Module 22 psych
... Mental disorders involve genetic, physiological, or neurological factors that cause systems that can be diagnosed and ...
... Mental disorders involve genetic, physiological, or neurological factors that cause systems that can be diagnosed and ...
Therapy Modalities Chart
... Directions: Write a “file note” (summaries of diseases and treatments) for a patient that you create under each kind of therapy. You may use a separate piece of paper if you feel cramped on space. The file note should reflect information you understood from the chart. Here’s an example using the fir ...
... Directions: Write a “file note” (summaries of diseases and treatments) for a patient that you create under each kind of therapy. You may use a separate piece of paper if you feel cramped on space. The file note should reflect information you understood from the chart. Here’s an example using the fir ...
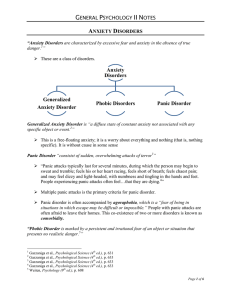
Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... There is a persistent and irrational fear present and it is an avoidance of the feared object There are a number of various types of phobias. Etiology of Anxiety Disorders: Gazzaniga et al6 point out several contributing factors to the development of anxiety disorders: o Temperment o Biased t ...
... There is a persistent and irrational fear present and it is an avoidance of the feared object There are a number of various types of phobias. Etiology of Anxiety Disorders: Gazzaniga et al6 point out several contributing factors to the development of anxiety disorders: o Temperment o Biased t ...
Psych Disorders Review Sheet
... Perspectives of Psychological Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders: Between normality and abnormality there is not a gulf but a somewhat arbitrary line. Where we draw this line depends on how atypical, disturbing, maladaptive, and unjustifiable a person’s behavior is. Understanding Psychologic ...
... Perspectives of Psychological Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders: Between normality and abnormality there is not a gulf but a somewhat arbitrary line. Where we draw this line depends on how atypical, disturbing, maladaptive, and unjustifiable a person’s behavior is. Understanding Psychologic ...
Mental Health
... and withdrawal, particularly alcohol, opioids, steroids and stimulants. Typically takes 4-8 weeks of clean time before substance-induced depression can be ruled out Older adults who abuse substances usually have ...
... and withdrawal, particularly alcohol, opioids, steroids and stimulants. Typically takes 4-8 weeks of clean time before substance-induced depression can be ruled out Older adults who abuse substances usually have ...
Tools for Screening and Measuring Progress
... 2. Do you ever use alcohol or drugs to Relax, feel better about yourself, or fit in? 3. Do you ever use alcohol/drugs while you are by yourself, Alone? 4. Do your Family or Friends ever tell you that you should cut down on your drinking or drug use? 5. Do you ever Forget things you did while using a ...
... 2. Do you ever use alcohol or drugs to Relax, feel better about yourself, or fit in? 3. Do you ever use alcohol/drugs while you are by yourself, Alone? 4. Do your Family or Friends ever tell you that you should cut down on your drinking or drug use? 5. Do you ever Forget things you did while using a ...
Chapter 16-Psychotherapy - Department of Psychology
... Discussion Question: • One of the main assumptions of behavior therapies is that behavior is a product of learning. On the surface, this seems like a straightforward and reasonable assumption, but do you think that some psychological disorders may develop as a result of genetic factors rather than ...
... Discussion Question: • One of the main assumptions of behavior therapies is that behavior is a product of learning. On the surface, this seems like a straightforward and reasonable assumption, but do you think that some psychological disorders may develop as a result of genetic factors rather than ...
Personality Disorders
... Experiences and Behaviors remarkably outside the norm (for culture). Causes significant distress or impairment Starts in adolescence/early adulthood Pervasive across settings Not GMC or Substance ...
... Experiences and Behaviors remarkably outside the norm (for culture). Causes significant distress or impairment Starts in adolescence/early adulthood Pervasive across settings Not GMC or Substance ...
Affective Disorders
... - if there is no significant improvement after an adequate trial of drugs ,consider a structured psychological therapy focused on depressive symptoms, problem solving ,improving social functioning, and medication concordance ...
... - if there is no significant improvement after an adequate trial of drugs ,consider a structured psychological therapy focused on depressive symptoms, problem solving ,improving social functioning, and medication concordance ...
anxiety disorders(1) - temp
... return to normal after a few hours. Patients with PTSD have a hypersecretion of corticotropinreleasing factor but demonstrate subnormal levels of cortisol at the time of trauma and chronically. Dysregulation of the HPA axis is postulated to be a risk factor for eventual development of PTSD. Neuroche ...
... return to normal after a few hours. Patients with PTSD have a hypersecretion of corticotropinreleasing factor but demonstrate subnormal levels of cortisol at the time of trauma and chronically. Dysregulation of the HPA axis is postulated to be a risk factor for eventual development of PTSD. Neuroche ...
Am J Psychiatry 167:487
... recent studies of personality disorders. An individual may have a state and trait at the same time—that is, state and trait can be comorbid. The organization of DSM-III, DSM-III-R, and DSM-IV into axis I and axis II was in great part intended to highlight such comorbidities and call clinical attenti ...
... recent studies of personality disorders. An individual may have a state and trait at the same time—that is, state and trait can be comorbid. The organization of DSM-III, DSM-III-R, and DSM-IV into axis I and axis II was in great part intended to highlight such comorbidities and call clinical attenti ...
Disorders - Fulton County Schools
... not been found in other countries. Critics’ Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
... not been found in other countries. Critics’ Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
Test 3
... first consideration as described in class when dealing with the patient with Anorexia? (hint: where is treatment likely to occur?). 25. Personality disorders are defined first and foremost as enduring and pervasive. Discuss what these mean and why they are important in the diagnosis of a personality ...
... first consideration as described in class when dealing with the patient with Anorexia? (hint: where is treatment likely to occur?). 25. Personality disorders are defined first and foremost as enduring and pervasive. Discuss what these mean and why they are important in the diagnosis of a personality ...
Continuing Education
... Mood disorders are characterized by a prolonged emotion – usually depression or elation – that impacts overall mental health. Key mood disorders include major depression, bipolar disorder, dysthymia and cyclothymia. Major depression is a common psychiatric symptom, syndrome (condition) and disorder. ...
... Mood disorders are characterized by a prolonged emotion – usually depression or elation – that impacts overall mental health. Key mood disorders include major depression, bipolar disorder, dysthymia and cyclothymia. Major depression is a common psychiatric symptom, syndrome (condition) and disorder. ...
Young Adults with Bipolar Disorder
... Have a greater difficulty with job longevity often losing a job during a depressive episode “People at risk for mania have also been found to have high educational and occupational attainment” (Kwapil, Miller, Zinser, Chapman, Chapman, & Eckblad, 2000) ...
... Have a greater difficulty with job longevity often losing a job during a depressive episode “People at risk for mania have also been found to have high educational and occupational attainment” (Kwapil, Miller, Zinser, Chapman, Chapman, & Eckblad, 2000) ...
Units 12-13 Guide
... These do not represent the entirety of what students must understand. They do, however, point people in the correct direction. Use these questions to see where the concepts above “fit.” Also, use the questions listed as a guide in your reading. 1. What is the difference between normality and disorde ...
... These do not represent the entirety of what students must understand. They do, however, point people in the correct direction. Use these questions to see where the concepts above “fit.” Also, use the questions listed as a guide in your reading. 1. What is the difference between normality and disorde ...
SECTION 7: MENTAL HEALTH Summary: This table is based on the
... violence committed. ASPD was present in 0.3% of adults aged 18 or over (0.6% of men and 0.1% of women). BPD is characterised by high levels of personal and emotional instability associated with significant impairment. People with BPD have severe difficulties with sustaining relationships, and self-h ...
... violence committed. ASPD was present in 0.3% of adults aged 18 or over (0.6% of men and 0.1% of women). BPD is characterised by high levels of personal and emotional instability associated with significant impairment. People with BPD have severe difficulties with sustaining relationships, and self-h ...
Tips for Living - Understanding Mood Disorders
... disorder may be sad, extremely tired, unmotivated, suicidal, have no interest in typical pleasurable activities, feel worthless or guilty, and be unable to sleep or eat. Some people with depression also experience mania, and the combination of the two is known as bipolar disorder. When a person expe ...
... disorder may be sad, extremely tired, unmotivated, suicidal, have no interest in typical pleasurable activities, feel worthless or guilty, and be unable to sleep or eat. Some people with depression also experience mania, and the combination of the two is known as bipolar disorder. When a person expe ...
ANXIETY DISORDERS Sharon Crews, RN
... Physician or mental health provider will ask detailed questions about symptoms Physician or mental health provider will ask detailed medical history Mental Health Professionals may utilize psychological questionnaire Physician may perform a physical examination to look for underlying medical con ...
... Physician or mental health provider will ask detailed questions about symptoms Physician or mental health provider will ask detailed medical history Mental Health Professionals may utilize psychological questionnaire Physician may perform a physical examination to look for underlying medical con ...
DSM-5 Understanding and Interpreting
... Consolidation into Autism Spectrum Disorder Autistic Disorder, Asperger’s Disorder, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder were consolidated into one group known as Autism Spectrum Disorder. Symptoms of these disorders represent a single continuum of mild to severe impairments in the two domains ...
... Consolidation into Autism Spectrum Disorder Autistic Disorder, Asperger’s Disorder, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder were consolidated into one group known as Autism Spectrum Disorder. Symptoms of these disorders represent a single continuum of mild to severe impairments in the two domains ...
Psychologie Anglophone
... 1. Statistical infrequency (how rare is the behaviour ?) A behaviour may be judged abnormal if it occurs infrequently in a given population. For example believing that others are plotting against you is statistically abnormal. However, having great intelligence, exceptional athletic abilities or an ...
... 1. Statistical infrequency (how rare is the behaviour ?) A behaviour may be judged abnormal if it occurs infrequently in a given population. For example believing that others are plotting against you is statistically abnormal. However, having great intelligence, exceptional athletic abilities or an ...
Child Psychiatry
... delayed or abnormal speech an obsessive desire for sameness onset in the first two years of life ...
... delayed or abnormal speech an obsessive desire for sameness onset in the first two years of life ...
Somatization Disorder
... The pain causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning Psychological factors are judged to have an important role in the onset, severity, exacerbation, or maintenance of the pain The symptom is not intentionally produced or feig ...
... The pain causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning Psychological factors are judged to have an important role in the onset, severity, exacerbation, or maintenance of the pain The symptom is not intentionally produced or feig ...
Stand: 20
... 3. Classification of mental disorders according to ICD 10 Psychopathology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, systematization, operationalization and classification of mental disorders Multiaxial classification scheme (MAS) according to ICD-10 in child and adolescent psychiatry: 1st Axis: Clinical ...
... 3. Classification of mental disorders according to ICD 10 Psychopathology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, systematization, operationalization and classification of mental disorders Multiaxial classification scheme (MAS) according to ICD-10 in child and adolescent psychiatry: 1st Axis: Clinical ...
Module 36 Chapter 110 Essentials of Understanding
... your sense of well-being Occasions of overwhelming high stress Prolonged depression – sense of helplessness Withdrawal from other people Chronic physical symptoms without a physical ...
... your sense of well-being Occasions of overwhelming high stress Prolonged depression – sense of helplessness Withdrawal from other people Chronic physical symptoms without a physical ...
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum disorder is a mental disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be ""not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups"". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively ""severe"" mental disorders through to relatively ""mild and nonclinical deficits"".In some cases, a spectrum approach joins together conditions that were previously considered separately. A notable example of this trend is the autism spectrum, where conditions on this spectrum may now all be referred to as autism spectrum disorders. In other cases, what was treated as a single disorder comes to be seen (or seen once again) as comprising a range of types, a notable example being the bipolar spectrum. A spectrum approach may also expand the type or the severity of issues which are included, which may lessen the gap with other diagnoses or with what is considered ""normal"". Proponents of this approach argue that it is in line with evidence of gradations in the type or severity of symptoms in the general population, and helps reduce the stigma associated with a diagnosis. Critics, however, argue that it can take attention and resources away from the most serious conditions associated with the most disability, or on the other hand could unduly medicalize problems which are simply challenges people face in life.