6. Life cycle and growth form - New Zealand Plant Conservation
... seed to flowering, and production of new seed: • Annual – The entire life cycle occurs within one year, and the plant dies, e.g., Atriplex species. • Biennial – A plant flowers and produces seed in the second year after it germinated, e.g., New Zealand gentians. • Perennial – Continue from one ye ...
... seed to flowering, and production of new seed: • Annual – The entire life cycle occurs within one year, and the plant dies, e.g., Atriplex species. • Biennial – A plant flowers and produces seed in the second year after it germinated, e.g., New Zealand gentians. • Perennial – Continue from one ye ...
Tree Dahlia (Dahlia imperialis)
... will be rewarded with a towering plant topped with floppy, handkerchief-like blooms. Two years later you will be bringing armloads of cuttings to The Plant Exchange. Plant cuttings either horizontally or vertically as you wish, as long as one or more “joints” are buried. Notes: They get leggy and ...
... will be rewarded with a towering plant topped with floppy, handkerchief-like blooms. Two years later you will be bringing armloads of cuttings to The Plant Exchange. Plant cuttings either horizontally or vertically as you wish, as long as one or more “joints” are buried. Notes: They get leggy and ...
Catchweed bedstraw
... THE DEFENSE: As this is a native plant there very little insects that can be used to reduce the impact of the weed. As with most annual plants hand pulling can be easy when the plants are young and are few. Once established herbicides are about the only thing left to reduce the harm that this plant ...
... THE DEFENSE: As this is a native plant there very little insects that can be used to reduce the impact of the weed. As with most annual plants hand pulling can be easy when the plants are young and are few. Once established herbicides are about the only thing left to reduce the harm that this plant ...
Chapter A3: Plants
... Big trees have a great many leaves instead of just a few very large leaves because having many small leaves allows the tree to absorb more light at all different times of day. Sunlight is trapped by a leaf’s chlorophyll. The leaves give off oxygen as waste. Water and carbon dioxide in the leaves ...
... Big trees have a great many leaves instead of just a few very large leaves because having many small leaves allows the tree to absorb more light at all different times of day. Sunlight is trapped by a leaf’s chlorophyll. The leaves give off oxygen as waste. Water and carbon dioxide in the leaves ...
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development
... Seedless vascular plants and most monocots; i.e. grasses ...
... Seedless vascular plants and most monocots; i.e. grasses ...
Plants junior
... The majority of existing and classified plants belong to the angiosperm group that has about 250,000 species that are characterised by the production of flowers and of seeds closed and protected within a fruit. Flowering plants also have a stem, leaves and roots. The roots and leaves contain the xyl ...
... The majority of existing and classified plants belong to the angiosperm group that has about 250,000 species that are characterised by the production of flowers and of seeds closed and protected within a fruit. Flowering plants also have a stem, leaves and roots. The roots and leaves contain the xyl ...
Plant adaptations - Parkland School District
... and that often comes all at the same time. The rest of the year is very dry. ...
... and that often comes all at the same time. The rest of the year is very dry. ...
Prairie Blazing Star: Liatris pycnostachya
... Cultivation: The preference is full sun and moist to mesic conditions. Established plants can tolerate some drought, but seedlings and transplants are vulnerable. The soil should consist of a rich loam or clay loam, and can contain rocky material. There is a tendency for the lower leaves to turn yel ...
... Cultivation: The preference is full sun and moist to mesic conditions. Established plants can tolerate some drought, but seedlings and transplants are vulnerable. The soil should consist of a rich loam or clay loam, and can contain rocky material. There is a tendency for the lower leaves to turn yel ...
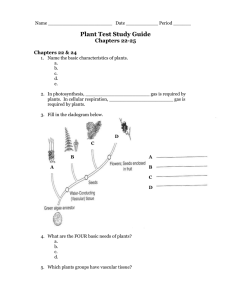
Plants Study Guide
... spores. The gametophyte stage is when they produce gametes (sex cells/sperm and egg). 5. List 3 the methods of seed dispersal: a. wind b. water c. other organisms 6. What are cotyledons? seed leaves 7. What type of vascular plant produces “naked seeds”? gymnosperms 8. What type of vascular plant pro ...
... spores. The gametophyte stage is when they produce gametes (sex cells/sperm and egg). 5. List 3 the methods of seed dispersal: a. wind b. water c. other organisms 6. What are cotyledons? seed leaves 7. What type of vascular plant produces “naked seeds”? gymnosperms 8. What type of vascular plant pro ...
Unit 9: Botany Content Outline: Plant Environmental Responses (9.4
... 1. For example, Bolting – This process is triggered by water (ligand) entering the seed. 2. For example, Greening – The plant begins producing chloroplasts in response to sunlight. C. Hormones are released to target tissues to relay information. (Remember, only need small amounts cell amplifies.) ...
... 1. For example, Bolting – This process is triggered by water (ligand) entering the seed. 2. For example, Greening – The plant begins producing chloroplasts in response to sunlight. C. Hormones are released to target tissues to relay information. (Remember, only need small amounts cell amplifies.) ...
Classification Puzzles
... parts called a head, a thorax and an abdomen. I have I a skeleton on the outside of my body called an exoskeleton, which Am isn’t made from bone. Fertilisation of my eggs takes placeAn inside my body and my young are laid in soft eggs. insect I can fly. Which group in the animal kingdom do I belong ...
... parts called a head, a thorax and an abdomen. I have I a skeleton on the outside of my body called an exoskeleton, which Am isn’t made from bone. Fertilisation of my eggs takes placeAn inside my body and my young are laid in soft eggs. insect I can fly. Which group in the animal kingdom do I belong ...
Alocasia cucullata
... the trip. It is not unusual for these plants to be quite wilted for a few days and some of the original leaves may even die, but new leaves will emerge from the base of the old ones. Don’t plant too deep, you should be able to see the original soil line by the color of the stalks – darker above the ...
... the trip. It is not unusual for these plants to be quite wilted for a few days and some of the original leaves may even die, but new leaves will emerge from the base of the old ones. Don’t plant too deep, you should be able to see the original soil line by the color of the stalks – darker above the ...
6-2.4 Summarize the basic functions of the structures of a flowering
... •Once the ovule is fertilized it develops into a seed. •A fruit (fleshy, pod, or shell) then develops to protect the seed. •Seeds are structures that contain the young plant surrounded by a protective covering. ...
... •Once the ovule is fertilized it develops into a seed. •A fruit (fleshy, pod, or shell) then develops to protect the seed. •Seeds are structures that contain the young plant surrounded by a protective covering. ...
DOS 8
... 2.) Alice sees a small plant in her backyard. To help her identify it she writes down characteristics she notices. What is its classification? * the plant does not have leaves * the plant never produced seeds * the plant grows on a moist rock ...
... 2.) Alice sees a small plant in her backyard. To help her identify it she writes down characteristics she notices. What is its classification? * the plant does not have leaves * the plant never produced seeds * the plant grows on a moist rock ...
Notes Chapter
... organism by the union of sperm and egg. • Fertilization joining of egg and sperm • Non Vascular plants reproduce by spores. ...
... organism by the union of sperm and egg. • Fertilization joining of egg and sperm • Non Vascular plants reproduce by spores. ...
Plant parts
... Roots are in the dirt. Roots hold the plant in place, and they get water and food from the dirt . Roots get water and food to the stem and the rest of the plant.* ...
... Roots are in the dirt. Roots hold the plant in place, and they get water and food from the dirt . Roots get water and food to the stem and the rest of the plant.* ...
Study Guide: Plants
... 22. Name the methods of seed dispersal. a. b. c. 23. What is seed dormancy? ...
... 22. Name the methods of seed dispersal. a. b. c. 23. What is seed dormancy? ...
Chilling Inquiry for Moapa - University of Nevada Cooperative
... When the weather in winter becomes unusually cold, even snowy, most of the outdoor plants we care for so tenderly become miserable. In the case of many vegetables, a mere few hours below freezing will turn them into a forlorn mush. This is certainly an unwelcome sight, but at least the blackened pla ...
... When the weather in winter becomes unusually cold, even snowy, most of the outdoor plants we care for so tenderly become miserable. In the case of many vegetables, a mere few hours below freezing will turn them into a forlorn mush. This is certainly an unwelcome sight, but at least the blackened pla ...
The Parts of a plant and their functions
... which has a particular purpose, or specialized function.If one part of the plant is not functioning properly the whole plant will suffer.But we may cut flowers off the plant or prune the roots.Such damage is only temporary and so the plant will continue to grow. The basic parts of a plant are the ro ...
... which has a particular purpose, or specialized function.If one part of the plant is not functioning properly the whole plant will suffer.But we may cut flowers off the plant or prune the roots.Such damage is only temporary and so the plant will continue to grow. The basic parts of a plant are the ro ...
Student Notes File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... All flowering plants – from tiny blades of grass to large shade trees – have the same basic parts. They have roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds. Each of these parts has a function that is described below. Fill in the name of the plant part that describes its job. 1. ___________________ ...
... All flowering plants – from tiny blades of grass to large shade trees – have the same basic parts. They have roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds. Each of these parts has a function that is described below. Fill in the name of the plant part that describes its job. 1. ___________________ ...
6-2.4 notes Plants - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... Store extra food for the plants. The more root space that is available, the more water and nutrients it can absorb. There are two types of root systems: fibrous roots and taproots. 1. Fibrous roots consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass of roots. Examples are grass, corn, and s ...
... Store extra food for the plants. The more root space that is available, the more water and nutrients it can absorb. There are two types of root systems: fibrous roots and taproots. 1. Fibrous roots consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass of roots. Examples are grass, corn, and s ...
Systems in Plants
... Root System - the part of the plant that anchors the plant and often grows below ground - It absorbs water and minerals as well as stores nutrient. - Contain root hairs – which are tiny extensions of the tissue that help with absorption ...
... Root System - the part of the plant that anchors the plant and often grows below ground - It absorbs water and minerals as well as stores nutrient. - Contain root hairs – which are tiny extensions of the tissue that help with absorption ...
Control Systems In Plants
... Photoperiodism synchronizes many plant responses to changes of season ...
... Photoperiodism synchronizes many plant responses to changes of season ...
Vocabulary for Plants
... 15. monocots – flowering plants whose embryos have one seed leaf. (monocotyledons ) 16. dicots – (dicotyledons) flowering plants whose embryos have two seed leaves. 17. wood – a fibrous material made up of dead cells that are part of the vascular system of some plants. 18. botany – the study of plan ...
... 15. monocots – flowering plants whose embryos have one seed leaf. (monocotyledons ) 16. dicots – (dicotyledons) flowering plants whose embryos have two seed leaves. 17. wood – a fibrous material made up of dead cells that are part of the vascular system of some plants. 18. botany – the study of plan ...
Plant morphology

Plant morphology or phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants. This is usually considered distinct from plant anatomy, which is the study of the internal structure of plants, especially at the microscopic level. Plant morphology is useful in the visual identification of plants.