Bipolar Disorders - Dr. Ron Remick`s website
... Presenteeism (lost productivity while at work) – likely a more significant problem with mood disorders than previously recognized in Canada Productivity loss from presenteeism due to depression is 4 hours/week while loss from absenteeism is but 1 hour/week (between $6-60 billion loss per annum)! ...
... Presenteeism (lost productivity while at work) – likely a more significant problem with mood disorders than previously recognized in Canada Productivity loss from presenteeism due to depression is 4 hours/week while loss from absenteeism is but 1 hour/week (between $6-60 billion loss per annum)! ...
Name: Mental Disorders Diagnosis There are 11 different scenarios
... the doctor that her symptoms include chronic worry, muscle tension, headaches, trouble concentrating and falling asleep, feelings of nervousness (anxiety), and she is always waiting for the worst to happen. Based on Sally’s symptoms, what type of mental health disorder does she have? ...
... the doctor that her symptoms include chronic worry, muscle tension, headaches, trouble concentrating and falling asleep, feelings of nervousness (anxiety), and she is always waiting for the worst to happen. Based on Sally’s symptoms, what type of mental health disorder does she have? ...
Depression
... Styron, and they describe his first episode of major depression This experience belongs to millions ...
... Styron, and they describe his first episode of major depression This experience belongs to millions ...
Disorders and treatment – KEY TERMS 1. Hallucinations 2
... • Describe contemporary and historical conceptions of what constitutes psychological disorders. • Recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Association as the primary reference for making diagnostic judgments. • Discuss ...
... • Describe contemporary and historical conceptions of what constitutes psychological disorders. • Recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Association as the primary reference for making diagnostic judgments. • Discuss ...
Chapter 5 powerpoint
... 2.) Major Depression- a medical condition requiring treatment. This is more severe and lasts much longer than reactive depression; may develop from reactive depression, or may be the result of a chemical imbalance in the brain or a ...
... 2.) Major Depression- a medical condition requiring treatment. This is more severe and lasts much longer than reactive depression; may develop from reactive depression, or may be the result of a chemical imbalance in the brain or a ...
Hypochondria: hypochondriasis
... At first they should meet every 4 week. The patient is help to interpret the symptoms properly rather than focusing on the intensity of the pain or where he’s felling it. If the patient is administer medication it must be limited and the time the PA will spend with him too. The PA must be caref ...
... At first they should meet every 4 week. The patient is help to interpret the symptoms properly rather than focusing on the intensity of the pain or where he’s felling it. If the patient is administer medication it must be limited and the time the PA will spend with him too. The PA must be caref ...
Mental Health Disorders
... organic cause that relates to emotions and may involve mood swings or mood extremes that interfere with everyday living ...
... organic cause that relates to emotions and may involve mood swings or mood extremes that interfere with everyday living ...
Atypical Antipsychotic Drug Use in Children and Adolescents
... Sivaprasad, L., Hassan, T., Handy, S. Survey of atypical antipsychotic medication use by child and adolescent psychiatrists. 2006; Child and Adoles Mental Hlth 11(3): 164-167. Taniguchi, T., Sumitani, S. et al. Effect of antipsychotic replacement with quetiapine on the symptoms and quality of life o ...
... Sivaprasad, L., Hassan, T., Handy, S. Survey of atypical antipsychotic medication use by child and adolescent psychiatrists. 2006; Child and Adoles Mental Hlth 11(3): 164-167. Taniguchi, T., Sumitani, S. et al. Effect of antipsychotic replacement with quetiapine on the symptoms and quality of life o ...
Abnormal Psychology - Western Carolina University
... Increase in goal-directed activity (either socially, at work or school, or sexually) or psychomotor agitation Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a high potential for painful consequences (e.g., engaging in unrestrained buying sprees, sexual indiscretions, or foolish ...
... Increase in goal-directed activity (either socially, at work or school, or sexually) or psychomotor agitation Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a high potential for painful consequences (e.g., engaging in unrestrained buying sprees, sexual indiscretions, or foolish ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Abnormal Psychology What are psychological disorders? How do we define them? When does a person’s quirky behavior cross the line between normal and dysfunctional? ...
... Abnormal Psychology What are psychological disorders? How do we define them? When does a person’s quirky behavior cross the line between normal and dysfunctional? ...
"Chronic non-malignant pain - Psychological Interventions
... 1989 to date: Medico-legal expert 2400+ reports to date ...
... 1989 to date: Medico-legal expert 2400+ reports to date ...
How common is bipolar disorder?
... 1. Treating the current episode of mania or depression 2. Preventing the recurrence of mania and depression 3. Managing the recovery Since both the mania and the depression need to be treated, treatment usually involves more than one medication and long-term treatment is usually necessary to prev ...
... 1. Treating the current episode of mania or depression 2. Preventing the recurrence of mania and depression 3. Managing the recovery Since both the mania and the depression need to be treated, treatment usually involves more than one medication and long-term treatment is usually necessary to prev ...
List of Symptoms Mood swings from elation to depression Periods of
... depression in boarding school is not accurate. In the Differential Diagnosis discussion of Major Depressive Disorder, the clue to Carla’s correct diagnosis is found: “The presence of Manic or Mixed Episodes (with or without Hypomanic Episodes) indicates a diagnosis of Bipolar I Disorder” (DSM-IV-TR ...
... depression in boarding school is not accurate. In the Differential Diagnosis discussion of Major Depressive Disorder, the clue to Carla’s correct diagnosis is found: “The presence of Manic or Mixed Episodes (with or without Hypomanic Episodes) indicates a diagnosis of Bipolar I Disorder” (DSM-IV-TR ...
Bianca_Paranoid Personality Disorder
... If a person has Paranoid Personality Disorder. It’s a slight increase risk that the disorder could be passed down to their children. ...
... If a person has Paranoid Personality Disorder. It’s a slight increase risk that the disorder could be passed down to their children. ...
Chapter 14 Review
... Dissociative Disorders Dissociative Identity Disorder- detach themselves form the experience of severe and prolonged abuse Dramatic increase in reported cases of dissociative identity disorder during the past 40 or dos years most strongly suggests that symptoms of this disorder involve DID D ...
... Dissociative Disorders Dissociative Identity Disorder- detach themselves form the experience of severe and prolonged abuse Dramatic increase in reported cases of dissociative identity disorder during the past 40 or dos years most strongly suggests that symptoms of this disorder involve DID D ...
Somatoform disorders
... • Pain in the absence of adequate physical findings or pathophysiological explanations and in association with psychological factors that seem to play an etiological role ...
... • Pain in the absence of adequate physical findings or pathophysiological explanations and in association with psychological factors that seem to play an etiological role ...
L15PsychologicalDisorders
... Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1998) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes 2. Common causes of depression ...
... Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1998) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes 2. Common causes of depression ...
Mood Spectrum Disorders
... impaired ______ . Typically, the low phases last for a few weeks, but sometimes they last only a few days ______ . Individuals with this type of pattern may experience a period of "normal" mood in between mood swings, during which their mood and energy level feels "right" and their ability to functi ...
... impaired ______ . Typically, the low phases last for a few weeks, but sometimes they last only a few days ______ . Individuals with this type of pattern may experience a period of "normal" mood in between mood swings, during which their mood and energy level feels "right" and their ability to functi ...
Depression
... • Fronto-Limbic Network (FLN) disturbances: • Vicissitudes of mood and affective lability characterize BD and BPD respectively. • Within FLN there are key regions of interest in emotion processing and regulation: – dorsolateral, ventrolateral and dorsomedial prefrontal cortices (dl-PFC, vl-PFC, dm-P ...
... • Fronto-Limbic Network (FLN) disturbances: • Vicissitudes of mood and affective lability characterize BD and BPD respectively. • Within FLN there are key regions of interest in emotion processing and regulation: – dorsolateral, ventrolateral and dorsomedial prefrontal cortices (dl-PFC, vl-PFC, dm-P ...
Depression Parent information from AAP`s Healthy - G
... chances that her pediatrician or mental health professional will detect any signs of developing depression, and that she will have someone to talk to about her feelings. A child with bipolar disorder and ADHD is prone to explosive outbursts, extreme mood swings (high, low, or mixed mood), and severe ...
... chances that her pediatrician or mental health professional will detect any signs of developing depression, and that she will have someone to talk to about her feelings. A child with bipolar disorder and ADHD is prone to explosive outbursts, extreme mood swings (high, low, or mixed mood), and severe ...
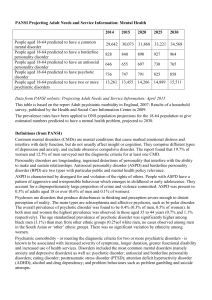
Mental Health Projections: PANSI 2015
... estimated numbers predicted to have a mental health problem, projected to 2030. Definitions (from PANSI) Common mental disorders (CMDs) are mental conditions that cause marked emotional distress and interfere with daily function, but do not usually affect insight or cognition. They comprise differen ...
... estimated numbers predicted to have a mental health problem, projected to 2030. Definitions (from PANSI) Common mental disorders (CMDs) are mental conditions that cause marked emotional distress and interfere with daily function, but do not usually affect insight or cognition. They comprise differen ...
Depressive Disorders
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood Mood disturbance plus three of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem or grandiosity Decreased need for sleep More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking Fligh ...
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood Mood disturbance plus three of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem or grandiosity Decreased need for sleep More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking Fligh ...
Schizophrenic Disorders
... D. Schizoaffective disorder and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features have been ruled out because either 1 ) no major depressive or manic episodes have occurred concurrently with the active-phase symptoms, or 2) if mood episodes have occurred during active-phase symptoms, they have ...
... D. Schizoaffective disorder and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features have been ruled out because either 1 ) no major depressive or manic episodes have occurred concurrently with the active-phase symptoms, or 2) if mood episodes have occurred during active-phase symptoms, they have ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.