Parts of Flowers Test Review 2014 (1)
... ______. It will protect the seed until it is ripe, then aid in seed dispersal. 21) The ______ is the place where the flower and the stem meet. 21) 22) _______ are special features that allow a plant or animal to 22) live in a particular place or habitat. 23) When a seed does not germinate immediatel ...
... ______. It will protect the seed until it is ripe, then aid in seed dispersal. 21) The ______ is the place where the flower and the stem meet. 21) 22) _______ are special features that allow a plant or animal to 22) live in a particular place or habitat. 23) When a seed does not germinate immediatel ...
Plant Life
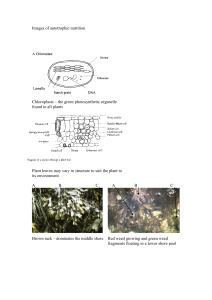
... air that is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and released when animals breathe chlorophyll – the green pigment in plants that captures light used in photosynthesis embryo – an undeveloped plant inside a seed flower – the reproductive part of a plant composed of petals, stamen, and carpel fru ...
... air that is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and released when animals breathe chlorophyll – the green pigment in plants that captures light used in photosynthesis embryo – an undeveloped plant inside a seed flower – the reproductive part of a plant composed of petals, stamen, and carpel fru ...
Study Guide for Plant Kingdom
... 1. __________________Kingdom of multicellular autotrophs that rely on energy from the sun to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. 2. __________________Process that occurs in the chloroplast of autotrophs that requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. 3. _________________ ...
... 1. __________________Kingdom of multicellular autotrophs that rely on energy from the sun to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. 2. __________________Process that occurs in the chloroplast of autotrophs that requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. 3. _________________ ...
What Does a Plant Need? PowerPoint
... Like all living things, a plant has certain needs. They need air, water, energy from food, and a place to live. However, unlike animals, green plants make their own food. To make food, plants need light, water and the gas carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas in the air. ...
... Like all living things, a plant has certain needs. They need air, water, energy from food, and a place to live. However, unlike animals, green plants make their own food. To make food, plants need light, water and the gas carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas in the air. ...
3.2 Helping Plants Grow Well 9780435133290.indd
... word snake or flower shape by joining them together so that your friends have to find the ten words. For example: plants, grow, water, food … and so on. Draw them in a flower shape, if you can. ...
... word snake or flower shape by joining them together so that your friends have to find the ten words. For example: plants, grow, water, food … and so on. Draw them in a flower shape, if you can. ...
Plant Parts and Functions
... 1. To recognize different plant structures 2. To understand different functions of plant structures 3. To learn the terminology used to identify plant structures ...
... 1. To recognize different plant structures 2. To understand different functions of plant structures 3. To learn the terminology used to identify plant structures ...
Modified Stems
... 1. To recognize different plant structures 2. To understand different functions of plant structures 3. To learn the terminology used to identify plant structures ...
... 1. To recognize different plant structures 2. To understand different functions of plant structures 3. To learn the terminology used to identify plant structures ...
Plants - Faculty
... • Production of a classification system that includes all plants, this provides a systematic organization of the diversity found in plants; • An understanding of relationships of plants that can be incorporated into classification systems, if we have a plant that has a useful characteristic, a class ...
... • Production of a classification system that includes all plants, this provides a systematic organization of the diversity found in plants; • An understanding of relationships of plants that can be incorporated into classification systems, if we have a plant that has a useful characteristic, a class ...
Plants-General information
... water through roots---therefore can inhabit dryer areas than nonvascular -________________control the size of pores on plants and balance the movement of CO2 into leaf w/outgoing water ...
... water through roots---therefore can inhabit dryer areas than nonvascular -________________control the size of pores on plants and balance the movement of CO2 into leaf w/outgoing water ...
Ch 7 lesson 1 RR
... D a vascular plant that uses pollen to produce seeds that are not enclosed in protective fruits ...
... D a vascular plant that uses pollen to produce seeds that are not enclosed in protective fruits ...
The Enemy: False–hellebore (Veratrum californicum) This lily family
... plant grows up to 4 foot tall, has thick rootstalks with very leafy stems that are sheathing at the base. The leaves are heavily veined and can grow as long as 12 inches. The plant is also called ‘Skunk cabbage’ as the leaves wrap around each other similar to how mature cabbage does. The plant produ ...
... plant grows up to 4 foot tall, has thick rootstalks with very leafy stems that are sheathing at the base. The leaves are heavily veined and can grow as long as 12 inches. The plant is also called ‘Skunk cabbage’ as the leaves wrap around each other similar to how mature cabbage does. The plant produ ...
Scientific Identification of Plants
... a plant seed germinates and grows producing leaves, stems and roots • Reproductive phase – when a plant flowers and produces fruit. • Dormant phase – when plant rests or grows very little – Plants go dormant in response to ...
... a plant seed germinates and grows producing leaves, stems and roots • Reproductive phase – when a plant flowers and produces fruit. • Dormant phase – when plant rests or grows very little – Plants go dormant in response to ...
Tall Pepperwort/Perennial Pepperweed
... high. Above ground parts begin to die back late summer or early fall. Plant has horseradish odor & taste. Where found: Salt marshes above high tide line, beaches, stream banks, floodplains, roadsides, ditches, fields. ...
... high. Above ground parts begin to die back late summer or early fall. Plant has horseradish odor & taste. Where found: Salt marshes above high tide line, beaches, stream banks, floodplains, roadsides, ditches, fields. ...
Culver`s Root: Veronicastrum, virginicum
... drought; otherwise they normally appear healthy and are not often bothered by disease. This plant has a tendency to flop over on slopes. Culver's root occurs in moist to mesic black soil prairies, sand prairies, openings and edges of woodlands, thickets, savannas, and swampy meadows along rivers and ...
... drought; otherwise they normally appear healthy and are not often bothered by disease. This plant has a tendency to flop over on slopes. Culver's root occurs in moist to mesic black soil prairies, sand prairies, openings and edges of woodlands, thickets, savannas, and swampy meadows along rivers and ...
Learn About Plants
... •Is called a carnivorous (meat eating) plant •Grows in wet, damp bogs •Can reach 1 foot in heighth Let's see other plants ...
... •Is called a carnivorous (meat eating) plant •Grows in wet, damp bogs •Can reach 1 foot in heighth Let's see other plants ...
EKOR KUCING Scientific name : Acalypha hispida Common name
... It can grow to be six to twelve feet (1.8-3.7 meters) tall. The plant is dioecious, and therefore there are distinct male and female members of the species. The female plant bears pistillate flowers which range in color from purple to bright red, and grow in clusters along catkins. This feature is t ...
... It can grow to be six to twelve feet (1.8-3.7 meters) tall. The plant is dioecious, and therefore there are distinct male and female members of the species. The female plant bears pistillate flowers which range in color from purple to bright red, and grow in clusters along catkins. This feature is t ...
Botany Review Questions
... 1. _______________ produce one seed leaf. Floral parts are usually in threes or multiples of threes, and leaves are often parallel-veined. ________________ produce two seed leaves. Floral parts are usually in multiples of fours or fives and leaves are generally net-veined. 2. ________________ is the ...
... 1. _______________ produce one seed leaf. Floral parts are usually in threes or multiples of threes, and leaves are often parallel-veined. ________________ produce two seed leaves. Floral parts are usually in multiples of fours or fives and leaves are generally net-veined. 2. ________________ is the ...
Chapter 5 Vocabulary- From Bacteria to Plants
... Fruit: the ripened ovary and other structures that enclose one or more seeds of an angiosperm (pg. 159) Monocot: an angiosperm that has only one seed leaf (pg. 157) Dicot: an angiosperm that has two seed leaves (pg. 157) Section 4 Tropism: the growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimul ...
... Fruit: the ripened ovary and other structures that enclose one or more seeds of an angiosperm (pg. 159) Monocot: an angiosperm that has only one seed leaf (pg. 157) Dicot: an angiosperm that has two seed leaves (pg. 157) Section 4 Tropism: the growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimul ...
Plant morphology

Plant morphology or phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants. This is usually considered distinct from plant anatomy, which is the study of the internal structure of plants, especially at the microscopic level. Plant morphology is useful in the visual identification of plants.