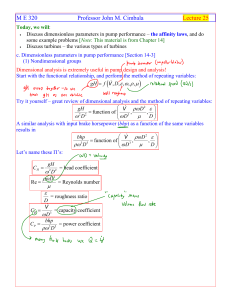
Section_10_Resistivi..
... where Dn nT / B2 is a diffusion coefficient, and VE B / B2 is the MHD velocity resulting from the applied electric field. The first term represents diffusion across the confining field lines, and the second is a generally inward convection. The characteristic time for diffusion of the plas ...
... where Dn nT / B2 is a diffusion coefficient, and VE B / B2 is the MHD velocity resulting from the applied electric field. The first term represents diffusion across the confining field lines, and the second is a generally inward convection. The characteristic time for diffusion of the plas ...
Physics 6B Hydrodynamics
... laminar (not turbulent) flow. But many fluids do not behave so nicely. To measure the importance of viscosity on a flowing fluid we can calculate its Reynolds number. ...
... laminar (not turbulent) flow. But many fluids do not behave so nicely. To measure the importance of viscosity on a flowing fluid we can calculate its Reynolds number. ...
11.2 Physics 6B Fluids - Hydrodynamics
... laminar (not turbulent) flow. But many fluids do not behave so nicely. To measure the importance of viscosity on a flowing fluid we can calculate its Reynolds number. ...
... laminar (not turbulent) flow. But many fluids do not behave so nicely. To measure the importance of viscosity on a flowing fluid we can calculate its Reynolds number. ...
How Airplanes Fly: Lift and Circulation
... ρhwv∞vy, and the upward force exerted on the wing by the air is −ρhwv∞vy which is > 0 because vy < 0. A vertical section of the closed path that includes vy contributes hvy < 0 to Γ. Thus the lifting force/length is Fy/w = −ρv∞Γ > 0. In 1902 Martin Kutta in Germany published “Lifting forces in flowi ...
... ρhwv∞vy, and the upward force exerted on the wing by the air is −ρhwv∞vy which is > 0 because vy < 0. A vertical section of the closed path that includes vy contributes hvy < 0 to Γ. Thus the lifting force/length is Fy/w = −ρv∞Γ > 0. In 1902 Martin Kutta in Germany published “Lifting forces in flowi ...
Week_2
... absence of any force the momentum of a body stays constant. This is another conservation principle. The only way momentum can change is by application of a force (Newton's 2nd law): d(mV)/dt=F. This statement is more general than, mdV/dt=F, because it allows for changes in mass. It illustrate well w ...
... absence of any force the momentum of a body stays constant. This is another conservation principle. The only way momentum can change is by application of a force (Newton's 2nd law): d(mV)/dt=F. This statement is more general than, mdV/dt=F, because it allows for changes in mass. It illustrate well w ...
Microsoft Word - 12.800 chapter 1,`06
... unchanged but otherwise act to deform it, as in the example above. Some materials can act as elastic solids when they are forced on short time scales, i.e. when they are sharply struck but deform in a manner like a liquid when the force operates over a long time, like silly putty. Or, a less “silly” ...
... unchanged but otherwise act to deform it, as in the example above. Some materials can act as elastic solids when they are forced on short time scales, i.e. when they are sharply struck but deform in a manner like a liquid when the force operates over a long time, like silly putty. Or, a less “silly” ...
Induced-charge Electro-osmosis
... Nonlinear electro-osmosis at a polarizable surface Sensitive to size, shape, voltage, time-dependence,… Unifies & extends ACEO, Russian colloid literature, ... Open theoretical questions ...
... Nonlinear electro-osmosis at a polarizable surface Sensitive to size, shape, voltage, time-dependence,… Unifies & extends ACEO, Russian colloid literature, ... Open theoretical questions ...
Chapter12_level_2
... The principal relationships that constitute the equation for the simplified law of hemodynamics are developed throughout the next group of slides. As with the resistance equation and the flow equation (continuity equation), instead of just writing the equation outright, we will consider different ph ...
... The principal relationships that constitute the equation for the simplified law of hemodynamics are developed throughout the next group of slides. As with the resistance equation and the flow equation (continuity equation), instead of just writing the equation outright, we will consider different ph ...
Small-size permanent magnet system for contactless
... resolution of the model experiments by using an arrangement of smaller permanent magnets. Introduction Local velocity or even volumetric flow rate measurements of liquid metals is still an unsolved problem. The commercial classical measurement techniques (fly-wheel, Pitot tube, hot wire probes, etc. ...
... resolution of the model experiments by using an arrangement of smaller permanent magnets. Introduction Local velocity or even volumetric flow rate measurements of liquid metals is still an unsolved problem. The commercial classical measurement techniques (fly-wheel, Pitot tube, hot wire probes, etc. ...
Principal technical particulars <
... With regards to working conditions, the UNI standards show the following: a) Normal use fans: Suitable fan for non-toxic, non corrosive, uninflammable air, without liquid or solid particles, with a maximum temperature of 80°C, or 40°C in case the motor and the fan supports are crossed by the conveye ...
... With regards to working conditions, the UNI standards show the following: a) Normal use fans: Suitable fan for non-toxic, non corrosive, uninflammable air, without liquid or solid particles, with a maximum temperature of 80°C, or 40°C in case the motor and the fan supports are crossed by the conveye ...
Fluid Pressure
... fluid increases, the pressure within decreases Lift allows birds, and planes to fly-creating an upward force Pascal’s Principle says pressure in a fluid is greater at the source of pressure ...
... fluid increases, the pressure within decreases Lift allows birds, and planes to fly-creating an upward force Pascal’s Principle says pressure in a fluid is greater at the source of pressure ...
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""