PHYS 221: Homework Assignment 3 This homework due just prior
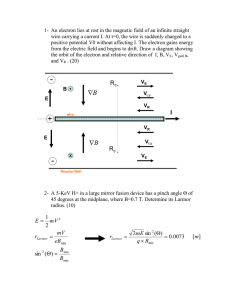
... is in a circular orbit of radius r moving with speed v. a) [4 points] What does the Bohr postulate say about the relationship between r and v? b) [8 points] In the Bohr model, the energy levels of a one-electron atom are given by En = − ...
... is in a circular orbit of radius r moving with speed v. a) [4 points] What does the Bohr postulate say about the relationship between r and v? b) [8 points] In the Bohr model, the energy levels of a one-electron atom are given by En = − ...
Chapter 31 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics
... numbers n, l, ml, and ms. This principle determines the way in which the electrons in multiple-electron atoms are distributed into shells and subshells. The arrangement of the periodic table of the elements is related to the exclusion principle. X-ray X-rays are electromagnetic waves emitted when hi ...
... numbers n, l, ml, and ms. This principle determines the way in which the electrons in multiple-electron atoms are distributed into shells and subshells. The arrangement of the periodic table of the elements is related to the exclusion principle. X-ray X-rays are electromagnetic waves emitted when hi ...
By: 3rd Period Chemistry Actinide Ionization Energy Probability
... Region with zero probability of finding an electron orbital Nuclear Model of the Atom Rutherford’s model nucleus with electrons around it Aristotle’s model ...
... Region with zero probability of finding an electron orbital Nuclear Model of the Atom Rutherford’s model nucleus with electrons around it Aristotle’s model ...
Thursday, 1/29/09 - Liberty Union High School District
... frequency was required to eject electron from metal •Problem-wave theory of light predicted light of any frequency could eject electron ...
... frequency was required to eject electron from metal •Problem-wave theory of light predicted light of any frequency could eject electron ...
Quantum mechanics in electronics
... Comparison with a normal computer for solving these problems ...
... Comparison with a normal computer for solving these problems ...
Electron-Positron Scattering
... To associate each diagram with an actual formula for the corresponding amplitude, we use what are called the Feynman rules. The rules tell us to write a brief formula for each part of a diagram (each external line, each internal line, and each vertex), then multiply these expressions together to obt ...
... To associate each diagram with an actual formula for the corresponding amplitude, we use what are called the Feynman rules. The rules tell us to write a brief formula for each part of a diagram (each external line, each internal line, and each vertex), then multiply these expressions together to obt ...
URL - StealthSkater
... When you change the electrical field vector of one, the other one will change to match it exactly. If you move it 10 degrees, the other photon will move its field vector 10 degrees. So you have this "communication" going on between photons even though they are separated by a very large distance. And ...
... When you change the electrical field vector of one, the other one will change to match it exactly. If you move it 10 degrees, the other photon will move its field vector 10 degrees. So you have this "communication" going on between photons even though they are separated by a very large distance. And ...
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... cannot know the instantaneous position and velocity of an electron (or any other particle) x – represents position p – represents momentum (velocity multiplied by mass) - represents a constant Δ – in this case, delta represents the uncertainty. ...
... cannot know the instantaneous position and velocity of an electron (or any other particle) x – represents position p – represents momentum (velocity multiplied by mass) - represents a constant Δ – in this case, delta represents the uncertainty. ...
Substance - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Note the negative energy (-1738 kJ) denotes the process is exothermic (energy was given off by the system.) If a 10,000 gram sample of gold absorbed all of this heat released from the water, what would be the change in temperature of the gold sample? The water gave off energy and the gold took in th ...
... Note the negative energy (-1738 kJ) denotes the process is exothermic (energy was given off by the system.) If a 10,000 gram sample of gold absorbed all of this heat released from the water, what would be the change in temperature of the gold sample? The water gave off energy and the gold took in th ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14.a.Find the energy eigen values of a particle of mass ‘m’ confined to a box of side ‘L’ (4) b.Three electrons are confined to a box of side 0.5Au. Find the lowest possible energy of the system if electron mass is 9.1 x 10-31kg and Planck’s constant h= 6.63x10-34Js (3.5) 15. Obtain the expression f ...
... 14.a.Find the energy eigen values of a particle of mass ‘m’ confined to a box of side ‘L’ (4) b.Three electrons are confined to a box of side 0.5Au. Find the lowest possible energy of the system if electron mass is 9.1 x 10-31kg and Planck’s constant h= 6.63x10-34Js (3.5) 15. Obtain the expression f ...
Structure of matter.
... the spin is not zero the nuclei have a magnetic moment i.e, they behave like small magnets NMR – nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in radiology are based on this property. ...
... the spin is not zero the nuclei have a magnetic moment i.e, they behave like small magnets NMR – nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in radiology are based on this property. ...
Quantum Mechanics Lecture Course for 4 Semester Students by W.B. von Schlippe
... closely specified nature which must be assigned to each isolated portion of energy and which depends on its eigenmass in accordance with the Planck-Einstein relation. Then the relativity theory requires the assignment to the uniform movement of each material point of the propagation of a certain wav ...
... closely specified nature which must be assigned to each isolated portion of energy and which depends on its eigenmass in accordance with the Planck-Einstein relation. Then the relativity theory requires the assignment to the uniform movement of each material point of the propagation of a certain wav ...
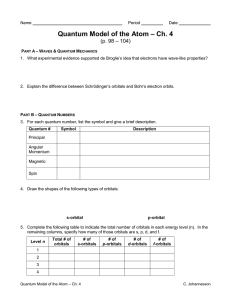
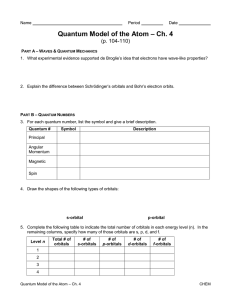
Quantum Model Worksheet
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
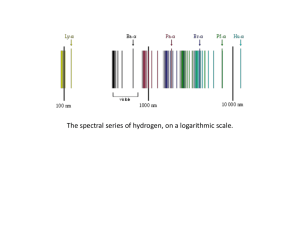
Chapter 12 Worksheet
... 8. Calculate the wavelengths (nm) emitted for the following electronic transitions in a Li2+ ion. a. n = 5 n = 3 b. n = 3 n = 1 9. An excited hydrogen atom with an electron in n = 5 state emits light having a frequency of 6.9 x 1014 s-1. Determine the principal quantum level (n) for the final st ...
... 8. Calculate the wavelengths (nm) emitted for the following electronic transitions in a Li2+ ion. a. n = 5 n = 3 b. n = 3 n = 1 9. An excited hydrogen atom with an electron in n = 5 state emits light having a frequency of 6.9 x 1014 s-1. Determine the principal quantum level (n) for the final st ...
Rutherford–Bohr model
... The Rutherford–Bohr model of the hydrogen atom (Z = 1) or a hydrogen-like ion (Z > 1), where the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of ...
... The Rutherford–Bohr model of the hydrogen atom (Z = 1) or a hydrogen-like ion (Z > 1), where the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.