Personality Disorder
... • Listen to your classmates as they read their case studies. • Determine the symptoms of the disorder they have included. • Are there any other symptoms they should have included? ...
... • Listen to your classmates as they read their case studies. • Determine the symptoms of the disorder they have included. • Are there any other symptoms they should have included? ...
DSM-5 - KVCC Docs
... Depersonalization Disorder is characterized by frequent feelings of detachment from oneself combined with an awareness of the detachment. To someone experiencing depersonalization, the external world feels strange and unreal and a person can even get the sense that they are watching themselves from ...
... Depersonalization Disorder is characterized by frequent feelings of detachment from oneself combined with an awareness of the detachment. To someone experiencing depersonalization, the external world feels strange and unreal and a person can even get the sense that they are watching themselves from ...
PPT
... S Axis I: Clinical Syndromes (Depression, Anxiety, OCD, Bipolar) S Axis II: Developmental and Personality Disorders (includes Autism ...
... S Axis I: Clinical Syndromes (Depression, Anxiety, OCD, Bipolar) S Axis II: Developmental and Personality Disorders (includes Autism ...
CHS284 Sociocultural Aspects of Mental Health
... • e.g., Mental illness among non-respondents greater among members of minority groups • Subcultural factors that influence responses to survey questions • e.g., Naysaying (to not loose face, violate cultural norms) greater ...
... • e.g., Mental illness among non-respondents greater among members of minority groups • Subcultural factors that influence responses to survey questions • e.g., Naysaying (to not loose face, violate cultural norms) greater ...
Document
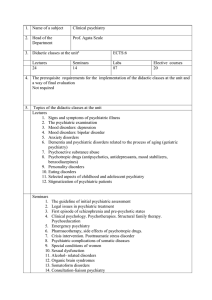
... 1. Signs and symptoms of psychiatric illness 2. The psychiatric examination 3. Mood disorders: depression 4. Mood disorders: bipolar disorder 5. Anxiety disorders 6. Dementia and psychiatric disorders related to the process of aging (geriatric psychiatry) 7. Psychoactive substance abuse 8. Psychotro ...
... 1. Signs and symptoms of psychiatric illness 2. The psychiatric examination 3. Mood disorders: depression 4. Mood disorders: bipolar disorder 5. Anxiety disorders 6. Dementia and psychiatric disorders related to the process of aging (geriatric psychiatry) 7. Psychoactive substance abuse 8. Psychotro ...
Personality Disorder
... • Listen to your classmates as they read their case studies. • Determine the symptoms of the disorder they have included. • Are there any other symptoms they should have included? ...
... • Listen to your classmates as they read their case studies. • Determine the symptoms of the disorder they have included. • Are there any other symptoms they should have included? ...
Mood Disorders - Texas Christian University
... DSM IV-TR-Classification of Suicide Four types of Suicide (Durkheim) ...
... DSM IV-TR-Classification of Suicide Four types of Suicide (Durkheim) ...
conversion disorder: a case report
... 10 – 15 minutes he could bend his knees and sit in a normal position for a brief period. His effort to move his lower limbs were encouraged and appreciated. The child was asked to continue the movement exercises at home and given a suggestion that he would flex his knees at right angles. In the seco ...
... 10 – 15 minutes he could bend his knees and sit in a normal position for a brief period. His effort to move his lower limbs were encouraged and appreciated. The child was asked to continue the movement exercises at home and given a suggestion that he would flex his knees at right angles. In the seco ...
Psy 120(2). - Highly Derivative
... More women suffer____, more men suffer ______ Describe the 3 principles of test construction: stadanrdized, relizable, ___ What are the baseline tests in the WAISR? If Joe has an IQ of 75, what does that mean? What’s a genogram? ...
... More women suffer____, more men suffer ______ Describe the 3 principles of test construction: stadanrdized, relizable, ___ What are the baseline tests in the WAISR? If Joe has an IQ of 75, what does that mean? What’s a genogram? ...
Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders
... BUT no physiological basis can be found Emotions Physical Symptoms ...
... BUT no physiological basis can be found Emotions Physical Symptoms ...
Anxiety and Somatoform Disorders
... diagnosed or under diagnosed because of the focus on physical symptoms. There are six types of somatoform disorders by the two most common are: Conversion Disorder – a change in or loss of physical functioning in a major part of the body with no medical explanation. Many show little concern about ...
... diagnosed or under diagnosed because of the focus on physical symptoms. There are six types of somatoform disorders by the two most common are: Conversion Disorder – a change in or loss of physical functioning in a major part of the body with no medical explanation. Many show little concern about ...
Child and Adolescent Psychopathology
... rare in children and clinicians believed that depression was expressed in behavioral disturbances such as behavior problems, enuresis, and somatic concerns. During the late 1970s, investigators demonstrated that many children and adolescents met full adult criteria for major depressive disorder (M ...
... rare in children and clinicians believed that depression was expressed in behavioral disturbances such as behavior problems, enuresis, and somatic concerns. During the late 1970s, investigators demonstrated that many children and adolescents met full adult criteria for major depressive disorder (M ...
1. Joe has an intense, irrational fear of snakes. He is suffering from a
... 16. A chronic state of low energy and self-esteem that is a bit less disabling than major depression is called a: A) generalized anxiety disorder. B) dysthymic disorder. C) dissociative disorder. D) phobia. E) bipolar disorder. 17. Which perspective suggests that explaining our own failures in terms ...
... 16. A chronic state of low energy and self-esteem that is a bit less disabling than major depression is called a: A) generalized anxiety disorder. B) dysthymic disorder. C) dissociative disorder. D) phobia. E) bipolar disorder. 17. Which perspective suggests that explaining our own failures in terms ...
Mental and Emotional Health
... Relaxation skills include taking deep, even breaths and doing exercises that relax your muscles. Quiet activities, such as reading a book, can help you relax and reduce stress. ...
... Relaxation skills include taking deep, even breaths and doing exercises that relax your muscles. Quiet activities, such as reading a book, can help you relax and reduce stress. ...
Lecture 6
... symptoms of major depression are milder but remain unchanged for at least two years can last 20 – 30 years – median duration of 5 years 79% with dysthymia have had a major ...
... symptoms of major depression are milder but remain unchanged for at least two years can last 20 – 30 years – median duration of 5 years 79% with dysthymia have had a major ...
Draft Module 6 - Structured Assessment and Screenings
... Pediatric Symptom Checklist Activities of Daily Living (Katz) ...
... Pediatric Symptom Checklist Activities of Daily Living (Katz) ...
Conversion Disorder in Young People
... The symptom or deficit, after appropriate investigation, cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or as a culturally lt ll sanctioned ti d behavior b h i or experience. i The symptom or deficit causes clinically significant distress or impairment i ...
... The symptom or deficit, after appropriate investigation, cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or as a culturally lt ll sanctioned ti d behavior b h i or experience. i The symptom or deficit causes clinically significant distress or impairment i ...
Emotional Health
... experiencing hallucinations (hearing or seeing things that are not real) and delusions (irrational beliefs that do not reflect reality). Characteristics of the psychotic also include disorganized thinking and personality changes. Although the above two terms are used quite frequently to describe an ...
... experiencing hallucinations (hearing or seeing things that are not real) and delusions (irrational beliefs that do not reflect reality). Characteristics of the psychotic also include disorganized thinking and personality changes. Although the above two terms are used quite frequently to describe an ...
Document
... Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved ...
... Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved ...
implications of mental illness for the search and rescue community
... In general, mental disorders can profoundly impact a person’s thinking, feeling, moods, ability to relate to others, and capacity to cope with everyday life. They are biologically-based brain disorders that can fall along a continuum of severity. They can affect anyone, and are not a sign of persona ...
... In general, mental disorders can profoundly impact a person’s thinking, feeling, moods, ability to relate to others, and capacity to cope with everyday life. They are biologically-based brain disorders that can fall along a continuum of severity. They can affect anyone, and are not a sign of persona ...
Abnormality_ch_1
... think of as normal were considered disorders: masturbation in nineteenth-century America was considered a hallmark of insanity, whereas today we recognize it to be almost universal in males and very common in females. Conversely, the Jerusalem Syndrome is now a clear disorder that warrants hospitali ...
... think of as normal were considered disorders: masturbation in nineteenth-century America was considered a hallmark of insanity, whereas today we recognize it to be almost universal in males and very common in females. Conversely, the Jerusalem Syndrome is now a clear disorder that warrants hospitali ...
Anxiety Disorders - U
... • Social phobia generalized type vs. performance anxiety • 13.3.% of population at some point in their lives (favors females only somewhat); onset 15 years of age • The most effective treatment is cognitive behavioral group therapy; medication in severe cases (antidepressants) ...
... • Social phobia generalized type vs. performance anxiety • 13.3.% of population at some point in their lives (favors females only somewhat); onset 15 years of age • The most effective treatment is cognitive behavioral group therapy; medication in severe cases (antidepressants) ...
Mental Disorder
... • Also known as : Manic – depressive disorder • Characterized by the following traits • Extreme mood changes • Extreme energy levels • Extreme behaviors ...
... • Also known as : Manic – depressive disorder • Characterized by the following traits • Extreme mood changes • Extreme energy levels • Extreme behaviors ...
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum disorder is a mental disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be ""not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups"". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively ""severe"" mental disorders through to relatively ""mild and nonclinical deficits"".In some cases, a spectrum approach joins together conditions that were previously considered separately. A notable example of this trend is the autism spectrum, where conditions on this spectrum may now all be referred to as autism spectrum disorders. In other cases, what was treated as a single disorder comes to be seen (or seen once again) as comprising a range of types, a notable example being the bipolar spectrum. A spectrum approach may also expand the type or the severity of issues which are included, which may lessen the gap with other diagnoses or with what is considered ""normal"". Proponents of this approach argue that it is in line with evidence of gradations in the type or severity of symptoms in the general population, and helps reduce the stigma associated with a diagnosis. Critics, however, argue that it can take attention and resources away from the most serious conditions associated with the most disability, or on the other hand could unduly medicalize problems which are simply challenges people face in life.