10-6 - Physics
... through a horizontal constricted pipe Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
... through a horizontal constricted pipe Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
Mathematical Formulation- System of PDE for the Two–Fluid
... Using the conservation laws and the thermodynamic relations, the two-fluid flow can be modeled with associated PDEs. To simplify the 3-D problem, we will first study the case where all quadratic terms and small terms are zero. To modify the equations, we make the assumption that the thermodynamic st ...
... Using the conservation laws and the thermodynamic relations, the two-fluid flow can be modeled with associated PDEs. To simplify the 3-D problem, we will first study the case where all quadratic terms and small terms are zero. To modify the equations, we make the assumption that the thermodynamic st ...
Chapter 6 - UniMAP Portal
... energy due to the position of the system in a potential field (such as a gravitational or electromagnetic field). Internal energy (U) all energy possessed by a system other than kinetic and potential energy; or Energy due to translation, rotation, vibration & electromagnetic interactions of ...
... energy due to the position of the system in a potential field (such as a gravitational or electromagnetic field). Internal energy (U) all energy possessed by a system other than kinetic and potential energy; or Energy due to translation, rotation, vibration & electromagnetic interactions of ...
Document
... Simulation Step • “Solve” Navier-Stokes equation for each grid cell to compute change in velocity: ...
... Simulation Step • “Solve” Navier-Stokes equation for each grid cell to compute change in velocity: ...
ConcepTest Question
... a. The mass flow into the control volume is equal to the mass flow out of the control volume b. The rate of change of the amount of mass in the control volume is balanced by the net rate at which mass flows out through the control surface c. The accumulation of mass in the control volume is balanced ...
... a. The mass flow into the control volume is equal to the mass flow out of the control volume b. The rate of change of the amount of mass in the control volume is balanced by the net rate at which mass flows out through the control surface c. The accumulation of mass in the control volume is balanced ...
Drag and Drag Coefficients
... general the drag cannot be predicted. For spheres and other regular shapes at low fluid velocities, the flow patterns and drag forces can be estimated from published correlations or by numerical calculations using the general momentum balance equations. ...
... general the drag cannot be predicted. For spheres and other regular shapes at low fluid velocities, the flow patterns and drag forces can be estimated from published correlations or by numerical calculations using the general momentum balance equations. ...
Lecture 5
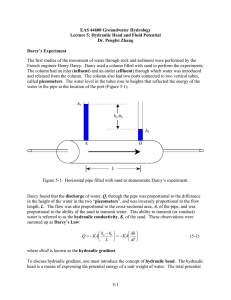
... In deriving the above expression for hydraulic head we have ignored the fact that moving fluid tends to remain in motion due to its kinetic energy (Ek). This energy is equal to one-half the product of the fluid mass (m) and the square of the fluid velocity (v): Ek = ...
... In deriving the above expression for hydraulic head we have ignored the fact that moving fluid tends to remain in motion due to its kinetic energy (Ek). This energy is equal to one-half the product of the fluid mass (m) and the square of the fluid velocity (v): Ek = ...
20-AEEM-641 - Department of Aerospace Engineering and
... H. Schlichting, Boundary Layer Theory, 7th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 1979. T. Cebeci and P. Bradshaw, Momentum Transfer in Boundary Layers, McGraw-Hill, 1977. ...
... H. Schlichting, Boundary Layer Theory, 7th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 1979. T. Cebeci and P. Bradshaw, Momentum Transfer in Boundary Layers, McGraw-Hill, 1977. ...
Entrainment is defined as the process whereby a material diffuses
... aspirator yielded some properties of entrainment. Using the principle of the conservation of momentum the behavior of the flow of water was predicted and tested. The prediction made was that entrainment would increase the volume measured at the downstream pipe and subsequently, decrease the speed of ...
... aspirator yielded some properties of entrainment. Using the principle of the conservation of momentum the behavior of the flow of water was predicted and tested. The prediction made was that entrainment would increase the volume measured at the downstream pipe and subsequently, decrease the speed of ...
Hopkins Imaging Conference Poster Contest
... the presence of axial contrast concentration gradients in obstructed arteries, but the mechanism responsible for this phenomenon is not well understood. We use computational fluid dynamics to study intracoronary contrast dispersion and the correlation of concentration gradients with intracoronary bl ...
... the presence of axial contrast concentration gradients in obstructed arteries, but the mechanism responsible for this phenomenon is not well understood. We use computational fluid dynamics to study intracoronary contrast dispersion and the correlation of concentration gradients with intracoronary bl ...
Lecture 5
... length/time! Examples of hydraulic conductivity (found experimentally) for various materials are given in our text on page 26 – Table 2.1. Notice that the hydraulic conductivity of gravel and sand is higher than that for silt or clay – does this make sense with which materials allow water to flow mo ...
... length/time! Examples of hydraulic conductivity (found experimentally) for various materials are given in our text on page 26 – Table 2.1. Notice that the hydraulic conductivity of gravel and sand is higher than that for silt or clay – does this make sense with which materials allow water to flow mo ...
17. Electrophoresis and Magnetohydrodynamics
... Figure 7. Absorbance versus time for both by electromagnets or permanent magnets, can be used to the upper and lower perform separations, injections, and manipulations in microfluidic channels while pulsating the magnetic field channels. (10 s on/20 s off) with Given the already widespread use of ma ...
... Figure 7. Absorbance versus time for both by electromagnets or permanent magnets, can be used to the upper and lower perform separations, injections, and manipulations in microfluidic channels while pulsating the magnetic field channels. (10 s on/20 s off) with Given the already widespread use of ma ...
Download PDF
... separates from the edge of the flow restriction is more predictable and consistent. This separation of the fluid creates the low pressure zone on the downstream side of the restriction, thus allowing that restriction to function as the primary element of a DP meter. Depending on the type of restrict ...
... separates from the edge of the flow restriction is more predictable and consistent. This separation of the fluid creates the low pressure zone on the downstream side of the restriction, thus allowing that restriction to function as the primary element of a DP meter. Depending on the type of restrict ...
The Physics of Sailing - University of Colorado Boulder
... where V∞ is the speed of the uniform fluid flow very far from the body and CL is the dimensionless lift coefficient. CL depends, in general, on the geometry of the body and on the orientation of the body in the fluid. Knowing CL for a given object at a given orientation in a fluid flow provides all ...
... where V∞ is the speed of the uniform fluid flow very far from the body and CL is the dimensionless lift coefficient. CL depends, in general, on the geometry of the body and on the orientation of the body in the fluid. Knowing CL for a given object at a given orientation in a fluid flow provides all ...
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""