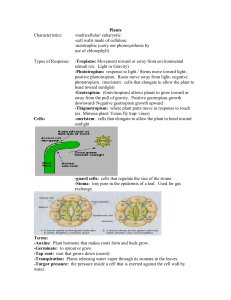
Seedless Plants, Chapter 27
... • Plants: multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic autotrophs • Terrestrial colonization: • Vascular tissue • The seed • The flower ...
... • Plants: multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic autotrophs • Terrestrial colonization: • Vascular tissue • The seed • The flower ...
gloxinia - Super Floral
... ORIGINS Gloxinias are native to Brazil. HISTORY The modern gloxinia is a hybrid of two Brazilian tropical species, Sinningia speciosa and S. maxima. It arose as a chance seedling raised by a Scottish gardener, John Fyfiana, in the 19th century. ...
... ORIGINS Gloxinias are native to Brazil. HISTORY The modern gloxinia is a hybrid of two Brazilian tropical species, Sinningia speciosa and S. maxima. It arose as a chance seedling raised by a Scottish gardener, John Fyfiana, in the 19th century. ...
Kingdom Plantae - Fulton County Schools
... seed coat – protective layer to keep in moisture many have means of dispersal ...
... seed coat – protective layer to keep in moisture many have means of dispersal ...
Chapter 24 Plant Hormones and Tropisms
... • Delays aging of leaves As a result of cytokinin the top carrot is 2x bigger than the other. ...
... • Delays aging of leaves As a result of cytokinin the top carrot is 2x bigger than the other. ...
Plant Transport and Tropisms
... – Pressure Flow Hypothesis (source-sink) • Food moves from an area of high pressure to low pressure ...
... – Pressure Flow Hypothesis (source-sink) • Food moves from an area of high pressure to low pressure ...
6-2.7 Summarize the processes required for plant survival (including
... 6-2.7 Summarize the processes required for plant survival (including photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration). Photosynthesis-Plants are organisms that make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival. The process by which they make this sugar is called photosynthesis. Chloroplasts, found in ...
... 6-2.7 Summarize the processes required for plant survival (including photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration). Photosynthesis-Plants are organisms that make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival. The process by which they make this sugar is called photosynthesis. Chloroplasts, found in ...
Growing Beans - Communication4All
... A bean is planted in the ground. It is dry and has a tough outer shell. It only takes a few things to make changes happen. ...
... A bean is planted in the ground. It is dry and has a tough outer shell. It only takes a few things to make changes happen. ...
Name - dublin.k12.ca.us
... Nonvascular plants lack true ___________________, __________________, and ______________________. These types of plants, which include _______________, absorb water and nutrients from their surroundings. The water carries everything from cell to cell directly, and this limits how ___________ these t ...
... Nonvascular plants lack true ___________________, __________________, and ______________________. These types of plants, which include _______________, absorb water and nutrients from their surroundings. The water carries everything from cell to cell directly, and this limits how ___________ these t ...
Chapter 2 science powerpoint
... What are the plants’ characteristics? • Plants are made up of many cells. • These cells all do different jobs in the plant • Plants have special cells they use to absorb water and nutrients from the soil • Plants contain Chlorophyll, which makes them green ...
... What are the plants’ characteristics? • Plants are made up of many cells. • These cells all do different jobs in the plant • Plants have special cells they use to absorb water and nutrients from the soil • Plants contain Chlorophyll, which makes them green ...
Spiny cocklebur - Stevens County
... The hooked spines of the fruit enable it to adhere to animals and be transported long distances The seeds and young cotyledon plants are toxic to livestock It grows in a wide variety of soil types and most frequently found in disturbed areas and barnyards but has also invaded pastures & fields ...
... The hooked spines of the fruit enable it to adhere to animals and be transported long distances The seeds and young cotyledon plants are toxic to livestock It grows in a wide variety of soil types and most frequently found in disturbed areas and barnyards but has also invaded pastures & fields ...
Plant Defense - Henriksen Science
... • Terpenes such as pyrethrum (from chrysanthemums) and azadirachtin (from the Asian and African Neem tree) can be used as “natural” insecticides in agricultural practices or in horticulture. ...
... • Terpenes such as pyrethrum (from chrysanthemums) and azadirachtin (from the Asian and African Neem tree) can be used as “natural” insecticides in agricultural practices or in horticulture. ...
Midtown Carnivores - Dionaea Plant Care Sheet
... GENERAL CARE: Place your plant’s pot into a bowl or container, and add water to the container until the water is ~¼ of the way up the side of the pot. Place the pot and its bowl outdoors in an area of bright sunlight, away from roof overhangs or structures that block sunlight at different times of d ...
... GENERAL CARE: Place your plant’s pot into a bowl or container, and add water to the container until the water is ~¼ of the way up the side of the pot. Place the pot and its bowl outdoors in an area of bright sunlight, away from roof overhangs or structures that block sunlight at different times of d ...
Test Review Sheet and Organization of Plant HW
... 1. Characteristics of all plants and general plant diversity – study plant diversity sheet 2. What is alternation of generations? How is the haploid different from the diploid? 3. From what did plants evolve? What to plants need to survive on land? 4. Four main groups - Bryophytes, (mosses), Ferns, ...
... 1. Characteristics of all plants and general plant diversity – study plant diversity sheet 2. What is alternation of generations? How is the haploid different from the diploid? 3. From what did plants evolve? What to plants need to survive on land? 4. Four main groups - Bryophytes, (mosses), Ferns, ...
Mr. Martin`s Chapter 31+32 PowerPoint
... XIII. Plant hormones A. Definition – an organic compounds produced in one part of a plant, transported to another part, where it stimulates a physiological response B. Five major types 1. Auxins a. Stimulates cell elongation in the stem and thereby phototropism of the plant b. Produces apical domin ...
... XIII. Plant hormones A. Definition – an organic compounds produced in one part of a plant, transported to another part, where it stimulates a physiological response B. Five major types 1. Auxins a. Stimulates cell elongation in the stem and thereby phototropism of the plant b. Produces apical domin ...
Dahlia Dahlietta
... therefore increase the number of flowers. The flowering will be delayed by 7 to 10 days. ...
... therefore increase the number of flowers. The flowering will be delayed by 7 to 10 days. ...
Plant Morphology
... Plant Morphology • Meristem Tissue- embryonic tissue located at the tips of roots and stem apices (herbaceous & woody plants) and cambium layers (woody plants). • Parenchyma - unspecialized cells occurring throughout the plant. ...
... Plant Morphology • Meristem Tissue- embryonic tissue located at the tips of roots and stem apices (herbaceous & woody plants) and cambium layers (woody plants). • Parenchyma - unspecialized cells occurring throughout the plant. ...
L A cell is the basic unit of all living things. Life processes are the
... A cell membrane is a thin layer surrounding all cells that allows water and dissolved materials into and out of the cell. Photosynthesis is the food-making process of plants. During photosynthesis plants take in sunlight, CO2, and water to make glucose (sugar) which they use for food. Plants then g ...
... A cell membrane is a thin layer surrounding all cells that allows water and dissolved materials into and out of the cell. Photosynthesis is the food-making process of plants. During photosynthesis plants take in sunlight, CO2, and water to make glucose (sugar) which they use for food. Plants then g ...
Plant physiology
.jpg?width=300)
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), cell biology, genetics, biophysics and molecular biology.Fundamental processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, plant nutrition, plant hormone functions, tropisms, nastic movements, photoperiodism, photomorphogenesis, circadian rhythms, environmental stress physiology, seed germination, dormancy and stomata function and transpiration, both parts of plant water relations, are studied by plant physiologists.