Personality Disorder
... procedures that act on the patient’s nervous system, curing him or her of psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of healing techniques depending upon the client’s ...
... procedures that act on the patient’s nervous system, curing him or her of psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of healing techniques depending upon the client’s ...
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
... --ODD children often do not see their own role in the problem, frequently blaming others instead. Parents are often told incorrect, horrible stories about teachers; fathers about mothers; and vice versa. --Open defiance may start to be accompanied by covert activities such as stealing or lying. Co- ...
... --ODD children often do not see their own role in the problem, frequently blaming others instead. Parents are often told incorrect, horrible stories about teachers; fathers about mothers; and vice versa. --Open defiance may start to be accompanied by covert activities such as stealing or lying. Co- ...
B1_Harvey Mental Health Workshop 2017_FOR
... 2. Does it meet at least two of the criteria? 3. If no – No Class 4. If yes – must look at harmful behavior 5. No harmful behavior – Class B 6. Harmful behavior – Class A ...
... 2. Does it meet at least two of the criteria? 3. If no – No Class 4. If yes – must look at harmful behavior 5. No harmful behavior – Class B 6. Harmful behavior – Class A ...
Anxiety Disorders - People Server at UNCW
... Theory of Panic • Perceived control and safety • Anxiety sensitivity as a vulnerability factor for panic • Safety behaviors and the persistence of panic • Cognitive biases and the maintenance of panic ...
... Theory of Panic • Perceived control and safety • Anxiety sensitivity as a vulnerability factor for panic • Safety behaviors and the persistence of panic • Cognitive biases and the maintenance of panic ...
DSM-5: CONCEPTS, CHANGES, AND CRITIQUE© by Joan Turkus
... o Signs and symptoms may be observed by others or self-report o Not a normal part of a cultural or religious practice, although described as possession in some cultures o In children, not explained by imaginary playmates or fantasy play, usually don’t present with identity changes, but more interfer ...
... o Signs and symptoms may be observed by others or self-report o Not a normal part of a cultural or religious practice, although described as possession in some cultures o In children, not explained by imaginary playmates or fantasy play, usually don’t present with identity changes, but more interfer ...
I. Introduction: Understanding Psychological Disorders
... immediately precedes or follows a bout with major depression. b. During a manic episode, people sleep very little and display boundless energy; wildly inflated self-esteem; grandiose ideas, all of which may represent delusional, or false, beliefs; and flight of ideas. c. Because the ability to funct ...
... immediately precedes or follows a bout with major depression. b. During a manic episode, people sleep very little and display boundless energy; wildly inflated self-esteem; grandiose ideas, all of which may represent delusional, or false, beliefs; and flight of ideas. c. Because the ability to funct ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... Major Depressive Disorder Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. Signs include: ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. Signs include: ...
ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF DEPRESSION
... conditions. Part of the assessment of depression is the exclusion of such conditions. The major differential diagnoses for depressive symptoms are: Drug and alcohol problems. These may produce significant depressive symptoms. Alcohol in particular is a powerful depressant and may produce not only ...
... conditions. Part of the assessment of depression is the exclusion of such conditions. The major differential diagnoses for depressive symptoms are: Drug and alcohol problems. These may produce significant depressive symptoms. Alcohol in particular is a powerful depressant and may produce not only ...
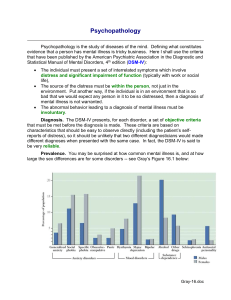
Psychopathology
... As noted earlier, there are similarities between depression and anxiety. Both anxious and depressed persons think of bad things. The anxious person worries about bad things that might happen. The depressed person thinks about all the bad things that have happened and concludes that life is miserable ...
... As noted earlier, there are similarities between depression and anxiety. Both anxious and depressed persons think of bad things. The anxious person worries about bad things that might happen. The depressed person thinks about all the bad things that have happened and concludes that life is miserable ...
Chapter 5: Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – Dissociative amnesia and fugue usually begin in adulthood – Both conditions show rapid onset and dissipation – Both conditions occur most often in females • Causes – Little is known, but trauma and stress seem heavily involved • Treatment – Persons with dissociative amnesia and fugue usually get b ...
... – Dissociative amnesia and fugue usually begin in adulthood – Both conditions show rapid onset and dissipation – Both conditions occur most often in females • Causes – Little is known, but trauma and stress seem heavily involved • Treatment – Persons with dissociative amnesia and fugue usually get b ...
Personality Disorders
... people, not you, who are the problem. If you also suffer from depression or anxiety, treatments that help other people likely don't work as well for you. Some of the commonalties associated with Personality Disorders include; 1. Disorders began early in life. 2. The disorders are disturbing to other ...
... people, not you, who are the problem. If you also suffer from depression or anxiety, treatments that help other people likely don't work as well for you. Some of the commonalties associated with Personality Disorders include; 1. Disorders began early in life. 2. The disorders are disturbing to other ...
PSYCHOSIS IN CHILDHOOD AND ADOLESCENCE
... Thought Disorder “Trouble with thinking clearly” Hallucinations “Strange experiences recently, hearing voices when no one there, people talking about you” Delusions “unusual events recently monitored in any way, strange experiences watching TV” ...
... Thought Disorder “Trouble with thinking clearly” Hallucinations “Strange experiences recently, hearing voices when no one there, people talking about you” Delusions “unusual events recently monitored in any way, strange experiences watching TV” ...
CONVERSION DISORDER
... Those with pseudo-seizures Those with mixed presentation Pathophysiology 1. Pathology of Disease o Not completely known underlying brain mechanisms still unproven o Links to functional changes in certain brain areas (decrease corticospinal tract activity in functional paresis, increase amygdal ...
... Those with pseudo-seizures Those with mixed presentation Pathophysiology 1. Pathology of Disease o Not completely known underlying brain mechanisms still unproven o Links to functional changes in certain brain areas (decrease corticospinal tract activity in functional paresis, increase amygdal ...
Introduction to Psychology
... overexcited state of mania formerly called manic-depressive disorder ...
... overexcited state of mania formerly called manic-depressive disorder ...
Exploring 9e
... Mood Disorders: Not just feeling “down;” not just sad about something Major Depressive Disorder: Stuck in dark withdrawal Bipolar Disorder: sometimes fleeing depression into mania Prevalence and Course of depression: Common, but ...
... Mood Disorders: Not just feeling “down;” not just sad about something Major Depressive Disorder: Stuck in dark withdrawal Bipolar Disorder: sometimes fleeing depression into mania Prevalence and Course of depression: Common, but ...
Mental Disorders
... D) Because the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder are all in the form of private mental experience, it is rarely diagnosed. 43. In the field of mental disorders, DSM refers to: A) a neurotransmitter system thought to underlie depression. B) a type of scan for brain areas involved in mental dis ...
... D) Because the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder are all in the form of private mental experience, it is rarely diagnosed. 43. In the field of mental disorders, DSM refers to: A) a neurotransmitter system thought to underlie depression. B) a type of scan for brain areas involved in mental dis ...
Chapter Outline
... personalities are aware of one another. However, even objective testing with physiological measurements produces conflicting findings about the existence of distinct personalities. Although this condition was once thought to be rare, there has been a dramatic increase in reported cases, perhaps beca ...
... personalities are aware of one another. However, even objective testing with physiological measurements produces conflicting findings about the existence of distinct personalities. Although this condition was once thought to be rare, there has been a dramatic increase in reported cases, perhaps beca ...
Module 13 Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness Powerpoint
... What Staff Can Do • Help resident learn to predict fluctuation in mood • Encourage medication compliance • Recognize symptoms early ...
... What Staff Can Do • Help resident learn to predict fluctuation in mood • Encourage medication compliance • Recognize symptoms early ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Distrustful even of close family and friends Reluctant to form close relationships Tend to blame others for their own shortcomings Pathological jealousy in intimate relationships Inappropriate outbursts of anger ...
... Distrustful even of close family and friends Reluctant to form close relationships Tend to blame others for their own shortcomings Pathological jealousy in intimate relationships Inappropriate outbursts of anger ...
Mental Health: Types of Mental Illness
... Anxiety disorders: People with anxiety disorders respond to certain objects or situations with fear and dread, as well as with physical signs of anxiety or nervousness, such as a rapid heartbeat and sweating. An anxiety disorder is diagnosed if the person's response is not appropriate for the situat ...
... Anxiety disorders: People with anxiety disorders respond to certain objects or situations with fear and dread, as well as with physical signs of anxiety or nervousness, such as a rapid heartbeat and sweating. An anxiety disorder is diagnosed if the person's response is not appropriate for the situat ...
somatoform disorder and homeopathy
... physiological cause. In Somatoform disorder, the symptoms are so intense that it can weaken a person’s potential to function. The patient is convinced that they are sick, but with no identifiable diagnosis. When no physical cause or underlying illness is determined on medical examination and lab res ...
... physiological cause. In Somatoform disorder, the symptoms are so intense that it can weaken a person’s potential to function. The patient is convinced that they are sick, but with no identifiable diagnosis. When no physical cause or underlying illness is determined on medical examination and lab res ...
b D I S O R D E R An Information Guide
... 3. a well state, during which many people feel normal and function well. The manias and depressions may be either “pure” episodes (they have only typical manic or depressive symptoms) or they may be “mixed” episodes (they may consist of a mixture of manic and depressive symptoms at the same time). T ...
... 3. a well state, during which many people feel normal and function well. The manias and depressions may be either “pure” episodes (they have only typical manic or depressive symptoms) or they may be “mixed” episodes (they may consist of a mixture of manic and depressive symptoms at the same time). T ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.