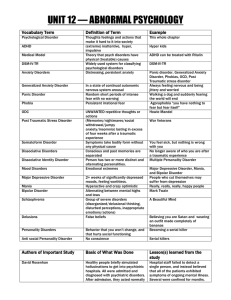
unit 12 — abnormal psychology
... any physical cause Conscious and past memories are separated Person has two or more distinct and alternating personalities. Emotional extremes 2+ weeks of significantly depressed moods, feeling worthless. Hyperactive and crazy optimistic Alternating between mental highs and lows Group of severe diso ...
... any physical cause Conscious and past memories are separated Person has two or more distinct and alternating personalities. Emotional extremes 2+ weeks of significantly depressed moods, feeling worthless. Hyperactive and crazy optimistic Alternating between mental highs and lows Group of severe diso ...
ADHD (TDAH)
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
Psychological Disorders
... Define Maladaptive Behavior What is the DSM-IV-TR Understand Psychotic Disorders Define Delusional Disorders Know the 5 types and delusional disorders and their characteristics (erotomanic, grandiose, etc) List the characteristics of schizophrenia Know the 4 types of schizophrenia Define Mood Disord ...
... Define Maladaptive Behavior What is the DSM-IV-TR Understand Psychotic Disorders Define Delusional Disorders Know the 5 types and delusional disorders and their characteristics (erotomanic, grandiose, etc) List the characteristics of schizophrenia Know the 4 types of schizophrenia Define Mood Disord ...
Mental Illness intro (Bipolar / mood Disorder
... may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday activities ...
... may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday activities ...
OCDR USC Sites Flyer_20150326_IRB Approved_No Riverside Ofc
... You Can Make a Difference! Research has shown that genes can make some people more likely than others to develop Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and Related Disorders (Hoarding Disorder, Body Dysmorphic Disorder, Hair Pulling Disorder/ Trichotillomania, and Skin Picking Disorder/Excoriation Disorder). ...
... You Can Make a Difference! Research has shown that genes can make some people more likely than others to develop Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and Related Disorders (Hoarding Disorder, Body Dysmorphic Disorder, Hair Pulling Disorder/ Trichotillomania, and Skin Picking Disorder/Excoriation Disorder). ...
Unit XII: Abnormal Behavior
... The goal of the Operation Beautiful website is to end negative self-talk or “Fat Talk.” ...
... The goal of the Operation Beautiful website is to end negative self-talk or “Fat Talk.” ...
Presentation1
... • Long tracts that extended outside frontal and temporal lobes were excluded as were short tracts that didn’t enter the fixed ROI’s. ...
... • Long tracts that extended outside frontal and temporal lobes were excluded as were short tracts that didn’t enter the fixed ROI’s. ...
Psychological Disorders When is behavior likely to be labeled as
... What role do obsessive thoughts play in anxiety? What role do compulsive behaviors play in anxiety? Why are some people more vulnerable to PTSD? How does knowing that there is a relationship between temperament and long term phobias illustrate the role of genetic predispositions in the development o ...
... What role do obsessive thoughts play in anxiety? What role do compulsive behaviors play in anxiety? Why are some people more vulnerable to PTSD? How does knowing that there is a relationship between temperament and long term phobias illustrate the role of genetic predispositions in the development o ...
Jason Bernard Christopher Rodriguez Christian Lopez
... Aggressive or violent behavior- Anger issues. Picture of Aggressive Behavior ...
... Aggressive or violent behavior- Anger issues. Picture of Aggressive Behavior ...
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
... almost 21 % of children ages 9 to 17 in the United States have a diagnosable mental or addictive disorder associated with at least minimum impairment (this chart shows 30.9%) ...
... almost 21 % of children ages 9 to 17 in the United States have a diagnosable mental or addictive disorder associated with at least minimum impairment (this chart shows 30.9%) ...
Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders
... Summary of Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders (cont.) ...
... Summary of Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders (cont.) ...
View Presentation
... Serious violations of rules Behaviors would constitute antisocial personality disorder if child were over 18 years ...
... Serious violations of rules Behaviors would constitute antisocial personality disorder if child were over 18 years ...
Anxiety Disorders
... – Amnesia + flight to a diff. environment – last from days to decades – New identity possibly est. – Escape from conflict ...
... – Amnesia + flight to a diff. environment – last from days to decades – New identity possibly est. – Escape from conflict ...
A mental or emotional condition that makes it difficult for
... Disturbance in a person’s mood…such as a depressive mood or a bipolar (split personality) mood. A disorder involving extreme moods. ...
... Disturbance in a person’s mood…such as a depressive mood or a bipolar (split personality) mood. A disorder involving extreme moods. ...
Mental and Emotional Illness
... • Intense and exaggerated fear of a specific situation or object • Examples: fear of animals, heights, flying ...
... • Intense and exaggerated fear of a specific situation or object • Examples: fear of animals, heights, flying ...
DSM-IV-TR in Action Powerpoint
... Witnessing events on television Witnessing events through electronic media Will also drop the criteria that the person must experience intense fear Symptoms may no longer need to involve feelings of dissociation ...
... Witnessing events on television Witnessing events through electronic media Will also drop the criteria that the person must experience intense fear Symptoms may no longer need to involve feelings of dissociation ...
PSYC+103+Ch
... Major depressive disorder: extreme sadness, loss of interest, lower self-esteem, somatic concerns, etc. Dysthymic disorder: milder, chronic form of depression Bipolar disorder: one or more manic episodes with periods of depression Cyclothymic disorder: milder, chronic form of bipolar Etiol ...
... Major depressive disorder: extreme sadness, loss of interest, lower self-esteem, somatic concerns, etc. Dysthymic disorder: milder, chronic form of depression Bipolar disorder: one or more manic episodes with periods of depression Cyclothymic disorder: milder, chronic form of bipolar Etiol ...
chapter 16 review
... Dissociative identity disorder (DID) Mood disorders Major depressive disorder Mania Bipolar disorder Schizophrenia Delusions Personality disorders Antisocial personality disorder ...
... Dissociative identity disorder (DID) Mood disorders Major depressive disorder Mania Bipolar disorder Schizophrenia Delusions Personality disorders Antisocial personality disorder ...
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
... Genetic Origin: • Evidence is beginning to accumulate suggesting that OCD might have a genetic origin. Appears with Tourette’s syndrome Brain Damage (from trauma) • Basal ganglia, cingulate, frontal cortex ...
... Genetic Origin: • Evidence is beginning to accumulate suggesting that OCD might have a genetic origin. Appears with Tourette’s syndrome Brain Damage (from trauma) • Basal ganglia, cingulate, frontal cortex ...
Disorders of Childhood
... and/or setting of the behavior) • Behavior is typically distressing and/or annoying to those in child’s social environment • Examples: ADHD, ODD, Conduct Disorder ...
... and/or setting of the behavior) • Behavior is typically distressing and/or annoying to those in child’s social environment • Examples: ADHD, ODD, Conduct Disorder ...
Kleptomania
... duration of illness is roughly 16 years. Some individuals report the onset of kleptomania as early as age five. While we do not know the causes of kleptomania, there is indirect evidence linking it with abnormalities in the brain chemical serotonin. Stressors such as major losses may also precipitat ...
... duration of illness is roughly 16 years. Some individuals report the onset of kleptomania as early as age five. While we do not know the causes of kleptomania, there is indirect evidence linking it with abnormalities in the brain chemical serotonin. Stressors such as major losses may also precipitat ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
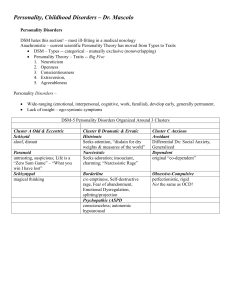
Dr. Mascolo Personality, Childhood Disorders
... Dx – consequences of a false positive -- but also -- a false negative “Sensitivity” it may be subtle, but the clinician makes the diagnosis “Specificity”– it may seem obvious, but the clinician does not make the diagnosis ADHD -- maybe is an example of a trait, not a type 3 subtypes – primaril ...
... Dx – consequences of a false positive -- but also -- a false negative “Sensitivity” it may be subtle, but the clinician makes the diagnosis “Specificity”– it may seem obvious, but the clinician does not make the diagnosis ADHD -- maybe is an example of a trait, not a type 3 subtypes – primaril ...