Check your answers - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
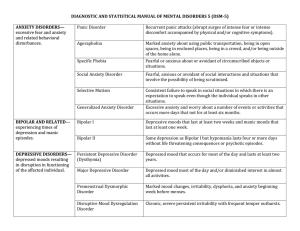
... 15. Disorders characterized by constant worry and fears-category ...
... 15. Disorders characterized by constant worry and fears-category ...
Mental Health Disorders
... As many as 13% of teens experience an anxiety disorder. There are several different types of anxiety disorders. ...
... As many as 13% of teens experience an anxiety disorder. There are several different types of anxiety disorders. ...
Depression and Anxiety Disorders
... Mood and anxiety disorders are common, and the mortality risk is due primarily to suicide, cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Depressive Disorders (unipolar) and Bipo ...
... Mood and anxiety disorders are common, and the mortality risk is due primarily to suicide, cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Depressive Disorders (unipolar) and Bipo ...
W_George___Post_Trau..._Stress_Disorder
... Higher number of traumatic events endured. Higher severity of trauma experienced. Having an emotional condition prior to the event. Having little social support in the form of family or friends. Children, females and people w/ learning disabilities/violence in the home. ...
... Higher number of traumatic events endured. Higher severity of trauma experienced. Having an emotional condition prior to the event. Having little social support in the form of family or friends. Children, females and people w/ learning disabilities/violence in the home. ...
Major Psychological Disorders
... Personality disorders Antisocial personality disorder – a disorder in which individuals show no regard for the moral and ethical rules of society or the rights of others. Borderline personality disorder – a disorder in which individuals have difficulty developing a secure sense of who they are. ...
... Personality disorders Antisocial personality disorder – a disorder in which individuals show no regard for the moral and ethical rules of society or the rights of others. Borderline personality disorder – a disorder in which individuals have difficulty developing a secure sense of who they are. ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
... idealize other people and then abruptly despise them. A consequence of all this was that they typically look for help from a therapist and then suddenly quit in terrible disappointment and anger. Underneath all these symptoms, therapists see in borderline people an inability to tolerate the levels o ...
... idealize other people and then abruptly despise them. A consequence of all this was that they typically look for help from a therapist and then suddenly quit in terrible disappointment and anger. Underneath all these symptoms, therapists see in borderline people an inability to tolerate the levels o ...
Psychological Disorders What is mental illness? Diagnostic and
... anorexia nervosa), having multiple physical complaints (as in somatization disorder), or having a serious illness (as in hypochondriasis), and the anxiety and worry do not occur exclusively during posttraumatic stress disorder. ...
... anorexia nervosa), having multiple physical complaints (as in somatization disorder), or having a serious illness (as in hypochondriasis), and the anxiety and worry do not occur exclusively during posttraumatic stress disorder. ...
Slide 1
... D. Schizoid Personality Disorder: a disorder characterized by an indifference to social or sexual relationships, as well as very limited emotional experience and expression. E. Schizotypal Personality Disorder: a disorder characterized by being peculiar and bizarre in the way one relates to others, ...
... D. Schizoid Personality Disorder: a disorder characterized by an indifference to social or sexual relationships, as well as very limited emotional experience and expression. E. Schizotypal Personality Disorder: a disorder characterized by being peculiar and bizarre in the way one relates to others, ...
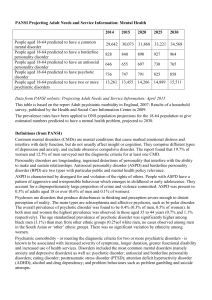
Mental Health Projections: PANSI 2015
... both men and women the highest prevalence was observed in those aged 35 to 44 years (0.7% and 1.1% respectively). The age standardised prevalence of psychotic disorder was significantly higher among black men (3.1%) than men from other ethnic groups (0.2%of white men, no cases observed among men in ...
... both men and women the highest prevalence was observed in those aged 35 to 44 years (0.7% and 1.1% respectively). The age standardised prevalence of psychotic disorder was significantly higher among black men (3.1%) than men from other ethnic groups (0.2%of white men, no cases observed among men in ...
A Diagramatic Approach to Individuals with Multiple Psychiatric
... • Present as sad, empty, having somatic and cognitive changes that affect ability to function including changes in sleep energy, lack of interest, low self esteem, hopelessness. • May be passive or very irritable. *High rates of comorbidity (including ADHD of 16% in first presentation) ...
... • Present as sad, empty, having somatic and cognitive changes that affect ability to function including changes in sleep energy, lack of interest, low self esteem, hopelessness. • May be passive or very irritable. *High rates of comorbidity (including ADHD of 16% in first presentation) ...
Adolescent Anxiety - Ilana Blatt
... • Panic attacks and OCD work a little differently • Focus on breathing during panic attacks can be counterproductive – more important to ride the wave, know what is happening, know that it won’t last forever • Exposure/habituation are key parts of treatment for these disorders and should probably b ...
... • Panic attacks and OCD work a little differently • Focus on breathing during panic attacks can be counterproductive – more important to ride the wave, know what is happening, know that it won’t last forever • Exposure/habituation are key parts of treatment for these disorders and should probably b ...
Anxiety Disorders - University of Delaware
... Vs. avoidant personality disorder May be classically conditioned May actually be less skilled & more awkward ...
... Vs. avoidant personality disorder May be classically conditioned May actually be less skilled & more awkward ...
Anxiety Disorders - Centre Londres 94
... Classification of Anxiety Disorders 1.) DSM Approach -The DSM IV describes several types of anxiety disorders. -Match the disorder to the respective definition: 1.Separation Anxiety Disorder ...
... Classification of Anxiety Disorders 1.) DSM Approach -The DSM IV describes several types of anxiety disorders. -Match the disorder to the respective definition: 1.Separation Anxiety Disorder ...
Mental Health and Mental Illness II
... What is the Cause of Bipolar Disorder? – No single cause has been identified in bipolar disorder. – Research suggests it be inherited. – It is thought to be caused by a lack of stability in the transmission of nerve impulses in the brain. ...
... What is the Cause of Bipolar Disorder? – No single cause has been identified in bipolar disorder. – Research suggests it be inherited. – It is thought to be caused by a lack of stability in the transmission of nerve impulses in the brain. ...
Chapter 5
... Occasional anxiety is natural response to life events; once the stressful situation is over, so is the anxiety it created ...
... Occasional anxiety is natural response to life events; once the stressful situation is over, so is the anxiety it created ...
ADHD (TDAH)
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
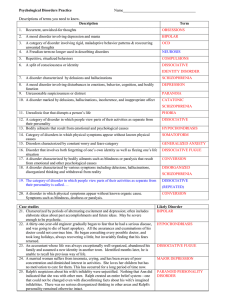
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... abnormal thoughts, feeling and behaviors in response to these symptoms. ...
... abnormal thoughts, feeling and behaviors in response to these symptoms. ...
Psychological Disorders
... • A legal, not psychological term • Means an individual is not legally responsible for his/her behavior due to a psychiatric illness or some other temporary or permanent mental condition ...
... • A legal, not psychological term • Means an individual is not legally responsible for his/her behavior due to a psychiatric illness or some other temporary or permanent mental condition ...
WHAT DOES FASD LOOK LIKE?
... such as phobias develop from traumatic or stressful situations such as a death, an accident or an abusive event. Other disorders can be inherited. Other disorders can result from an injury or a physical disorder that effects the brain . ...
... such as phobias develop from traumatic or stressful situations such as a death, an accident or an abusive event. Other disorders can be inherited. Other disorders can result from an injury or a physical disorder that effects the brain . ...
Somatoform Disorders
... body. All of these disorders share one thing in common = no identifiable medical condition causing the physical complaints. Hypochondriasis: physical complaints without a clear cause; anxiety focused on the possibility of having a serious disease. Shares many features with panic disorder Essenti ...
... body. All of these disorders share one thing in common = no identifiable medical condition causing the physical complaints. Hypochondriasis: physical complaints without a clear cause; anxiety focused on the possibility of having a serious disease. Shares many features with panic disorder Essenti ...
Terms in Psychiatry - Northwest Technology Center
... abnormal impulse toward something or someone ...
... abnormal impulse toward something or someone ...
Abnormal Psychology
... The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship between psychological disorders and violence What would most mental health workers believe the influences are that lead to disordered behavior? What is the M’Naughton Rule? What is insanity? criteria for determining disordered behavior: a) a ...
... The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship between psychological disorders and violence What would most mental health workers believe the influences are that lead to disordered behavior? What is the M’Naughton Rule? What is insanity? criteria for determining disordered behavior: a) a ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.