Ch 16 Powerpt - Plain Local Schools
... A. Most bacteria do not cause disease and many can be helpful to humans or other organisms B. Prokaryotes help cycle nutrients between organisms, the soil and the atmosphere C. The are two Types of Prokaryotes 1. Archaea- which means “ancient” live in some of the most extreme environments on Earth 2 ...
... A. Most bacteria do not cause disease and many can be helpful to humans or other organisms B. Prokaryotes help cycle nutrients between organisms, the soil and the atmosphere C. The are two Types of Prokaryotes 1. Archaea- which means “ancient” live in some of the most extreme environments on Earth 2 ...
APES-Cycles-of
... Phosphorus is an important building block of DNA and ATP; all living things must have phosphorus P is found in rocks, and enters food webs when plants take up phosphorus found in soil Only one that doesn’t cycle through the atmosphere! (no gaseous form) P is a limiting factor for primary productivit ...
... Phosphorus is an important building block of DNA and ATP; all living things must have phosphorus P is found in rocks, and enters food webs when plants take up phosphorus found in soil Only one that doesn’t cycle through the atmosphere! (no gaseous form) P is a limiting factor for primary productivit ...
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
... Packaging of these molecules into “protobionts” droplets with membranes that maintained an internal chemistry different from the surroundings. ...
... Packaging of these molecules into “protobionts” droplets with membranes that maintained an internal chemistry different from the surroundings. ...
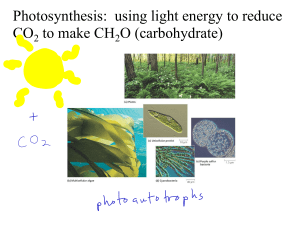
Photosynthesis
... Green plants [that is plants containing chlorophyll] make their own basic food by the process of photosynthesis. This process can be represented by the following summary equation – Carbon dioxide 6CO2 ...
... Green plants [that is plants containing chlorophyll] make their own basic food by the process of photosynthesis. This process can be represented by the following summary equation – Carbon dioxide 6CO2 ...
Guided Reading and Study Chapter 3.3 Photosynthesis Teacher
... 3. a. Capturing the sun’s energy b. Producing sugars 4. Chlorophyll 5. true 6. Stomata are small openings on the undersides of the leaves through which carbobn dioxide enters the plant. 7. c,d 8. false 9. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O - C6H12O6 + 6 O2 10. Yields 11. a, c 12. a, b, c REVIEW & REINFORCE ...
... 3. a. Capturing the sun’s energy b. Producing sugars 4. Chlorophyll 5. true 6. Stomata are small openings on the undersides of the leaves through which carbobn dioxide enters the plant. 7. c,d 8. false 9. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O - C6H12O6 + 6 O2 10. Yields 11. a, c 12. a, b, c REVIEW & REINFORCE ...
File - Hawk Nation Biology
... Lacks organelles Variety of shapes Variety of growth patterns Two kingdoms: Eubacteria and Archaebacteria ...
... Lacks organelles Variety of shapes Variety of growth patterns Two kingdoms: Eubacteria and Archaebacteria ...
Plant Cell Structures Quiz - cK-12
... c) They capture light energy from the sun and use it with carbon dioxide and oxygen to produce sugars for food. d) They capture light energy from the sun and use it with sugars to produce water and carbon dioxide. ...
... c) They capture light energy from the sun and use it with carbon dioxide and oxygen to produce sugars for food. d) They capture light energy from the sun and use it with sugars to produce water and carbon dioxide. ...
Photosynthesis Occurs in the Chloroplasts
... • the solar panel of the plant • arranged on the stem to maximize light absorption • used to capture light energy for photosynthesis • the chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis So where does most photosynthesis take place in the leaf? ...
... • the solar panel of the plant • arranged on the stem to maximize light absorption • used to capture light energy for photosynthesis • the chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis So where does most photosynthesis take place in the leaf? ...
Transpiration 1. Plants lose water through the stomata in their leaves
... Photosynthesis, Respiration, Transpiration Photosynthesis 1. Sunlight hits the chloroplasts in the plant cells and starts a chemical reaction. 2. Plants take in water through their roots and carbon dioxide through the stomata on their leaves. 3. The water and carbon dioxide are combined, in t ...
... Photosynthesis, Respiration, Transpiration Photosynthesis 1. Sunlight hits the chloroplasts in the plant cells and starts a chemical reaction. 2. Plants take in water through their roots and carbon dioxide through the stomata on their leaves. 3. The water and carbon dioxide are combined, in t ...
Additional
... very fact that fish and bacteria survived as one does not mean that animals will be able to photosynthesize anytime soon. ...
... very fact that fish and bacteria survived as one does not mean that animals will be able to photosynthesize anytime soon. ...
Gene Duplication in the Mo-Fe Protein of Nitrogenase
... plants • catalyzes the conversion of molecular nitrogen (N2) from the air into ammonia (NH3). • It is found in a variety of bacteria, some of them symbiotic with plants. ...
... plants • catalyzes the conversion of molecular nitrogen (N2) from the air into ammonia (NH3). • It is found in a variety of bacteria, some of them symbiotic with plants. ...
No Slide Title
... fix carbon are called C3 plants. Ex. cereals, peanuts, tobacco, spinach, sugar beets, soybeans, most trees & lawn grasses. ...
... fix carbon are called C3 plants. Ex. cereals, peanuts, tobacco, spinach, sugar beets, soybeans, most trees & lawn grasses. ...
Document
... Nearly all 1500 species are marine Include kelp and some of largest algae Some are annuals some live up to 7 years Most are found in temperate or polar habitats ...
... Nearly all 1500 species are marine Include kelp and some of largest algae Some are annuals some live up to 7 years Most are found in temperate or polar habitats ...
Simplified Photosynthesis
... Thylakoids are arranged in stacks known as grana(plural) or granum(singular). (stack or stacks of pancake) The Calvin cycle or Dark Reaction takes place in the stroma, the region outside the thylakoid membranes. (syrup surrounding the pancakes) ...
... Thylakoids are arranged in stacks known as grana(plural) or granum(singular). (stack or stacks of pancake) The Calvin cycle or Dark Reaction takes place in the stroma, the region outside the thylakoid membranes. (syrup surrounding the pancakes) ...
Tree of Life
... In lecture 2 we discussed Earth’s early environment (hot, rocky!), gave a very basic definition of what life is (not all agreed), and described how the first polymers (long-chained molecules) of nucleotides and polypeptides probably came into being from the most basic and common elements (CHON- PS) ...
... In lecture 2 we discussed Earth’s early environment (hot, rocky!), gave a very basic definition of what life is (not all agreed), and described how the first polymers (long-chained molecules) of nucleotides and polypeptides probably came into being from the most basic and common elements (CHON- PS) ...
Notes Photosynthesis
... Capture light energy for photosynthesis Use sunlight to make ATP and NADPH In thylakoid membranes of chloroplast H2O is a substrate provides electrons and hydrogen ions O2 is a product of this reaction ...
... Capture light energy for photosynthesis Use sunlight to make ATP and NADPH In thylakoid membranes of chloroplast H2O is a substrate provides electrons and hydrogen ions O2 is a product of this reaction ...
Quizlet Voc Ch 18 19 Classification
... kingdom composed of heterotrophs; many obtain energy and nutrients from dead organic matter, have cell walls made of chitin; once grouped with plants ...
... kingdom composed of heterotrophs; many obtain energy and nutrients from dead organic matter, have cell walls made of chitin; once grouped with plants ...
Photosynthesis
... Plants are green because they reflect the green wavelengths and absorb (and use) the others. ...
... Plants are green because they reflect the green wavelengths and absorb (and use) the others. ...
Exam #2
... dry ice (CO2). Reduced forms of many elements - C, S, N, H, metals, etc. are completely missing. Preexisting organic compounds, combined forms of N-compounds, and nitrate (as in fertilizers) are also absent. Assuming the temperature could be raised to make water available for life, consider the pros ...
... dry ice (CO2). Reduced forms of many elements - C, S, N, H, metals, etc. are completely missing. Preexisting organic compounds, combined forms of N-compounds, and nitrate (as in fertilizers) are also absent. Assuming the temperature could be raised to make water available for life, consider the pros ...
Topic 2.5 Function
... create these fuels • E.g. Limestone (calcium carbonate)formed by shells/corals being crushed and compressed into sedimentary rock • Weathering of Limestone, acid rain, and burning of fossil fuels return Carbon back into atmosphere ...
... create these fuels • E.g. Limestone (calcium carbonate)formed by shells/corals being crushed and compressed into sedimentary rock • Weathering of Limestone, acid rain, and burning of fossil fuels return Carbon back into atmosphere ...
Where does a tree get its mass? - Biology 1510 Biological Principles
... • Light energy is used to generate a proton gradient across a membrane for chemiosmotic ATP synthesis. • Light energy is used to reduce electron carriers that are used, in turn, to reduce inorganic carbon (CO2) to make carbohydrate (CH2O). • A key innovation enabled cyanobacteria to take electrons f ...
... • Light energy is used to generate a proton gradient across a membrane for chemiosmotic ATP synthesis. • Light energy is used to reduce electron carriers that are used, in turn, to reduce inorganic carbon (CO2) to make carbohydrate (CH2O). • A key innovation enabled cyanobacteria to take electrons f ...
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria /saɪˌænoʊbækˈtɪəriə/, also known as Cyanophyta, is a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis. The name ""cyanobacteria"" comes from the color of the bacteria (Greek: κυανός (kyanós) = blue). They are often called blue-green algae (but some consider that name a misnomer, as cyanobacteria are prokaryotic and algae should be eukaryotic, although other definitions of algae encompass prokaryotic organisms).By producing gaseous oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis, cyanobacteria are thought to have converted the early reducing atmosphere into an oxidizing one, causing the ""rusting of the Earth"" and causing the Great Oxygenation Event, dramatically changing the composition of life forms on Earth by stimulating biodiversity and leading to the near-extinction of anaerobic organisms (that is, oxygen-intolerant). Symbiogenesis argues that the chloroplasts found in plants and eukaryotic algae evolved from cyanobacterial ancestors via endosymbiosis. Cyanobacteria are arguably the most successful group of microorganisms on earth. They are the most genetically diverse; they occupy a broad range of habitats across all latitudes, widespread in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems, and they are found in the most extreme niches such as hot springs, salt works, and hypersaline bays. Photoautotrophic, oxygen-producing cyanobacteria created the conditions in the planet's early atmosphere that directed the evolution of aerobic metabolism and eukaryotic photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria fulfill vital ecological functions in the world's oceans, being important contributors to global carbon and nitrogen budgets.– Stewart and Falconer