THE WORLD OF ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
... COLLEGE COURSE PSYCH 219 Dr. Mary Ann Woodman Rogue Community College ...
... COLLEGE COURSE PSYCH 219 Dr. Mary Ann Woodman Rogue Community College ...
The Bipolar Child - VA Association of Visiting Teachers
... also strongly supported the hypothesis that the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are different than those seen in adults. ...
... also strongly supported the hypothesis that the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are different than those seen in adults. ...
Diagnosis and Classification of Psychological Problems
... Diagnosis = The process of determining whether the presenting problem(s) fit the criteria for a particular mental disorder ...
... Diagnosis = The process of determining whether the presenting problem(s) fit the criteria for a particular mental disorder ...
Types of Psychological Disorders
... Causes of Schizophrenia • There have been a variety of different theoretical explanations over time, but it has a clear biological basis • A Biological predisposition activated by stress – Positive symptoms seem to be the result of the overproduction of Dopamine (Can be treated by Chlorpromazine [b ...
... Causes of Schizophrenia • There have been a variety of different theoretical explanations over time, but it has a clear biological basis • A Biological predisposition activated by stress – Positive symptoms seem to be the result of the overproduction of Dopamine (Can be treated by Chlorpromazine [b ...
mental health issues - Eudora Schools Sites
... Phobia: An unrealistic and overwhelming fear of some objects or situation. Generalized anxiety disorder: A pattern of excessive, unrealistic worry not attributable to any recent experience. Panic disorder: Terrifying panic attacks that include physical symptoms such as rapid heart beat and dizziness ...
... Phobia: An unrealistic and overwhelming fear of some objects or situation. Generalized anxiety disorder: A pattern of excessive, unrealistic worry not attributable to any recent experience. Panic disorder: Terrifying panic attacks that include physical symptoms such as rapid heart beat and dizziness ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS AND TREATMENT
... Axis IV Psycho-social stressors and Environmental Problems Axis V Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) The DSM-5 has collapsed Axis I, II, and III into one Axis that contains “all psychiatric and general medical diagnoses. “DSM-IV is a categorical classification that divides mental disorders into ...
... Axis IV Psycho-social stressors and Environmental Problems Axis V Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) The DSM-5 has collapsed Axis I, II, and III into one Axis that contains “all psychiatric and general medical diagnoses. “DSM-IV is a categorical classification that divides mental disorders into ...
Common Psychological Histories
... •Biological symptoms: sleep, energy •Future thoughts: hopelessness, suicidal •Normal mood interspersed with depression and manic episodes •Mania episodes: irritable, elevated mood, fast speech, flight of ideas, grandiosity, excessive spending/drinking, insomnia, auditory hallucinations, delusions of ...
... •Biological symptoms: sleep, energy •Future thoughts: hopelessness, suicidal •Normal mood interspersed with depression and manic episodes •Mania episodes: irritable, elevated mood, fast speech, flight of ideas, grandiosity, excessive spending/drinking, insomnia, auditory hallucinations, delusions of ...
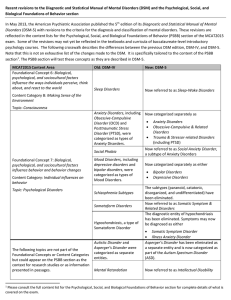
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
Psychological Disorders
... Behavioral- somatoform symptoms reinforce an escape from anxiety Other psychologists claim that patients literally “convert” mental stress to medical problems ...
... Behavioral- somatoform symptoms reinforce an escape from anxiety Other psychologists claim that patients literally “convert” mental stress to medical problems ...
FEEDING AND EATING DISORDERS
... inappropriate behaviors such as self-induced vomiting to avoid weight gain. DSM-5 criteria reduce the frequency of binge eating and compensatory behaviors that people with bulimia nervosa must exhibit, to once a week from twice weekly as specified in DSM-IV. ...
... inappropriate behaviors such as self-induced vomiting to avoid weight gain. DSM-5 criteria reduce the frequency of binge eating and compensatory behaviors that people with bulimia nervosa must exhibit, to once a week from twice weekly as specified in DSM-IV. ...
(HCL-32 R1) Manual
... Over a lifetime every human being experiences significant changes in energy, activity and mood, such as lows (sadness, loss, bereavement) and highs (romantic love, personal success and achievement) of shorter (hours, days) or longer (weeks, months) duration. There is a continuum from normal lows and ...
... Over a lifetime every human being experiences significant changes in energy, activity and mood, such as lows (sadness, loss, bereavement) and highs (romantic love, personal success and achievement) of shorter (hours, days) or longer (weeks, months) duration. There is a continuum from normal lows and ...
Psychological Disorders notes 16-1 objectives 1-4
... When physicians discovered that syphilis led to mental disorders, they started using medical models to review the physical causes of these disorders. ...
... When physicians discovered that syphilis led to mental disorders, they started using medical models to review the physical causes of these disorders. ...
Psychology 2 Final Exam Review PPT
... • Schizophrenia is characterized by a broad range of unusual behaviors that cause profound disruption in the lives of people suffering from the condition, as well as in the lives of the people around them. One of the most obvious kinds of impairment caused by schizophrenia involves how a person thin ...
... • Schizophrenia is characterized by a broad range of unusual behaviors that cause profound disruption in the lives of people suffering from the condition, as well as in the lives of the people around them. One of the most obvious kinds of impairment caused by schizophrenia involves how a person thin ...
What are the symptoms of bipolar disorder?
... For example, in the 1940s, people were brought to state hospitals and psychiatric facilities for depression. Depression was misunderstood and many people thought that depressed people were melancholy and since they could not "snap out of it" they were deemed fit for the psychiatric ward. Today, we k ...
... For example, in the 1940s, people were brought to state hospitals and psychiatric facilities for depression. Depression was misunderstood and many people thought that depressed people were melancholy and since they could not "snap out of it" they were deemed fit for the psychiatric ward. Today, we k ...
CHAPTER 13: Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
... week of the luteal phase, began to remit within a few days after the onset of the follicular phase, and were absent in the week postmenses, with at least one of the symptoms being either (1), (2), (3), or (4): (1) markedly depressed mood, feelings of hopelessness, or self-deprecating thoughts (2) ma ...
... week of the luteal phase, began to remit within a few days after the onset of the follicular phase, and were absent in the week postmenses, with at least one of the symptoms being either (1), (2), (3), or (4): (1) markedly depressed mood, feelings of hopelessness, or self-deprecating thoughts (2) ma ...
Psych8_Lecture_Ch16
... This illness is now considered a spectrum disorder. It's a group of related mental disorders that share some symptoms. They affect your sense of what's real. They change how you think, feel, and act. Delusional Disorder, Psychotic Disorders, Schizophreniform (similar to schizophrenia, less severe) ...
... This illness is now considered a spectrum disorder. It's a group of related mental disorders that share some symptoms. They affect your sense of what's real. They change how you think, feel, and act. Delusional Disorder, Psychotic Disorders, Schizophreniform (similar to schizophrenia, less severe) ...
conversion disorder
... seeing something extremely unpleasant and suddenly going blind). If you experience any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to conversion disorder. These symptoms may be caused by other, less serious health conditions. If you experience any one of them, see your physician. ...
... seeing something extremely unpleasant and suddenly going blind). If you experience any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to conversion disorder. These symptoms may be caused by other, less serious health conditions. If you experience any one of them, see your physician. ...
Chapter 16 Notes
... Section 3 – Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders 1. Somatoform Disorders – when anxiety creates a variety of physical symptoms for which no physical cause is apparent a. Also known as hysteria – unexplainable fainting, paralysis or deafness, used in Freud’s time b. Conversion Disorders i. Conversio ...
... Section 3 – Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders 1. Somatoform Disorders – when anxiety creates a variety of physical symptoms for which no physical cause is apparent a. Also known as hysteria – unexplainable fainting, paralysis or deafness, used in Freud’s time b. Conversion Disorders i. Conversio ...
List of Symptoms Mood swings from elation to depression Periods of
... thought disorder must be considered. It is possible that receiving a letter from her brother could trigger an onset of a Schizoaffective Disorder, Schizophrenia, or a Delusional Disorder. However, there is no gradual onset of symptoms as is the usual course in this disorders, and Carla’s delusions a ...
... thought disorder must be considered. It is possible that receiving a letter from her brother could trigger an onset of a Schizoaffective Disorder, Schizophrenia, or a Delusional Disorder. However, there is no gradual onset of symptoms as is the usual course in this disorders, and Carla’s delusions a ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.