Boundary between ASD and the Schizophrenias
... Mood disorders, including a suggested links link between Asperger’s and bipolar disorder ...
... Mood disorders, including a suggested links link between Asperger’s and bipolar disorder ...
정신질환의 분류
... DSM-II (1968): Influenced by Psychodynamic Theory DSM-III (1980): Development of Classification System DSM-IV (1994): Characterized as the “Biologic” or “Syndromal” Approach to Diagnosis DSM-IV-TR (2000): Evidence-based text revision of DSM-IV ...
... DSM-II (1968): Influenced by Psychodynamic Theory DSM-III (1980): Development of Classification System DSM-IV (1994): Characterized as the “Biologic” or “Syndromal” Approach to Diagnosis DSM-IV-TR (2000): Evidence-based text revision of DSM-IV ...
College Student`s Mental Health
... • Myth #7: Depression and other illnesses, such as anxiety disorders, do not affect children or adolescents. Any problems they have are just a part of growing up. • Myth #8: If you have a mental illness, you can will it away. Being treated for a psychiatric disorder means an individual has in some w ...
... • Myth #7: Depression and other illnesses, such as anxiety disorders, do not affect children or adolescents. Any problems they have are just a part of growing up. • Myth #8: If you have a mental illness, you can will it away. Being treated for a psychiatric disorder means an individual has in some w ...
chapter 13
... c. behavioral (include the terms “self-defeating,” “paradox,” “avoidance learning,” and “anxiety reduction hypothesis”) d. cognitive 20. Define what is meant by the term “psychosis.” 21. Define “delusion.” 22. Define “hallucination” and name the most common type. 23. Describe the emotion, communicat ...
... c. behavioral (include the terms “self-defeating,” “paradox,” “avoidance learning,” and “anxiety reduction hypothesis”) d. cognitive 20. Define what is meant by the term “psychosis.” 21. Define “delusion.” 22. Define “hallucination” and name the most common type. 23. Describe the emotion, communicat ...
Depression and Anxiety Disorder
... cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Unipolar (depression) and Bipolar Disorders (manic depressive). Dysthymia is chronic low-grade depression that does not meet the cr ...
... cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Unipolar (depression) and Bipolar Disorders (manic depressive). Dysthymia is chronic low-grade depression that does not meet the cr ...
Anxiety Disorders
... that increase Serotonin activity are somewhat effective in treating OCD Serotonin is also active in 2 brain areas that have been associated with OCD: the orbital region of the frontal cortex and caudate ...
... that increase Serotonin activity are somewhat effective in treating OCD Serotonin is also active in 2 brain areas that have been associated with OCD: the orbital region of the frontal cortex and caudate ...
Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses
... • Sudden onset of positive symptoms that last more than one day but remit within 30 days. • Criteria includes a return to the premorbid level of functioning. • Should be provisional • A specifier is used to indicate whether there is a discernable stressor that has triggered the episode. ...
... • Sudden onset of positive symptoms that last more than one day but remit within 30 days. • Criteria includes a return to the premorbid level of functioning. • Should be provisional • A specifier is used to indicate whether there is a discernable stressor that has triggered the episode. ...
Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology and the Treatment of Psychological
... recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) as the primary reference for making diagnostic judgments with specific attention to five axis, and identify the positive and negative consequences of diagnostic labels (e.g., the Rosenhan study). 12-2. Discuss the m ...
... recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) as the primary reference for making diagnostic judgments with specific attention to five axis, and identify the positive and negative consequences of diagnostic labels (e.g., the Rosenhan study). 12-2. Discuss the m ...
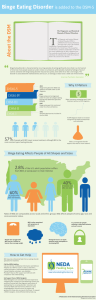
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
Personality Disorder
... Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. George Wesley Bellows, Dancer in a Madhouse, 1907. © 1997 The Art Institute of Chicago ...
... Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. George Wesley Bellows, Dancer in a Madhouse, 1907. © 1997 The Art Institute of Chicago ...
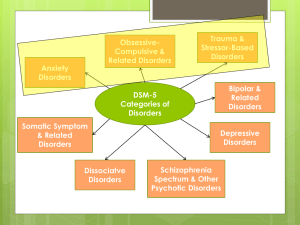
Psychiatric Classification
... 1 sexual/reproductive 1 pseudoneurological If within a medical condition, XS sxs Lab abnormalities absent Not intentionally feigned or produced ...
... 1 sexual/reproductive 1 pseudoneurological If within a medical condition, XS sxs Lab abnormalities absent Not intentionally feigned or produced ...
- National Affairs
... of symptoms; it doesn't actually matter which subset of symptoms is present, so long as there are enough of them. The list includes self-damaging impulsivity, intolerance of being alone, chronic feelings of boredom, a pattern of unstable relationships, emotional instability, recurrent accidents, and ...
... of symptoms; it doesn't actually matter which subset of symptoms is present, so long as there are enough of them. The list includes self-damaging impulsivity, intolerance of being alone, chronic feelings of boredom, a pattern of unstable relationships, emotional instability, recurrent accidents, and ...
presentation
... result in a diminished capacity for coping with the ordinary demands of life. Serious psychiatric disabilities include major depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and borderline personality disorder. The good news about mental illness is that recovery is p ...
... result in a diminished capacity for coping with the ordinary demands of life. Serious psychiatric disabilities include major depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and borderline personality disorder. The good news about mental illness is that recovery is p ...
Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders
... identity confusion or takes on a new identity. Depersonalization disorders involve persistent or recurrent episodes of depersonalization (a feeling that things are unreal or that you are not yourself) that are of sufficient severity to cause significant distress or impairment in functioning. Somatof ...
... identity confusion or takes on a new identity. Depersonalization disorders involve persistent or recurrent episodes of depersonalization (a feeling that things are unreal or that you are not yourself) that are of sufficient severity to cause significant distress or impairment in functioning. Somatof ...
Child and Adolescent Mental Health
... Level of thinking allows the person to transfer information from one situation to another, deal efficiently with complex problems, and plan realistically for the future. Physical development precedes cognitive development The last part of the brain to mature is the prefrontal cortex Adolescence is a ...
... Level of thinking allows the person to transfer information from one situation to another, deal efficiently with complex problems, and plan realistically for the future. Physical development precedes cognitive development The last part of the brain to mature is the prefrontal cortex Adolescence is a ...
PS 4251 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY - The American College of
... well as social scientist who wants to gain insight into the dynamics of abnormal psychology. ...
... well as social scientist who wants to gain insight into the dynamics of abnormal psychology. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... – One’s risk of developing schizophrenia increases as genetic relatedness to an individual with schizophrenia increases – Excess levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain are associated with schizophrenia – There are even structural differences in the brains of individuals with schizophrenia ...
... – One’s risk of developing schizophrenia increases as genetic relatedness to an individual with schizophrenia increases – Excess levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain are associated with schizophrenia – There are even structural differences in the brains of individuals with schizophrenia ...
Chapter 16 Part I Intro to Abnormal Psychology,
... Please utilize Barron’s Book for this chapter! 4/3 Chapter 16 quiz – Intro to abnormal, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and mood disorders quiz (25 MC questions) ...
... Please utilize Barron’s Book for this chapter! 4/3 Chapter 16 quiz – Intro to abnormal, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and mood disorders quiz (25 MC questions) ...
Somatoform disorders
... • Somatic sx, which suggest a physical disorder, but where there is no organic ...
... • Somatic sx, which suggest a physical disorder, but where there is no organic ...
Document
... • often no memory of a traumatic experience • traumatic experience may not produce phobia ...
... • often no memory of a traumatic experience • traumatic experience may not produce phobia ...
View Presentation
... Clinical onset of panic disorder is later. The role of heredity appears to be greater in panic disorder. The ratio of women to men is greater in panic disorder. Alcoholism is more common in people suffering from panic disorder. Depression is more common in panic disorder. ...
... Clinical onset of panic disorder is later. The role of heredity appears to be greater in panic disorder. The ratio of women to men is greater in panic disorder. Alcoholism is more common in people suffering from panic disorder. Depression is more common in panic disorder. ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... reassurance to the contrary – Typically begins in early adulthood and has a chronic course. – Comorbid with mood or anxiety disorders – Prevalence rate is 5% of the general population – The term ‘hypochondriasis’ has become pejorative and tends to be called ‘health anxiety disorder’ ...
... reassurance to the contrary – Typically begins in early adulthood and has a chronic course. – Comorbid with mood or anxiety disorders – Prevalence rate is 5% of the general population – The term ‘hypochondriasis’ has become pejorative and tends to be called ‘health anxiety disorder’ ...
CHAPTER 14 Psychological Disorders
... additions to or exaggerations of normal thought processes & behaviors (e.g., bizarre delusions & hallucinations) 2. Negative schizophrenia symptoms: loss of or absence of normal thought processes & behaviors (e.g., impaired attention, toneless speech, flattened affect, social withdrawal) ...
... additions to or exaggerations of normal thought processes & behaviors (e.g., bizarre delusions & hallucinations) 2. Negative schizophrenia symptoms: loss of or absence of normal thought processes & behaviors (e.g., impaired attention, toneless speech, flattened affect, social withdrawal) ...
Abnormal psychology slides
... Comorbid = more than one disorder at a time Most severe disorders in a small group of people 6% of population have 3 or more disorders ...
... Comorbid = more than one disorder at a time Most severe disorders in a small group of people 6% of population have 3 or more disorders ...
a PowerPoint presentation of Module 51
... include all of the following, EXCEPT: A. there is no evidence that humans can experience a divided consciousness. B. symptoms of the disorder are most dramatic after the patient has begun therapy. C. in some countries, the disorder is ...
... include all of the following, EXCEPT: A. there is no evidence that humans can experience a divided consciousness. B. symptoms of the disorder are most dramatic after the patient has begun therapy. C. in some countries, the disorder is ...
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum disorder is a mental disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be ""not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups"". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively ""severe"" mental disorders through to relatively ""mild and nonclinical deficits"".In some cases, a spectrum approach joins together conditions that were previously considered separately. A notable example of this trend is the autism spectrum, where conditions on this spectrum may now all be referred to as autism spectrum disorders. In other cases, what was treated as a single disorder comes to be seen (or seen once again) as comprising a range of types, a notable example being the bipolar spectrum. A spectrum approach may also expand the type or the severity of issues which are included, which may lessen the gap with other diagnoses or with what is considered ""normal"". Proponents of this approach argue that it is in line with evidence of gradations in the type or severity of symptoms in the general population, and helps reduce the stigma associated with a diagnosis. Critics, however, argue that it can take attention and resources away from the most serious conditions associated with the most disability, or on the other hand could unduly medicalize problems which are simply challenges people face in life.