Torres: Copenhagen Quantum Mechanics
... None of this could happen on the visible scale “it becomes important to remember that science is concerned only with observable things and that we can observe an object only by letting it interact with some outside influence” -Dirac This interaction, observation, causes a disturbance on the quan ...
... None of this could happen on the visible scale “it becomes important to remember that science is concerned only with observable things and that we can observe an object only by letting it interact with some outside influence” -Dirac This interaction, observation, causes a disturbance on the quan ...
ECE-301 ELECTRICAL NETWORKS I
... University Press, 1995. Supriyo Datta, Quantum Transport Atom to Transistor, Cambridge, 2005. David K. Ferry and Stephen M. Goodnick, Transport in Nanostructures, Cambridge University Press, 1997. Coherent Transport: Single band effective mass Schroedinger’s equation. Single band tight binding Ham ...
... University Press, 1995. Supriyo Datta, Quantum Transport Atom to Transistor, Cambridge, 2005. David K. Ferry and Stephen M. Goodnick, Transport in Nanostructures, Cambridge University Press, 1997. Coherent Transport: Single band effective mass Schroedinger’s equation. Single band tight binding Ham ...
PPT | 345.5 KB - Joint Quantum Institute
... Physicists supported by the PFC at the Joint Quantum Institute have developed a new source of “entangled” photons – fundamental units of light whose properties are so intertwined that if the condition of one is measured, the condition of the other is instantaneously known, even if the photons are th ...
... Physicists supported by the PFC at the Joint Quantum Institute have developed a new source of “entangled” photons – fundamental units of light whose properties are so intertwined that if the condition of one is measured, the condition of the other is instantaneously known, even if the photons are th ...
Historical Introduction to the Elementary Particles
... the two charges, each electron continually emitting them and continually absorbing them. And the same goes for any noncontact force: where classically we interpret “action at a distance” as “mediated” by afield, we now say that it is mediated by an exchange of particles (the quanta of the field). In ...
... the two charges, each electron continually emitting them and continually absorbing them. And the same goes for any noncontact force: where classically we interpret “action at a distance” as “mediated” by afield, we now say that it is mediated by an exchange of particles (the quanta of the field). In ...
Development of the Model of the Atom
... de Broglie wondered that if light has a waveparticle duality, then maybe electrons may have the same nature. Scientists knew any wave confined to a space can have only certain frequencies. De Broglie suggested that electrons be considered waves confined to the space around an atomic nucleus. Exper ...
... de Broglie wondered that if light has a waveparticle duality, then maybe electrons may have the same nature. Scientists knew any wave confined to a space can have only certain frequencies. De Broglie suggested that electrons be considered waves confined to the space around an atomic nucleus. Exper ...
midterm answers
... tunnel effect, yes is does, potential energy is U, total energy is E and also U + KE, the latter being kinetic energy, so U > E implies negative kinetic energy which does not exist classically, in quantum mechanics this is not a problem at all, the wave function above is for such a scenario U > E, t ...
... tunnel effect, yes is does, potential energy is U, total energy is E and also U + KE, the latter being kinetic energy, so U > E implies negative kinetic energy which does not exist classically, in quantum mechanics this is not a problem at all, the wave function above is for such a scenario U > E, t ...
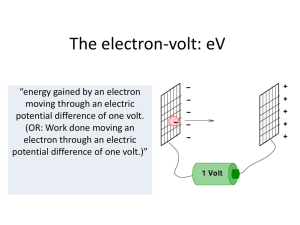
The electron-volt - Hockerill Students
... moving through an electric potential difference of one volt. (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
... moving through an electric potential difference of one volt. (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
Some essential questions to be able to answer in Lecturer: McGreevy
... What information does this encode? Under what circumstances does the resulting ρA describe a pure state? 5. The density matrix encodes a probability distribution on state vectors: In its spectral representation X ρ= pa |aiha| a ...
... What information does this encode? Under what circumstances does the resulting ρA describe a pure state? 5. The density matrix encodes a probability distribution on state vectors: In its spectral representation X ρ= pa |aiha| a ...
Aufbau Diagram Directions
... Aufbau: Electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first Pauli Exclusion: an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons (each electron will have a different spin) Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitas contain one elect ...
... Aufbau: Electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first Pauli Exclusion: an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons (each electron will have a different spin) Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitas contain one elect ...
Ch. 13 Worksheet blank
... 1. Which orbital is the first to be filled in any atom? __________ 2. How many electrons can each orbital hold? s = _______, p = _______, d = ______, f = ______ 3. The third energy level (n=3) can hold a maximum of _______ electrons and is divided into a total of _______ sublevels. 4. According to B ...
... 1. Which orbital is the first to be filled in any atom? __________ 2. How many electrons can each orbital hold? s = _______, p = _______, d = ______, f = ______ 3. The third energy level (n=3) can hold a maximum of _______ electrons and is divided into a total of _______ sublevels. 4. According to B ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. Distinguish between first and second order transitions of the time dependent perturbation theory with the help of schematic diagrams. 8. What is dipole approximation in emission/absorption process of an atom? 9. What is the limitation of Klein-Gordon equation? 10. Write down the Dirac matrices in ...
... 7. Distinguish between first and second order transitions of the time dependent perturbation theory with the help of schematic diagrams. 8. What is dipole approximation in emission/absorption process of an atom? 9. What is the limitation of Klein-Gordon equation? 10. Write down the Dirac matrices in ...
Glossary Chapter 4
... electromagnetic radiation a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space (91) electromagnetic spectrum all the forms of electromagnetic radiation (91) electron configuration the arrangement of electrons in an atom (105) excited state a state in which an atom has a highe ...
... electromagnetic radiation a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space (91) electromagnetic spectrum all the forms of electromagnetic radiation (91) electron configuration the arrangement of electrons in an atom (105) excited state a state in which an atom has a highe ...
The Wave Nature of Matter - Waterford Public Schools
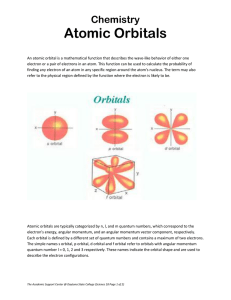
... finding an electron in a particular infinitesimally small volume of space in an atom • Because we are treating electrons as waves (not particles), we cannot pinpoint the specific location of an electron! • Instead, mathematical solutions to the wave functions give 3dimensional shapes (orbitals) with ...
... finding an electron in a particular infinitesimally small volume of space in an atom • Because we are treating electrons as waves (not particles), we cannot pinpoint the specific location of an electron! • Instead, mathematical solutions to the wave functions give 3dimensional shapes (orbitals) with ...
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW GUIDE
... 7. What is the difference between the Bohr model and the Quantum-Mechanical Model. ORBIT -> ORBITAL 7a. Explain the contributions of DeBroglie, Heisenberg and Schrodinger to our current understanding of the atom (quantum-mechanical model). ...
... 7. What is the difference between the Bohr model and the Quantum-Mechanical Model. ORBIT -> ORBITAL 7a. Explain the contributions of DeBroglie, Heisenberg and Schrodinger to our current understanding of the atom (quantum-mechanical model). ...
1 QED: Its state and its problems (Version 160815) The aim of this
... motion led people to abandon it in favor of an informal expansion of a scattering matrix. This approach gave rise to the so-called "perturbative formulation" of quantum field theory. A straight-forward expansion of the scattering matrix, however, inherits all the difficulties from the illdefined equ ...
... motion led people to abandon it in favor of an informal expansion of a scattering matrix. This approach gave rise to the so-called "perturbative formulation" of quantum field theory. A straight-forward expansion of the scattering matrix, however, inherits all the difficulties from the illdefined equ ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.