSWER: Know the four things that cells need to maintain homeostasis: obtain and use energy, make new cells, exchange materials, and eliminate ...
organs-on-a-chip - Federation of American Societies for
... The National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health, the US Food and Drug Administration, and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency are funding a number of projects to advance organs- and humans-on-chips. These groups and other international agencies ...
... The National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health, the US Food and Drug Administration, and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency are funding a number of projects to advance organs- and humans-on-chips. These groups and other international agencies ...
Press Release - MWM
... Professor Schöler: Simplifying the Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Until recently, all four transcription factors of the quartet Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc and Klf4 were essential to successfully reprogram adult stem cells into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. In 2009 the research group of ...
... Professor Schöler: Simplifying the Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Until recently, all four transcription factors of the quartet Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc and Klf4 were essential to successfully reprogram adult stem cells into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. In 2009 the research group of ...
Cells and Organs
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
TWO TYPES OF CELLS
... Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die ...
... Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die ...
Cells - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
Q11 Outline the formation, structure and function of the adult red
... Myeloid progenitor à differentiates into erythroid line The erythroid line begins with the proerythroblast, a nucleated cell. As it differentiates into a reticulocyte it decreases in size, gradually losing ...
... Myeloid progenitor à differentiates into erythroid line The erythroid line begins with the proerythroblast, a nucleated cell. As it differentiates into a reticulocyte it decreases in size, gradually losing ...
Unit A: Chapter 1: Comparing Living Things Lesson 1: Is It Living or
... All living things are made up of cells, which are the smallest units of life. A cell membrane keeps cell contents contained and acts as a protective barrier between the cell’s external environment and its interior. The nucleus controls the functions of other cell parts and is surrounded by cytoplasm ...
... All living things are made up of cells, which are the smallest units of life. A cell membrane keeps cell contents contained and acts as a protective barrier between the cell’s external environment and its interior. The nucleus controls the functions of other cell parts and is surrounded by cytoplasm ...
of the cell - MrMsciences
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
Lab 4: Unicellular Algae, and Multicellular Algae
... genus of algae. Plants are less than a meter in length. Each branch has a thickened midrib and thinner tissue on either side. Some species form gas bladders that provide buoyancy when the plant is submerged in calm water. Fucus forms specialized reproductive structures at the end of its branches cal ...
... genus of algae. Plants are less than a meter in length. Each branch has a thickened midrib and thinner tissue on either side. Some species form gas bladders that provide buoyancy when the plant is submerged in calm water. Fucus forms specialized reproductive structures at the end of its branches cal ...
Human Anatomy
... Organs – different tissues working together to do a special function Organ Systems – several organs working together ...
... Organs – different tissues working together to do a special function Organ Systems – several organs working together ...
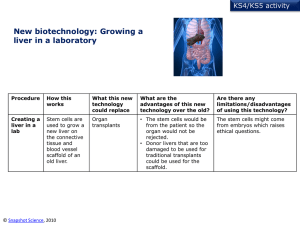
Multicellular Organisms - Thomas A. Stewart Secondary School
... begin as stem cells. These are unspecialized cells capable of developing into many different types of cell. Stem cells found in embryos are called embryonic stem cells and develop into all the different types of cell in the body. In the earliest stages of development, stem cells simply divide to pro ...
... begin as stem cells. These are unspecialized cells capable of developing into many different types of cell. Stem cells found in embryos are called embryonic stem cells and develop into all the different types of cell in the body. In the earliest stages of development, stem cells simply divide to pro ...
Living Systems
... • A cell is the basic unit of a living system. • A group of specialized cells that performs a particular function is called a tissue. • An organ is a group of tissues that works together to carry out a set of functions. • A group of organs that works together to perform a set of functions is called ...
... • A cell is the basic unit of a living system. • A group of specialized cells that performs a particular function is called a tissue. • An organ is a group of tissues that works together to carry out a set of functions. • A group of organs that works together to perform a set of functions is called ...
Cells and Systems Notes Topic 1 1. What are five characteristics that
... 9. What 2 parts of a plant cell aren’t found in an animal cell and explain why they aren’t found in animal cells? ...
... 9. What 2 parts of a plant cell aren’t found in an animal cell and explain why they aren’t found in animal cells? ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CELLS
... Organism- any living thing Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smallest part of ...
... Organism- any living thing Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smallest part of ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.