* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter A3: Plants
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
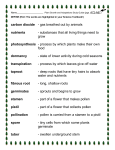
Science Chapter A3 Study Guide Plant Growth and Adaptations carbon dioxide- gas breathed out by animals dormancy- state of lower activity during cold seasons fibrous roots- long, shallow roots germinates- sprouts and begins to grow nutrients- substances that all living things need to grow photosynthesis- process by which plants make their own food pistil- part of a flower that collects pollen pollination- pollen is carried from a stamen to a pistil spores- tiny cells from which some plants germinate stamen- part of a flower that makes pollen taproots- deep roots that have tiny hairs to absorb water and nutrients transpiration- process by which leaves give off water tuber- swollen underground stem Grass is an example of a plant with fibrous roots. Since photo means light and synthesis means putting together, photosynthesis describes the process by which a plant makes it own food because plants use light energy to put together carbon dioxide and water to make their own food. Spores grow in capsules. Plants with active traps (like the Venus fly trap) are found in areas that have poor soil because the poor soil that these plants grow in does not provide the plants with the nutrients they need. Therefore they must get nutrients in other ways. Grafting is the process that joins a cut stem of one plant to a slice in the stem of another plant. Big trees have a great many leaves instead of just a few very large leaves because having many small leaves allows the tree to absorb more light at all different times of day. Sunlight is trapped by a leaf’s chlorophyll. The leaves give off oxygen as waste. Water and carbon dioxide in the leaves combine to make sugar. The roots take in water. For the seed of a flowering plant to begin to grow, it needs warmth, water, and air. The seed sprouts and becomes a seedling. Animals such as birds and bees feed on its nectar, which helps the plant prepare more seeds. A cactus has roots that grow near the surface to help it obtain water. A lily pad has roots to help it absorb nutrients from the mud. Climbing plants have stems that can cling to other objects in order to reach toward the sunlight.