Earth`s Layers
... How do Scientists know? • About the interior? • Using observations to make a claim about something we can’t see directly. – Based on inferences. – Scientists use seismic waveswaves produced by earthquakes. • They act differently as they travel through the Earth and they reveal the different layers. ...
... How do Scientists know? • About the interior? • Using observations to make a claim about something we can’t see directly. – Based on inferences. – Scientists use seismic waveswaves produced by earthquakes. • They act differently as they travel through the Earth and they reveal the different layers. ...
11/4/2015 1 Earth: The Active Planet Chapter 11
... Where plates move toward each other, Where plates move away from plates can be pushed upward and each other, molten lava can rise up downward → formation of mountain from below → volcanic activity ranges, some with volcanic activity, earthquakes ...
... Where plates move toward each other, Where plates move away from plates can be pushed upward and each other, molten lava can rise up downward → formation of mountain from below → volcanic activity ranges, some with volcanic activity, earthquakes ...
Chapter Three: The Dynamic Earth
... Made of the geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere Life requires water, moderate temperatures, and a source of energy ...
... Made of the geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere Life requires water, moderate temperatures, and a source of energy ...
Mid-Term exam Study Guide KEY link
... 52) How is Earth’s atmosphere warmed by the greenhouse effect? Earth's atmosphere is warmed by the greenhouse effect because heat radiated from Earth's surface is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere. 53) Where do the rays of the sun strike the Earth the most directly? at the equator 54) What is the ...
... 52) How is Earth’s atmosphere warmed by the greenhouse effect? Earth's atmosphere is warmed by the greenhouse effect because heat radiated from Earth's surface is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere. 53) Where do the rays of the sun strike the Earth the most directly? at the equator 54) What is the ...
Final Exam question sheet Which lines are parallel? latitude Which
... 41. Landslides that occur in mountainous areas with thick accumulations of snow are called avalanche. 42. Preventative measures to minimize disasters is trenches built to divert water around a slope, not building on steep slopes, and building retaining walls to help from rock slides. 43. A large mov ...
... 41. Landslides that occur in mountainous areas with thick accumulations of snow are called avalanche. 42. Preventative measures to minimize disasters is trenches built to divert water around a slope, not building on steep slopes, and building retaining walls to help from rock slides. 43. A large mov ...
“Meteorology”? - U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Resources Page
... • The condensation of water in the atmosphere • Rising air mass cools causing the water vapor to condense into minute ...
... • The condensation of water in the atmosphere • Rising air mass cools causing the water vapor to condense into minute ...
Mtg01
... Notice how the temperature in the vertical varies systematically defining the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere and the thermosphere. The troposphere ends when the temperature ceases to decrease with increasing height, at the so-called tropopause. The temperature ceases to decrease in th ...
... Notice how the temperature in the vertical varies systematically defining the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere and the thermosphere. The troposphere ends when the temperature ceases to decrease with increasing height, at the so-called tropopause. The temperature ceases to decrease in th ...
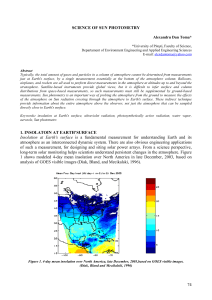
SCIENCE OF SUN PHOTOMETRY
... would produce if there were no atmosphere between the detector and the Sun. Obviouslly, it is not practical actually to measure the voltage outside the atmosphere. However, it is possible to infer what this voltage would be. If a sun photometer views the Sun through various values of relative air ma ...
... would produce if there were no atmosphere between the detector and the Sun. Obviouslly, it is not practical actually to measure the voltage outside the atmosphere. However, it is possible to infer what this voltage would be. If a sun photometer views the Sun through various values of relative air ma ...
Chapter 2
... s is expressed as the number of grams of dissolved salts per kg of fresh water (parts per thousand. Symbol is permille: h) Sea water contains ∼34-36h. ...
... s is expressed as the number of grams of dissolved salts per kg of fresh water (parts per thousand. Symbol is permille: h) Sea water contains ∼34-36h. ...
The Role of the Bacterioneuston in Air
... identified and locally abundant BUT difficult to culture ...
... identified and locally abundant BUT difficult to culture ...
Climate
... NH is tilted most toward the Sun – longest day of the year and shortest night (Summer Solstice – June 21st) NH is tilted most away from the sun – longest night of the year and shortest day (Winter Solstice – December 21st) Day and night are = o Autumnal Equinox – September 21st o Vernal Equinox – Ma ...
... NH is tilted most toward the Sun – longest day of the year and shortest night (Summer Solstice – June 21st) NH is tilted most away from the sun – longest night of the year and shortest day (Winter Solstice – December 21st) Day and night are = o Autumnal Equinox – September 21st o Vernal Equinox – Ma ...
Earth Systems
... • Air deflected by rotation, to right in N hemisphere, to left in S hemisphere ...
... • Air deflected by rotation, to right in N hemisphere, to left in S hemisphere ...
Your Weather Knowledge Study Guide
... Accumulation – when precipitation goes into the ground and/or runs off into a lake, river, ocean or other body of water Evaporation - when liquid water changes into a gas and goes into the air as water vapor. Evaporation occurs faster in warmer climates. Condensation - the process where water vapor ...
... Accumulation – when precipitation goes into the ground and/or runs off into a lake, river, ocean or other body of water Evaporation - when liquid water changes into a gas and goes into the air as water vapor. Evaporation occurs faster in warmer climates. Condensation - the process where water vapor ...
AP Chapter 5 Study Guide - Bennatti
... seismic waves- vibrations that move through rock as a result of an earthquake faults- a fracture in the crust along which rock moves forward and backward, up and down, or side to side. Faults are often found along plate boundaries. focus- the place within the Earth that an earthquake originates epic ...
... seismic waves- vibrations that move through rock as a result of an earthquake faults- a fracture in the crust along which rock moves forward and backward, up and down, or side to side. Faults are often found along plate boundaries. focus- the place within the Earth that an earthquake originates epic ...
The Hadean Outline •Theories on Formation of Solar System, Universe
... –Early Earth “seeded” with life forms (panspermia)? –Not impossible •Search for fossilized life from elsewhere=same criteria as Earth •Search=fruitless The Oxygen Revolution •Early atmosphere=no free oxygen/no ozone layer •Early oceans –rich in dissolved iron/silica ...
... –Early Earth “seeded” with life forms (panspermia)? –Not impossible •Search for fossilized life from elsewhere=same criteria as Earth •Search=fruitless The Oxygen Revolution •Early atmosphere=no free oxygen/no ozone layer •Early oceans –rich in dissolved iron/silica ...
Earth`s Natural Resources
... ocean, and fresh river water mixes with salty ocean water Water monitoring- how? Source of life: water in our environment video ...
... ocean, and fresh river water mixes with salty ocean water Water monitoring- how? Source of life: water in our environment video ...
Khamsi_Spacegrant_pres - Arizona Space Grant Consortium
... Opaque to visible, near-IR wavelengths ...
... Opaque to visible, near-IR wavelengths ...
Chapter 1
... gas constant, T is the mean temperature in the layer between p and p0 , and g is the acceleration due to gravity. ...
... gas constant, T is the mean temperature in the layer between p and p0 , and g is the acceleration due to gravity. ...
Differential Heating, Convection, and Air Pressure
... 100 ml of dry soil. Each container was placed in the sunshine for 20 minutes and then in the shade for 20 minutes. ...
... 100 ml of dry soil. Each container was placed in the sunshine for 20 minutes and then in the shade for 20 minutes. ...
: 3.8 MB - Okala Practitioner
... Over Eme, exposure of liquid lava to water created granite. Lighter per unit volume than lava, granite floated above the lava to form the conEnental plates. Extraordinarily, photosyntheEc algae evolved, g ...
... Over Eme, exposure of liquid lava to water created granite. Lighter per unit volume than lava, granite floated above the lava to form the conEnental plates. Extraordinarily, photosyntheEc algae evolved, g ...
117 Ways to Pass the Earth Science Regents
... 29. The half-life of a radioactive element cannot be changed! 30. Ocean crust is thin and made of basalt. 31. Continental crust is thick and made of granite! ...
... 29. The half-life of a radioactive element cannot be changed! 30. Ocean crust is thin and made of basalt. 31. Continental crust is thick and made of granite! ...
AP Chapter 5 Study Guide - Bennatti
... nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. Some of the pollutants in photochemical smog include peroxyacetyl nitrates (PANs), ozone, and aldehydes. Acid deposition- sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions that react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids that return to the surface as either ...
... nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. Some of the pollutants in photochemical smog include peroxyacetyl nitrates (PANs), ozone, and aldehydes. Acid deposition- sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions that react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids that return to the surface as either ...
Atmosphere of Earth

The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation).The common name air is given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis. By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air content and atmospheric pressure vary at different layers, and air suitable for the survival of terrestrial plants and terrestrial animals is found only in Earth's troposphere and artificial atmospheres.The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15×1018 kg, three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. The Kármán line, at 100 km (62 mi), or 1.57% of Earth's radius, is often used as the border between the atmosphere and outer space. Atmospheric effects become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft at an altitude of around 120 km (75 mi). Several layers can be distinguished in the atmosphere, based on characteristics such as temperature and composition.The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology). Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann.