Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... to this hypothesis, insults to the brain during sensitive phases of prenatal development or during birth can cause subtle neurological damage that elevates individuals’ vulnerabiltiy to schizophrenia years later in adolecence and early adulthood… Thus far, research has focused on viral infections or ...
... to this hypothesis, insults to the brain during sensitive phases of prenatal development or during birth can cause subtle neurological damage that elevates individuals’ vulnerabiltiy to schizophrenia years later in adolecence and early adulthood… Thus far, research has focused on viral infections or ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Coffee: More Than Just a Jolt in the
... informed about the serious, long-term risks to their mental and physical health. Studies show that alcohol prohibits antidepressants and antipsychotics from working. When the two are combined, there is a higher occurrence of psychotic episodes and more drastic symptoms of intoxication. People who ta ...
... informed about the serious, long-term risks to their mental and physical health. Studies show that alcohol prohibits antidepressants and antipsychotics from working. When the two are combined, there is a higher occurrence of psychotic episodes and more drastic symptoms of intoxication. People who ta ...
somatization disorder
... -Accept that patients can have distressing, real physical symptoms and medical conditions with coexisting psychiatric disturbance without malingering or feigning symptoms -Consider and discuss the possibility of somatoform disorders with the patient early in the work-up, if suspected, and make a psy ...
... -Accept that patients can have distressing, real physical symptoms and medical conditions with coexisting psychiatric disturbance without malingering or feigning symptoms -Consider and discuss the possibility of somatoform disorders with the patient early in the work-up, if suspected, and make a psy ...
Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... i. Memory loss that has no biological explanation ii. May be an attempt to escape from problems by blotting them out entirely iii. Remember how to speak and retain general knowledge, but don’t know who they are, where they are from, how they got where they are iv. Most often results from a traumatic ...
... i. Memory loss that has no biological explanation ii. May be an attempt to escape from problems by blotting them out entirely iii. Remember how to speak and retain general knowledge, but don’t know who they are, where they are from, how they got where they are iv. Most often results from a traumatic ...
The improvement of living. How do people cope with modern
... and language, and PDD-NOS, diagnosed when full criteria for the other two disorders are not met. Autism has a strong genetic basis, although the genetics of autism are complex and it is unclear whether ASD is explained more by rare mutations, or by rare combinations of common genetic variants. In ra ...
... and language, and PDD-NOS, diagnosed when full criteria for the other two disorders are not met. Autism has a strong genetic basis, although the genetics of autism are complex and it is unclear whether ASD is explained more by rare mutations, or by rare combinations of common genetic variants. In ra ...
Mental Status PPT
... that does not have basis in reality, not a part of religion or culture. The patient holding a delusion cannot be talked out of it, even with evidence to the contrary. ...
... that does not have basis in reality, not a part of religion or culture. The patient holding a delusion cannot be talked out of it, even with evidence to the contrary. ...
DSM-IV-TR/DSM-5, AN EVIDENCE-BASED COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
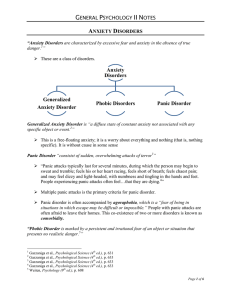
... family cohesion may be associated with a reduced likelihood of having an anxiety disorder(Priest & Denton, 2012). Somali: *Kuenzli (2012) reports that anxiety is a concept that is seeing within the Somali culture as a general lack of well-being. *Somali’s beliefs perceived as an effective ...
... family cohesion may be associated with a reduced likelihood of having an anxiety disorder(Priest & Denton, 2012). Somali: *Kuenzli (2012) reports that anxiety is a concept that is seeing within the Somali culture as a general lack of well-being. *Somali’s beliefs perceived as an effective ...
Dissociative Disorders
... identity disorder, the person has two or more distinct identities that take turns controlling his or her behavior. • Some researchers regard this as a culturally created phenomenon, not a true psychological disorder. Multiple identities, they say, are just a more extreme version of the normal human ...
... identity disorder, the person has two or more distinct identities that take turns controlling his or her behavior. • Some researchers regard this as a culturally created phenomenon, not a true psychological disorder. Multiple identities, they say, are just a more extreme version of the normal human ...
Regier DA. Time for a fresh start? Rethinking psychosis in DSM-V.
... information gleaned from recent research and investigations now underway. That said, it is timely to describe here the transition from the ‘‘planning’’ phase to the ‘‘action’’ phase of the DSM-V/ICD-11 revisions. The conference agenda reflected continuing interest in the range of phenomenological ma ...
... information gleaned from recent research and investigations now underway. That said, it is timely to describe here the transition from the ‘‘planning’’ phase to the ‘‘action’’ phase of the DSM-V/ICD-11 revisions. The conference agenda reflected continuing interest in the range of phenomenological ma ...
DSM-IV
... Only 33% said they would take medication for depression (vs. 69% of general population) 67% believed prayer & faith alone would successfully treat depression “almost all of the time or some of the time.” ...
... Only 33% said they would take medication for depression (vs. 69% of general population) 67% believed prayer & faith alone would successfully treat depression “almost all of the time or some of the time.” ...
Anxiety and Mood Disorders - Hobart and William Smith
... people exposed to traumatic event e.g., high rate of psychological blindness in Cambodian women after Khmer Rouge reign of terror in 1970s ...
... people exposed to traumatic event e.g., high rate of psychological blindness in Cambodian women after Khmer Rouge reign of terror in 1970s ...
Mental Disorder Intro-Student - health and physical education
... What is an anxiety disorder? What is the key difference between a phobia and generalized anxiety disorder? What is a compulsion? How does a compulsion differ from an obsession? What are some symptoms of a mood disorder? Explain how someone who has frequent unexpected panic attacks might develop a ...
... What is an anxiety disorder? What is the key difference between a phobia and generalized anxiety disorder? What is a compulsion? How does a compulsion differ from an obsession? What are some symptoms of a mood disorder? Explain how someone who has frequent unexpected panic attacks might develop a ...
Name - Louisiana Counseling Association
... childhood-related disorders (Reactive Attachment Disorder, Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder, & Posttraumatic Stress Disorder for Children 6 years and Younger), Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, Acute Stress Disorder, and Adjustment Disorders all into one classification of disorders in which a __ ...
... childhood-related disorders (Reactive Attachment Disorder, Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder, & Posttraumatic Stress Disorder for Children 6 years and Younger), Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, Acute Stress Disorder, and Adjustment Disorders all into one classification of disorders in which a __ ...
جامعة بنها
... 6- Decrease excessive stimuli and approved quiet environment. 7- Walk with pacing patient to give him support 8- Increase level of supervision for acutely patient to minimize selfinjury or loss control 9- Allow patient to use defenses as long as physical well-being is not at ...
... 6- Decrease excessive stimuli and approved quiet environment. 7- Walk with pacing patient to give him support 8- Increase level of supervision for acutely patient to minimize selfinjury or loss control 9- Allow patient to use defenses as long as physical well-being is not at ...
Psychiatric Rehabilitation
... Usually occurs during late adolescence to early adulthood. Onset is rare outside of this age range. ...
... Usually occurs during late adolescence to early adulthood. Onset is rare outside of this age range. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Understanding Mood Disorders • Causes behavioral and cognitive changes • Widespread • Women twice as vulnerable • Most major episodes terminate on their own • Stressful events can precede depression: work, marriage, death • With each new generation depression hitting earlier. Highest rates in devel ...
... Understanding Mood Disorders • Causes behavioral and cognitive changes • Widespread • Women twice as vulnerable • Most major episodes terminate on their own • Stressful events can precede depression: work, marriage, death • With each new generation depression hitting earlier. Highest rates in devel ...
Abnormal Psychology
... grandiosity (either in fantasy or actual behavior), an overwhelming need for admiration, and usually a complete lack of empathy toward others. ...
... grandiosity (either in fantasy or actual behavior), an overwhelming need for admiration, and usually a complete lack of empathy toward others. ...
Depressive Disorders
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood Mood disturbance plus three of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem or grandiosity Decreased need for sleep More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking Fligh ...
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood Mood disturbance plus three of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem or grandiosity Decreased need for sleep More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking Fligh ...
Emotional Health
... Psychoses are a number of severe mental disorders caused by physical or emotional disturbances, or both. A psychotic person generally fails at functioning in all areas of life. He or she is often unable to recognize reality, experiencing hallucinations (hearing or seeing things that are not real) an ...
... Psychoses are a number of severe mental disorders caused by physical or emotional disturbances, or both. A psychotic person generally fails at functioning in all areas of life. He or she is often unable to recognize reality, experiencing hallucinations (hearing or seeing things that are not real) an ...
introduction to child psychiatry
... All adult anxiety disorders may be seen in children. PTSD - may be a result of abuse Separation Anxiety Disorder – Developmentally inappropriate and excessive anxiety about separation from caretakers or home, of at least 4 weeks duration with onset before 18 years – Can lead to school refusal (schoo ...
... All adult anxiety disorders may be seen in children. PTSD - may be a result of abuse Separation Anxiety Disorder – Developmentally inappropriate and excessive anxiety about separation from caretakers or home, of at least 4 weeks duration with onset before 18 years – Can lead to school refusal (schoo ...
Chap16
... balance, paralysis, weakness, difficulty swallowing or lump in throat, double vision, blindness or deafness, seizures. The more medically naïve the person, the more implausible the symptoms. ...
... balance, paralysis, weakness, difficulty swallowing or lump in throat, double vision, blindness or deafness, seizures. The more medically naïve the person, the more implausible the symptoms. ...
Working with youth who have ED/BD diagnoses
... Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders (delusional disorder, schizophrenia, etc) Bipolar and related disorders (BP1, BP2, Cyclothymic) Depressive Disorders (Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder, Major Depressive Disorder, Persistent Depressive Disorder) ...
... Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders (delusional disorder, schizophrenia, etc) Bipolar and related disorders (BP1, BP2, Cyclothymic) Depressive Disorders (Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder, Major Depressive Disorder, Persistent Depressive Disorder) ...
Emotional Disturbance - National Association of Special Education
... symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. This term includes schizophrenia, but does not include students who are socially maladjusted, unless they have a serious emotional disturbance. ...
... symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. This term includes schizophrenia, but does not include students who are socially maladjusted, unless they have a serious emotional disturbance. ...
File
... diagnostic criteria are the same for both single and recurrent with the exception of frequency. To meet the criteria for a major depressive disorder, single episode there must be indication of a single major episode. For a major depressive disorder, recurrent two or more major depressive episodes ha ...
... diagnostic criteria are the same for both single and recurrent with the exception of frequency. To meet the criteria for a major depressive disorder, single episode there must be indication of a single major episode. For a major depressive disorder, recurrent two or more major depressive episodes ha ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.