Atomic Structure
... •Unstable isotopes called radioisotopes undergo changes and release energy to become more stable. These isotopes have many uses which we will discuss in the Nuclear Chemistry section of our class. Now, let’s compare the three isotopes of Lithium! How many protons does Lithium-6 have? ________ How ma ...
... •Unstable isotopes called radioisotopes undergo changes and release energy to become more stable. These isotopes have many uses which we will discuss in the Nuclear Chemistry section of our class. Now, let’s compare the three isotopes of Lithium! How many protons does Lithium-6 have? ________ How ma ...
Looking for Patterns in Chemical Reactivity
... A chemical bond forms between two atoms when their valence electrons form a stable arrangement together. ...
... A chemical bond forms between two atoms when their valence electrons form a stable arrangement together. ...
notes - van Maarseveen
... different mass numbers. The atomic mass is the average of the mass numbers of all the isotopes of the element. Because some isotopes are much more common than others, the atomic mass might be very close to the mass of one isotope. A good example is carbon. The atomic mass is very close to 12, becaus ...
... different mass numbers. The atomic mass is the average of the mass numbers of all the isotopes of the element. Because some isotopes are much more common than others, the atomic mass might be very close to the mass of one isotope. A good example is carbon. The atomic mass is very close to 12, becaus ...
Structure - Mole Cafe
... The majority of the elements are metals. They occupy the entire left side and center of the periodic table. Nonmetals occupy the upper-right-hand ...
... The majority of the elements are metals. They occupy the entire left side and center of the periodic table. Nonmetals occupy the upper-right-hand ...
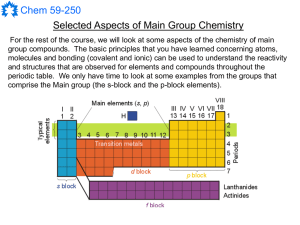
Main Group Notes 1
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 16 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np4 electron configuration, neutral group 16 compounds can form up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state f ...
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 16 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np4 electron configuration, neutral group 16 compounds can form up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state f ...
Review Chemistry KEY - cms16-17
... 32. List each element in the following compounds and the number of atoms of each element present and the total number of atoms. a. C6H8O6 (Vitamin C): i. Elements: C, H, and O_____________________________________ ii. Atoms: C=6, H=8, and O=6 Total number of atoms=20___________ b. C8H10O2N4H2O (Caffe ...
... 32. List each element in the following compounds and the number of atoms of each element present and the total number of atoms. a. C6H8O6 (Vitamin C): i. Elements: C, H, and O_____________________________________ ii. Atoms: C=6, H=8, and O=6 Total number of atoms=20___________ b. C8H10O2N4H2O (Caffe ...
Chapter 4
... The periodic table helps determine electron arrangement Horizontal rows (L - R) in the periodic table are called periods ...
... The periodic table helps determine electron arrangement Horizontal rows (L - R) in the periodic table are called periods ...
Phys Sci I, Quiz #3 - Electriciy and Magnetism, Atomic and Nuclear
... B) quark C) electromagnetic D) gravitational ...
... B) quark C) electromagnetic D) gravitational ...
The Periodic Table
... elements, numbered 1-7) Group or Family – a vertical row of elements (numbered 1-18 on the modern table) (long ago: roman numerals) ...
... elements, numbered 1-7) Group or Family – a vertical row of elements (numbered 1-18 on the modern table) (long ago: roman numerals) ...
Element Symbol
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
TEST REVIEW S Valence Electrons TEST REVIEW SHEET 2017
... NOTE: If an element has <4 valence electrons it will give them away during an ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their oute ...
... NOTE: If an element has <4 valence electrons it will give them away during an ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their oute ...
Key Terms Democritus - (born c. 460 — died c. 370 BC) Greek
... Law of Definite Proportions - elements composing a compound are always present in the same proportions by mass Law of Multiple Proportions - law stating that when two elements can combine to form more than one compound the amounts of one of them that combines with a fixed amount of the other will ex ...
... Law of Definite Proportions - elements composing a compound are always present in the same proportions by mass Law of Multiple Proportions - law stating that when two elements can combine to form more than one compound the amounts of one of them that combines with a fixed amount of the other will ex ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 1. atom is the smallest unit of matter 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy ...
... 1. atom is the smallest unit of matter 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy ...
How to write up a practical: General review
... electrons and neutrons and some of their properties TO BE ABLE draw the basic structure of the atom. TO UNDERSTAND how these particles are physically arranged in relation to each other. ...
... electrons and neutrons and some of their properties TO BE ABLE draw the basic structure of the atom. TO UNDERSTAND how these particles are physically arranged in relation to each other. ...
Chapter 2 - U of L Class Index
... If the # protons changes, then it is not the same element. eg. The carbon atom has 6 protons in the nucleus. If you remove 1 proton from the carbon nucleus, you change the nature of the element. C - p → B if you add 1 proton to the carbon nucleus you get nitrogen. C + p → N These are nuclear reactio ...
... If the # protons changes, then it is not the same element. eg. The carbon atom has 6 protons in the nucleus. If you remove 1 proton from the carbon nucleus, you change the nature of the element. C - p → B if you add 1 proton to the carbon nucleus you get nitrogen. C + p → N These are nuclear reactio ...
Ch10-Atomic Theory
... Schrödinger- develops Schrodinger eq’n to better approx. behavior of atoms more complicated than hydrogen (1926) ...
... Schrödinger- develops Schrodinger eq’n to better approx. behavior of atoms more complicated than hydrogen (1926) ...
Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
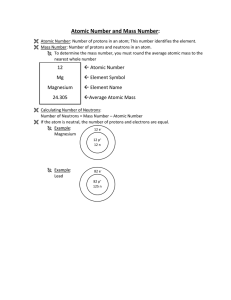
... Atomic terms - ATOMIC NUMBER: The number of protons in the atomic nucleus. Each ELEMENT has the SAME NUMBER OF PROTONS in every nucleus. In neutral atoms, the number of ELECTRONS is also equal to the atomic number. Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its ...
... Atomic terms - ATOMIC NUMBER: The number of protons in the atomic nucleus. Each ELEMENT has the SAME NUMBER OF PROTONS in every nucleus. In neutral atoms, the number of ELECTRONS is also equal to the atomic number. Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its ...
The Atomic Theory of Matter
... • The rest of the subatomic particles were found when scientists made theories on where the electrons were in an atom. In 1910, a scientist named Rutherford examined the effects of passing alpha rays through a gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foi ...
... • The rest of the subatomic particles were found when scientists made theories on where the electrons were in an atom. In 1910, a scientist named Rutherford examined the effects of passing alpha rays through a gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foi ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... Dalton’s atomic theory of matter • each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms • all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other any other element ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory of matter • each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms • all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other any other element ...