Middle Ear Fluid and Tubes
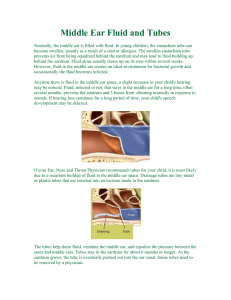
... Normally, the middle ear is filled with fluid. In young children, the eustachian tube can become swollen, usually as a result of a cold or allergies. The swollen eustachian tube prevents air from being equalized behind the eardrum and may lead to fluid building up behind the eardrum. Fluid alone usu ...
... Normally, the middle ear is filled with fluid. In young children, the eustachian tube can become swollen, usually as a result of a cold or allergies. The swollen eustachian tube prevents air from being equalized behind the eardrum and may lead to fluid building up behind the eardrum. Fluid alone usu ...
Cone-jet Electrosprays, or Colloid Thrusters
... Using data for Formamide and assuming ηmin = 0.5 and K = 2 Si/m, we get Emax = 1.63 V/nm. It is known experimentally that at normal fields in the range 1 − 2 V/nm individual ions begin to be extracted from the liquid by field evaporation. Once the threshold field is reached, field emission increases ...
... Using data for Formamide and assuming ηmin = 0.5 and K = 2 Si/m, we get Emax = 1.63 V/nm. It is known experimentally that at normal fields in the range 1 − 2 V/nm individual ions begin to be extracted from the liquid by field evaporation. Once the threshold field is reached, field emission increases ...
LES_of_Tube_Bundles_S_Banhamadouche,_I_Afgan,_D_Laurance,_C_Moulinec,_Nureth_11_France.pdf
... any shape), one can take ∆ = 2Ω , where Ω is the volume of a cell. The Smagorinsky constant, CS, is set to 0.065 . In the collocated finite volume approach used here, all variables are located at the centers of gravity of the cells (which can be of any shape). The momentum equations are solved by co ...
... any shape), one can take ∆ = 2Ω , where Ω is the volume of a cell. The Smagorinsky constant, CS, is set to 0.065 . In the collocated finite volume approach used here, all variables are located at the centers of gravity of the cells (which can be of any shape). The momentum equations are solved by co ...
Tuesday March 18 - University of Florida
... Fluids take the form of the container. When shear stress is applied they flow. The molecules in fluids are in constant random motion (Brownian motion). ...
... Fluids take the form of the container. When shear stress is applied they flow. The molecules in fluids are in constant random motion (Brownian motion). ...
chapter 9 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Viscosity is usually studied by allowing the fluid to flow through a tube of circular cross section and measuring the rate of flow. From this rate, and with the knowledge of the pressure acting and the dimensions of the tube, the coefficient of viscosity can be calculated on the basis of a theory de ...
... Viscosity is usually studied by allowing the fluid to flow through a tube of circular cross section and measuring the rate of flow. From this rate, and with the knowledge of the pressure acting and the dimensions of the tube, the coefficient of viscosity can be calculated on the basis of a theory de ...
Tracking Space-Filling Structures in Turbulent Flows
... O( nmlog(nCmax )) and adapted it to our purpose [2]. The algorithm is based on the idea that a LSAP can be solved by transforming it into a flow network and solving the corresponding maximum-weight flow problem. To transform a bi-partite graph G into a flow network N, a source node and a sink node a ...
... O( nmlog(nCmax )) and adapted it to our purpose [2]. The algorithm is based on the idea that a LSAP can be solved by transforming it into a flow network and solving the corresponding maximum-weight flow problem. To transform a bi-partite graph G into a flow network N, a source node and a sink node a ...
Pressure field and buoyancy. Elementary fluid dynamics. Bernoulli
... (SG=0.9). Determine new differential reading of pressure in A decreased by 25 kPa. • 2.61 An open tank contains gasoline r=700kg/cm at a depth of 4m. The gate is 4m high and 2m wide. Water is slowly added to the empty side of the tank. At what depth h the gate ...
... (SG=0.9). Determine new differential reading of pressure in A decreased by 25 kPa. • 2.61 An open tank contains gasoline r=700kg/cm at a depth of 4m. The gate is 4m high and 2m wide. Water is slowly added to the empty side of the tank. At what depth h the gate ...
L6 Protoplanetary disks Part II
... Benz, R. Kallenbach & G.W. Lugmair, Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht). They however agree on the fact that turbulence must play a certain role in causing the abnormal viscosity. ...
... Benz, R. Kallenbach & G.W. Lugmair, Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht). They however agree on the fact that turbulence must play a certain role in causing the abnormal viscosity. ...
Numerical Simulation of Blood Flow in Centrifugal Heart
... damages by determining theareas of circulation flow and high pressure gradient and shear stress, although the amount of damage is not realized. Therefore, the possible damages can be reduced by evaluating the locations in which return flow or vertex occurs or disturbance is higher than other areas a ...
... damages by determining theareas of circulation flow and high pressure gradient and shear stress, although the amount of damage is not realized. Therefore, the possible damages can be reduced by evaluating the locations in which return flow or vertex occurs or disturbance is higher than other areas a ...
Coriolis Mass Flowmeters
... The FMC-5000 Series Coriolis Flowmeters should be installed in the orientation that can ensure the measuring tube is filled. For the horizontal installation, the measuring tube should be installed under the pipeline when the process medium is liquid or slurry (shown on Drawing 9) and above the pipel ...
... The FMC-5000 Series Coriolis Flowmeters should be installed in the orientation that can ensure the measuring tube is filled. For the horizontal installation, the measuring tube should be installed under the pipeline when the process medium is liquid or slurry (shown on Drawing 9) and above the pipel ...
Fluids and Fluid Mechanics Fluids in motion – Dynamics Equation of
... Δt Volume Volume Δt Volume ...
... Δt Volume Volume Δt Volume ...
Fluid Mechanics - GTU e
... • Show where fluid mechanics concepts are common with those of solid mechanics and indicate some fundamental areas of difference. • Introduce viscosity and show what are Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids • Define the appropriate physical properties and show how these allow differentiation between s ...
... • Show where fluid mechanics concepts are common with those of solid mechanics and indicate some fundamental areas of difference. • Introduce viscosity and show what are Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids • Define the appropriate physical properties and show how these allow differentiation between s ...
SIMULATION OF FLUID FLOW WITH INTERACTING PARTICLES
... The idea for coexistence of continuous and particle approach in this paper is mainly based on works of Schwarzer et al. [2–4], however new elements have been added to the method and original simulations have been performed. The Finite Difference Method used by Schwarzer has been replaced by Finite E ...
... The idea for coexistence of continuous and particle approach in this paper is mainly based on works of Schwarzer et al. [2–4], however new elements have been added to the method and original simulations have been performed. The Finite Difference Method used by Schwarzer has been replaced by Finite E ...
Materials - UCSI A
... Measure the masses in kilograms of a wide range of solid objects. Then measure their voumes. Use a micrometer or vernier callipers to measure their dimensions if they are regular, or use the method of displacement of a volume of water by a solid with irregular shape. The density can be calculated by ...
... Measure the masses in kilograms of a wide range of solid objects. Then measure their voumes. Use a micrometer or vernier callipers to measure their dimensions if they are regular, or use the method of displacement of a volume of water by a solid with irregular shape. The density can be calculated by ...
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""