Psychiatric illnesses in Children and Adolescents: types and treatment
... Does not listen even when spoken to directly avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort (such as schoolwork or homework) difficulty organizing tasks and activities fails to give close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in schoolwork, work, ...
... Does not listen even when spoken to directly avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort (such as schoolwork or homework) difficulty organizing tasks and activities fails to give close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in schoolwork, work, ...
CHAPTER 11
... hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one origin ...
... hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one origin ...
Transitions_anxiety_responses_and_disorders
... paroxetine, fluoxetine, and sertraline, with mean improvement in obsessions and compulsions of approximately 20% to 40%. ...
... paroxetine, fluoxetine, and sertraline, with mean improvement in obsessions and compulsions of approximately 20% to 40%. ...
Slide 1 - My Haiku
... What is a mental health disorder? A mental disorder is a diagnosable illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about him/herself or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •He/she may have difficulty deal ...
... What is a mental health disorder? A mental disorder is a diagnosable illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about him/herself or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •He/she may have difficulty deal ...
chapter 16 lecture notes: psychological disorders
... Anxiety disorders: distressing, persistent anxiety or maladaptive behaviors that increase anxiety Generalized Anxiety Disorder: client tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal Phobia: persistent, irrational fear of a specific object or situation Obsessive-Compu ...
... Anxiety disorders: distressing, persistent anxiety or maladaptive behaviors that increase anxiety Generalized Anxiety Disorder: client tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal Phobia: persistent, irrational fear of a specific object or situation Obsessive-Compu ...
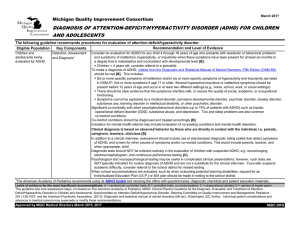
diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd)
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
File - Old Dominion Medical Society
... Deficits in executive functioning Genetic & Neurobiological contributors: perinatal stress, low birth weight, TBI, maternal smoking, severe early deprivation ...
... Deficits in executive functioning Genetic & Neurobiological contributors: perinatal stress, low birth weight, TBI, maternal smoking, severe early deprivation ...
PERSONALITY DISORDERS GUIDED PRACTICE PERSONALITY
... appropriate PERSONALITY DISORDER on the organizer: I have added other disorders & their symptoms that are also categorized as PERSONALITY DISORDERS. Match up each symptom to its correct disorder & add my additional SYMPTOMS into your PERSONALITY DISORDER ORGANIZER SYMPTOMS A. distrust and suspicion ...
... appropriate PERSONALITY DISORDER on the organizer: I have added other disorders & their symptoms that are also categorized as PERSONALITY DISORDERS. Match up each symptom to its correct disorder & add my additional SYMPTOMS into your PERSONALITY DISORDER ORGANIZER SYMPTOMS A. distrust and suspicion ...
Criteria for Depressive Disorder (summary of the guideline)
... Criteria for Depressive Disorder (summary of the guideline) Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. 1. Dep ...
... Criteria for Depressive Disorder (summary of the guideline) Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. 1. Dep ...
Anxiety Disorders - Perfectionism and Psychopathology Lab
... Differ from other disorders in that source of anxiety is external Extremely debilitating: May reexperience event for months, years, ...
... Differ from other disorders in that source of anxiety is external Extremely debilitating: May reexperience event for months, years, ...
Memory
... In dissociative disorders conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. Many people experience feelings of dissociation on occasion without experiencing a disorder. Facing a trauma, this detachment may even protect a person from being overwhelmed ...
... In dissociative disorders conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. Many people experience feelings of dissociation on occasion without experiencing a disorder. Facing a trauma, this detachment may even protect a person from being overwhelmed ...
Psychological Disorders
... neurotic disorder - a psychological disorder that is usually distressing but that allows one to think rationally and function socially. psychotic disorder - a psychological disorder in which a person loses contact with reality, experiencing irrational ideas and distorted perceptions I. Anxiety Disor ...
... neurotic disorder - a psychological disorder that is usually distressing but that allows one to think rationally and function socially. psychotic disorder - a psychological disorder in which a person loses contact with reality, experiencing irrational ideas and distorted perceptions I. Anxiety Disor ...
Psych Disorder Notes
... neurotic disorder - a psychological disorder that is usually distressing but that allows one to think rationally and function socially. psychotic disorder - a psychological disorder in which a person loses contact with reality, experiencing irrational ideas and distorted perceptions I. Anxiety Disor ...
... neurotic disorder - a psychological disorder that is usually distressing but that allows one to think rationally and function socially. psychotic disorder - a psychological disorder in which a person loses contact with reality, experiencing irrational ideas and distorted perceptions I. Anxiety Disor ...
Unit IV: Anxiety Disorders and Crises
... of variable length, at times to the point of terror, and are often accompanied by feelings of doom. Panic attacks often occur in familiar places, where there is seemingly nothing threatening to the individual. Physical symptoms include: increased pulse elevated blood pressure trembling diaph ...
... of variable length, at times to the point of terror, and are often accompanied by feelings of doom. Panic attacks often occur in familiar places, where there is seemingly nothing threatening to the individual. Physical symptoms include: increased pulse elevated blood pressure trembling diaph ...
Psychological Disorders
... Very rare; .5% - 1% suffer from this disorder Characterized by a loss of contact with reality Can develop gradually or very quickly Worsens over time Very difficult to treat 20% with schizophrenia will attempt suicide; 10% of ...
... Very rare; .5% - 1% suffer from this disorder Characterized by a loss of contact with reality Can develop gradually or very quickly Worsens over time Very difficult to treat 20% with schizophrenia will attempt suicide; 10% of ...
Somatoform disorders
... • Pain in the absence of adequate physical findings or pathophysiological explanations and in association with psychological factors that seem to play an etiological role ...
... • Pain in the absence of adequate physical findings or pathophysiological explanations and in association with psychological factors that seem to play an etiological role ...
item[`#file`]
... Prevalence – 2 in 10,000; more common in women, usually in adolescence/young adulthood Etiology – explained by psychoanalytic theory & biological factors o Psychoanalytic theory – conversion of psychiatric anxiety into unconscious physical debilitation o Biological factors – can see some physica ...
... Prevalence – 2 in 10,000; more common in women, usually in adolescence/young adulthood Etiology – explained by psychoanalytic theory & biological factors o Psychoanalytic theory – conversion of psychiatric anxiety into unconscious physical debilitation o Biological factors – can see some physica ...
Psychological Disorders
... A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or please in most activities. Manic episode A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept tha ...
... A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or please in most activities. Manic episode A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept tha ...
Mental Disorders
... 1)Huntington disease-a genetic disease that consists of abnormal movements, dementia, and psychological problems. 2. Multiple Sclerosis-An immune system disorder that affects the central nervous system (brain & spinal cord). 3. Senile dementia-Alzheimer’s type 4. Parkinson’s Disease-Nerve disorder t ...
... 1)Huntington disease-a genetic disease that consists of abnormal movements, dementia, and psychological problems. 2. Multiple Sclerosis-An immune system disorder that affects the central nervous system (brain & spinal cord). 3. Senile dementia-Alzheimer’s type 4. Parkinson’s Disease-Nerve disorder t ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... • Conversion disorder is changing emotional difficulties into a loss of specific body function – No actual physical damage is present – They usually accept the loss with relative calm – They invent physical symptoms to gain freedom from an unbearable conflict ...
... • Conversion disorder is changing emotional difficulties into a loss of specific body function – No actual physical damage is present – They usually accept the loss with relative calm – They invent physical symptoms to gain freedom from an unbearable conflict ...
SS04 - Psychology
... 62. Dr. Penn believes that dissociative amnesias are due to avoidance of unpleasant emotional conflicts. People with this disorder run from stressful situations by blocking out all disturbing thoughts of them. Furthermore, they gain attention by developing these symptoms. Dr. Penn probably supports ...
... 62. Dr. Penn believes that dissociative amnesias are due to avoidance of unpleasant emotional conflicts. People with this disorder run from stressful situations by blocking out all disturbing thoughts of them. Furthermore, they gain attention by developing these symptoms. Dr. Penn probably supports ...
Final Exam Practice Questions
... A) cognitive psychologist. B) behaviorist. C) humanist. D) biological psychologist. 4. Which modern psychological perspective focuses on how healthy people strive to reach their full potential? A) humanistic B) behavioral C) psychodynamic D) cognitive 5. In a naturalistic observation study, the rese ...
... A) cognitive psychologist. B) behaviorist. C) humanist. D) biological psychologist. 4. Which modern psychological perspective focuses on how healthy people strive to reach their full potential? A) humanistic B) behavioral C) psychodynamic D) cognitive 5. In a naturalistic observation study, the rese ...
Methods of carrying out research: • case study, experiment
... • Erikson: psychosocial crisis, trust versus mistrust, autonomy versus shame or doubt, initiative versus guilt, industry versus inferiority, identity versus identity confusion, intimacy versus isolation, generativity versus ...
... • Erikson: psychosocial crisis, trust versus mistrust, autonomy versus shame or doubt, initiative versus guilt, industry versus inferiority, identity versus identity confusion, intimacy versus isolation, generativity versus ...
Psikologi Anak Pertemuan 10 Emotional Disorders
... Early rejection, criticism by or loss of a parent Unrealistic expectations of self Cognitive Triad (self, events, the future) Major loss/disappointment will trigger a depressive reaction Maintained by distorted thinking patterns ...
... Early rejection, criticism by or loss of a parent Unrealistic expectations of self Cognitive Triad (self, events, the future) Major loss/disappointment will trigger a depressive reaction Maintained by distorted thinking patterns ...
Anxiety Disorders - Health People, Inc.
... relive the event in their mind, have nightmares or flashbacks. They may have difficulty with normal emotional responses; feel detached from others, anxious, problems sleeping, memory, and concentrating. A person with PTSD will go out of their way to avoid situations that remind them of their traumat ...
... relive the event in their mind, have nightmares or flashbacks. They may have difficulty with normal emotional responses; feel detached from others, anxious, problems sleeping, memory, and concentrating. A person with PTSD will go out of their way to avoid situations that remind them of their traumat ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.














![item[`#file`]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010071913_1-d22cdf4c5f760b7835c7265d64df00c8-300x300.png)