Mental Health Nursing II NURS 2310
... frequent and severe than is typically observed in individuals at same developmental level Hyperactivity = excessive psychomotor activity that may be purposeful or aimless, accompanied by physical movements that are usually more rapid than normal Impulsitivity = acting without reflection and with ...
... frequent and severe than is typically observed in individuals at same developmental level Hyperactivity = excessive psychomotor activity that may be purposeful or aimless, accompanied by physical movements that are usually more rapid than normal Impulsitivity = acting without reflection and with ...
The sections in the book that correspond to this quiz are modules 29
... 19. A person who is convinced that she has more than one personality and “blacks out” for hours while another personality takes over is likely to be diagnosed with which of the following? A) dissociative identity disorder B) dissociative schizophrenia C) dissociative amnesia D) dissociative fugue 20 ...
... 19. A person who is convinced that she has more than one personality and “blacks out” for hours while another personality takes over is likely to be diagnosed with which of the following? A) dissociative identity disorder B) dissociative schizophrenia C) dissociative amnesia D) dissociative fugue 20 ...
Anxiety
... Chills/Hot flashes – Tremors & Shaking – GI distress Nausea Diarrhea – Fear of dying and/or going crazy – Depersonalization ...
... Chills/Hot flashes – Tremors & Shaking – GI distress Nausea Diarrhea – Fear of dying and/or going crazy – Depersonalization ...
medications for anxiety - Austin Community College
... Don’t stop benzodiazepine therapy abruptly ...
... Don’t stop benzodiazepine therapy abruptly ...
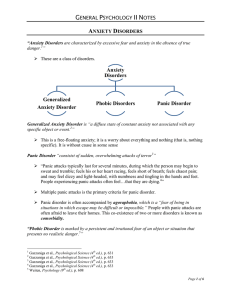
Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder is “a diffuse state of constant anxiety not associated with any specific object or event.2” This is a free-floating anxiety; it is a worry about everything and nothing (that is, nothing specific). It is without cause in some sense Panic Disorder “consistst of sudden, o ...
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder is “a diffuse state of constant anxiety not associated with any specific object or event.2” This is a free-floating anxiety; it is a worry about everything and nothing (that is, nothing specific). It is without cause in some sense Panic Disorder “consistst of sudden, o ...
Somatic Symptom and Related Disorder
... -Major depression (Not made if concern is only there during depressive episodes) -Psychotic disorders (often more bizzare, e.g. rotting organs) ...
... -Major depression (Not made if concern is only there during depressive episodes) -Psychotic disorders (often more bizzare, e.g. rotting organs) ...
Module 12: Effects of Stress
... •An anxiety disorder characterized by sudden bouts of intense, unexplained anxiety •Often associated with physical symptoms like choking sensations or shortness of breath ...
... •An anxiety disorder characterized by sudden bouts of intense, unexplained anxiety •Often associated with physical symptoms like choking sensations or shortness of breath ...
Psychobehavioral
... of 1.5-2.0 mEq/L. Dehydration, salt restriction, diuretic use, childbirth and infection predispose patients to these side effects. Which of the following is NOT one of these side effects? A. Diarrhea B. Vomiting C. Drowsiness D. muscular weakness E. lack of coordination ...
... of 1.5-2.0 mEq/L. Dehydration, salt restriction, diuretic use, childbirth and infection predispose patients to these side effects. Which of the following is NOT one of these side effects? A. Diarrhea B. Vomiting C. Drowsiness D. muscular weakness E. lack of coordination ...
The 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale had high sensitivity
... in primary care patients. The prevalence of >1 anxiety disorder was quite high (19.5%), confirming the importance of assessing both depression and anxiety disorders in this setting. A 2-item form of the GAD-7 was as informative as the 7-item form for GAD and other anxiety disorders. The authors’ con ...
... in primary care patients. The prevalence of >1 anxiety disorder was quite high (19.5%), confirming the importance of assessing both depression and anxiety disorders in this setting. A 2-item form of the GAD-7 was as informative as the 7-item form for GAD and other anxiety disorders. The authors’ con ...
Psychiatric Classification
... No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...
... No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...
Anxiety, anxiety disorders, somatoform disorders
... common feature trait anxiety anxiety disorders treating anxiety ...
... common feature trait anxiety anxiety disorders treating anxiety ...
Holden Caulfield Patient File: Psychological Evaluation
... Inability to respond to or feel empathy others’ feelings High levels of judgmental opinions toward others ...
... Inability to respond to or feel empathy others’ feelings High levels of judgmental opinions toward others ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 48
... obsessive-compulsive disorder. generalized anxiety disorder. post-traumatic stress disorder. dysthymic disorder. ...
... obsessive-compulsive disorder. generalized anxiety disorder. post-traumatic stress disorder. dysthymic disorder. ...
Durand and Barlow Chapter 4: Anxiety Disorders
... – Most with OCD are female – Onset is typically in early adolescence or young adulthood ...
... – Most with OCD are female – Onset is typically in early adolescence or young adulthood ...
Durand and Barlow Chapter 4: Anxiety Disorders
... – Most with OCD are female – Onset is typically in early adolescence or young adulthood ...
... – Most with OCD are female – Onset is typically in early adolescence or young adulthood ...
Psychological Disorders Review Sheet (Chapter 15)
... argues disorders are caused by neurochemical or hormonal imbalances; abnormal brain structures or genetics. ...
... argues disorders are caused by neurochemical or hormonal imbalances; abnormal brain structures or genetics. ...
Psychological (or Mental) Disorders
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder • Excessively nervous, tense, worrying more than necessary on most days for at least 6 months • Impairs functioning; sleep problems & anxiety–related physical complaints are common • Used to be called “free-floating anxiety” • Affects about 1 in 20 adults (5%), is more c ...
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder • Excessively nervous, tense, worrying more than necessary on most days for at least 6 months • Impairs functioning; sleep problems & anxiety–related physical complaints are common • Used to be called “free-floating anxiety” • Affects about 1 in 20 adults (5%), is more c ...
Psychiatric Classification
... Symptoms are preceded by stressors Symptoms are not intentionally feigned or produced No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...
... Symptoms are preceded by stressors Symptoms are not intentionally feigned or produced No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...
Disorders of Childhood
... inappropriate given the age of the child and/or setting of the behavior) • Behavior is typically distressing and/or annoying to those in child’s social environment • Examples: ADHD, ODD, Conduct Disorder ...
... inappropriate given the age of the child and/or setting of the behavior) • Behavior is typically distressing and/or annoying to those in child’s social environment • Examples: ADHD, ODD, Conduct Disorder ...
Using audit support
... Using audit support The audit support document can be used to measure current practice in generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults against the recommendations in the NICE guideline. Use it for a local audit project either by using the whole tool or by ...
... Using audit support The audit support document can be used to measure current practice in generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults against the recommendations in the NICE guideline. Use it for a local audit project either by using the whole tool or by ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Possible Origins and Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder The cause of Borderline Personality disorder is still unclear. Research shows that chemical imbalances in the brain and other biological factors may be involved, such as heredity. Childhood trauma, such as abuse and neglect, have also be ...
... Possible Origins and Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder The cause of Borderline Personality disorder is still unclear. Research shows that chemical imbalances in the brain and other biological factors may be involved, such as heredity. Childhood trauma, such as abuse and neglect, have also be ...
An Overview of Psychiatric Disorders Commonly Seen in
... evaluated by history, physical and labs ( CBC,CMP, thyroid studies, and vitamin D level) to rule out secondary medical causes , such as Thyroid Disease, Substance Abuse or Vitamin D Insuffiency. Distinguish Unipolar vs. Bipolar Depression – screen for ...
... evaluated by history, physical and labs ( CBC,CMP, thyroid studies, and vitamin D level) to rule out secondary medical causes , such as Thyroid Disease, Substance Abuse or Vitamin D Insuffiency. Distinguish Unipolar vs. Bipolar Depression – screen for ...
Presentation18_Stude..
... and older — about __________________adults — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year. When applied to the 2004 U.S. Census residential population estimate for ages 18 and older, this figure translates to 57.7 million people. Mental disorders are the leading cause of ___________ ...
... and older — about __________________adults — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year. When applied to the 2004 U.S. Census residential population estimate for ages 18 and older, this figure translates to 57.7 million people. Mental disorders are the leading cause of ___________ ...
Anxiety Disorder - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Anxiety is a diffuse, vague apprehension associated with feelings on uncertainty and helplessness. This emotion has no specific object. It is subjectively experienced and communicated interpersonally. It is different from fear, which is the intellectual appraisal of danger. Anxiety is the emotional ...
... Anxiety is a diffuse, vague apprehension associated with feelings on uncertainty and helplessness. This emotion has no specific object. It is subjectively experienced and communicated interpersonally. It is different from fear, which is the intellectual appraisal of danger. Anxiety is the emotional ...
chapter #5 notes final
... Make clear that you know they want to end their pain- but suicide is not the answer. Ask if they have a specific plan and means to follow through with it. Suggest they talk to a trusted adult. ...
... Make clear that you know they want to end their pain- but suicide is not the answer. Ask if they have a specific plan and means to follow through with it. Suggest they talk to a trusted adult. ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.