PASS Study Guide - McColl Elementary Middle School
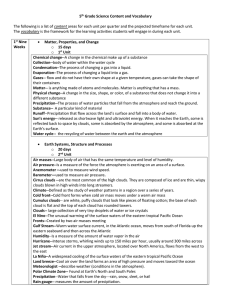
... Exosphere (This is the area where satellites and space shuttles are) Thermosphere (Thickest layer; Contains ionosphere which is electrically charged particles) Mesosphere (Has meteors) Stratosphere (Contains the ozone layer) Troposphere (Layer closest to Earth; Where all weather occurs) *Air pressur ...
... Exosphere (This is the area where satellites and space shuttles are) Thermosphere (Thickest layer; Contains ionosphere which is electrically charged particles) Mesosphere (Has meteors) Stratosphere (Contains the ozone layer) Troposphere (Layer closest to Earth; Where all weather occurs) *Air pressur ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field, Atmosphere and Geology
... • Has the atmosphere always been the same as it is now? How has the atmosphere interacted with the surface? • What kinds of physical processes have produced the planet’s landforms? • Is there life on the planet? How does it interact with the various ecosystems? ...
... • Has the atmosphere always been the same as it is now? How has the atmosphere interacted with the surface? • What kinds of physical processes have produced the planet’s landforms? • Is there life on the planet? How does it interact with the various ecosystems? ...
C1.7 Earth and its a..
... of tectonic plates that are moving very slowly. Give two pieces of evidence that have helped to convince these scientists that the tectonic plates are moving. ...
... of tectonic plates that are moving very slowly. Give two pieces of evidence that have helped to convince these scientists that the tectonic plates are moving. ...
science vocabulary for 5th grade
... Warm front--occur when a particularly warm air mass meets a cooler air mass. Weather --The state of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. Weather is described in terms of variable conditions such as temperature, humidity, wind velocity, precipitation, and barometric pressure. Wind-- Is the ...
... Warm front--occur when a particularly warm air mass meets a cooler air mass. Weather --The state of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. Weather is described in terms of variable conditions such as temperature, humidity, wind velocity, precipitation, and barometric pressure. Wind-- Is the ...
Key Ideas
... differs from those of the other terrestrial planets in its chemical composition, circulation pattern, and temperature profile. The Earth’s atmosphere evolved from being mostly water vapor to being rich in carbon dioxide. A strong greenhouse effect kept the Earth warm enough for water to remain liqui ...
... differs from those of the other terrestrial planets in its chemical composition, circulation pattern, and temperature profile. The Earth’s atmosphere evolved from being mostly water vapor to being rich in carbon dioxide. A strong greenhouse effect kept the Earth warm enough for water to remain liqui ...
Earth Science Spring Semester Final Answer Key
... a. oxides and carbonates. b. ions and isotopes c. silicates and magnetics. d. inorganics and halides. 44. Color is not often a useful identification property because a. some minerals are colorless b. the same mineral can be different colors c. different minerals can be different colors d. some miner ...
... a. oxides and carbonates. b. ions and isotopes c. silicates and magnetics. d. inorganics and halides. 44. Color is not often a useful identification property because a. some minerals are colorless b. the same mineral can be different colors c. different minerals can be different colors d. some miner ...
Unit Three Worksheet – Meteorology/Oceanography
... Difference in height between successive high and low tides Time interval between the passage of successive crests at a stationary point The vertical distance between the trough and crest of a ...
... Difference in height between successive high and low tides Time interval between the passage of successive crests at a stationary point The vertical distance between the trough and crest of a ...
Chapter 3 Jig-Saw
... What is above me? What is below me? What am I made of? What’s my temperature? What state of matter do I consist of? What is my thickness? Why are tectonic plates significant? Describe in your report and in your visual aid how tectonic plates move. Group 2: Asthenosphere What is abo ...
... What is above me? What is below me? What am I made of? What’s my temperature? What state of matter do I consist of? What is my thickness? Why are tectonic plates significant? Describe in your report and in your visual aid how tectonic plates move. Group 2: Asthenosphere What is abo ...
Energy - eBoard
... 24 hours of daylight at 90o North. 57. Winter Solstice in the northern hemisphere is 21 December. Duration of insolation is the shortest. Intensity of insolation is the least. 24 hours of daylight at 90o South. 58. The equatorial region always has approximately 12 hours of daylight all year. Weather ...
... 24 hours of daylight at 90o North. 57. Winter Solstice in the northern hemisphere is 21 December. Duration of insolation is the shortest. Intensity of insolation is the least. 24 hours of daylight at 90o South. 58. The equatorial region always has approximately 12 hours of daylight all year. Weather ...
WEATHER
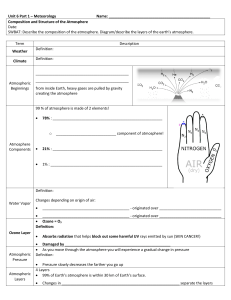
... - 310 miles 2000 oC or higher -50 miles/ -120 oC -31 miles/ 0 oC -ozone layer - 11 miles/ -80 oC - weather takes place ...
... - 310 miles 2000 oC or higher -50 miles/ -120 oC -31 miles/ 0 oC -ozone layer - 11 miles/ -80 oC - weather takes place ...
Version A - Partners4results
... A. The heat in your house will turn on when it gets too cold B. Increase in water vapor in the atmosphere decreases temperature C. If you are tired and get any sleep your level of fatigue decreases D. An increased number of foreclosures on house decrease property value which leads to more foreclosur ...
... A. The heat in your house will turn on when it gets too cold B. Increase in water vapor in the atmosphere decreases temperature C. If you are tired and get any sleep your level of fatigue decreases D. An increased number of foreclosures on house decrease property value which leads to more foreclosur ...
The Difference Between Weather and Climate
... *Condensation: occurs when water vapor condenses *Precipitation: rain, sleet, hail, or snow due to gravity *Ground Water: liquid water collected on the surface of earth *Transpiration: the process of releasing water from plants ...
... *Condensation: occurs when water vapor condenses *Precipitation: rain, sleet, hail, or snow due to gravity *Ground Water: liquid water collected on the surface of earth *Transpiration: the process of releasing water from plants ...
Interior Crust Hydrosphere Atmosphere Magnetosphere Tides
... 238U, which has a half-life of 4.5 billion years, comparable to the age of the Earth. The dating process involves measuring the ratio between the parent nucleus and the daughter nucleus (206Pb in the case of 238U) The Sun and planets should have about the same age. Dating of rocks on Earth, on ...
... 238U, which has a half-life of 4.5 billion years, comparable to the age of the Earth. The dating process involves measuring the ratio between the parent nucleus and the daughter nucleus (206Pb in the case of 238U) The Sun and planets should have about the same age. Dating of rocks on Earth, on ...
Meteorology Chapter 3 Worksheet 2 Name: Circle the letter that
... T F 25) The daily temperature range is greater at higher elevations. T F 26) The influence of altitude upon temperature results in surface temperatures falling more rapidly with height than the normal lapse rate value. T F 27) A leeward coastal city will display climate patterns typical of a ...
... T F 25) The daily temperature range is greater at higher elevations. T F 26) The influence of altitude upon temperature results in surface temperatures falling more rapidly with height than the normal lapse rate value. T F 27) A leeward coastal city will display climate patterns typical of a ...
Quick Review
... warm humid air rises and more warm air rushes in to replace it; begins to rotate as it rises and forms a funnel; sucks objects upward as air rises ...
... warm humid air rises and more warm air rushes in to replace it; begins to rotate as it rises and forms a funnel; sucks objects upward as air rises ...
File
... __________________________________________- lines that connect points of equal temperature By studying isotherm maps you can detect patterns and see the effects of phenomena. ...
... __________________________________________- lines that connect points of equal temperature By studying isotherm maps you can detect patterns and see the effects of phenomena. ...
Astro ch 20
... 2. Earth’s Atmosphere Ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation, and is good conductor Reflects radio waves in the AM range, but transparent to FM and TV ...
... 2. Earth’s Atmosphere Ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation, and is good conductor Reflects radio waves in the AM range, but transparent to FM and TV ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Words
... Unit 3A: Hydrologic Cycle – Create a poster explaining the hydrologic cycle. Be sure to include all vocabulary words. Your poster should act as an advertisement for water ...
... Unit 3A: Hydrologic Cycle – Create a poster explaining the hydrologic cycle. Be sure to include all vocabulary words. Your poster should act as an advertisement for water ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #3 (Chapters 5 and 6
... 7. The most stable type of atmosphere is one in which the temperature actually increases with height. This is called an ________________________________. When there is large scale sinking in the atmosphere (high pressure systems) this is called a _____________________________________________________ ...
... 7. The most stable type of atmosphere is one in which the temperature actually increases with height. This is called an ________________________________. When there is large scale sinking in the atmosphere (high pressure systems) this is called a _____________________________________________________ ...
Introduction to Meteorology Homework #3 (Chapters 5 and 6) Due
... 7. The most stable type of atmosphere is one in which the temperature actually increases with height. This is called an ________________________________. When there is large scale sinking in the atmosphere (high pressure systems) this is called a _____________________________________________________ ...
... 7. The most stable type of atmosphere is one in which the temperature actually increases with height. This is called an ________________________________. When there is large scale sinking in the atmosphere (high pressure systems) this is called a _____________________________________________________ ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Words
... describe the weather for 10 days. Your description must include relative humidity, air pressure, any fronts and pressure systems coming in and the weather they will bring. Air mass ...
... describe the weather for 10 days. Your description must include relative humidity, air pressure, any fronts and pressure systems coming in and the weather they will bring. Air mass ...
ATMO 201: Atmospheric Science
... ◦ Convection: Heat transfer by a fluid (such as water or air): Warm, less-dense air rising In meteorology, we only call vertical motions “convection”, and we use “advection” for horizontal motions such as the wind ...
... ◦ Convection: Heat transfer by a fluid (such as water or air): Warm, less-dense air rising In meteorology, we only call vertical motions “convection”, and we use “advection” for horizontal motions such as the wind ...
document
... ◦ Convection: Heat transfer by a fluid (such as water or air): Warm, less-dense air rising In meteorology, we only call vertical motions “convection”, and we use “advection” for horizontal motions such as the wind ...
... ◦ Convection: Heat transfer by a fluid (such as water or air): Warm, less-dense air rising In meteorology, we only call vertical motions “convection”, and we use “advection” for horizontal motions such as the wind ...
Atmosphere of Earth

The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation).The common name air is given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis. By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air content and atmospheric pressure vary at different layers, and air suitable for the survival of terrestrial plants and terrestrial animals is found only in Earth's troposphere and artificial atmospheres.The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15×1018 kg, three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. The Kármán line, at 100 km (62 mi), or 1.57% of Earth's radius, is often used as the border between the atmosphere and outer space. Atmospheric effects become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft at an altitude of around 120 km (75 mi). Several layers can be distinguished in the atmosphere, based on characteristics such as temperature and composition.The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology). Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann.