![Keq = [A] [B] [C] [D]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014463360_1-50a2de0db1e8b9a361c4b31c6e85c28d-300x300.png)
mass mass calc
... Given the following balanced chemical equation: C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of m ...
... Given the following balanced chemical equation: C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of m ...
Net ionic equation
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
Physical chemistry and transition elements 5.1 Rates, equilibrium
... e.g. The Haber process uses iron as a catalyst; N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) ...
... e.g. The Haber process uses iron as a catalyst; N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) ...
Chapter 5: Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... composed of two hydrogen atoms for every oxygen atom. The Chemical Formula A chemical formula (also called molecular formula) is a concise way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound. It identifies each type of element by its chemical symbol and ident ...
... composed of two hydrogen atoms for every oxygen atom. The Chemical Formula A chemical formula (also called molecular formula) is a concise way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound. It identifies each type of element by its chemical symbol and ident ...
Document
... E.Q.: What mathematical relationships can be determined from a balanced chemical equation? ...
... E.Q.: What mathematical relationships can be determined from a balanced chemical equation? ...
1. What energy changes occur when chemical bonds are formed
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
Second Year - WordPress.com
... (A) Directly proportional to square of effective nuclear charges (B) Inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge (C) Inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge (D) Directly proportional to effective nuclear charge. ...
... (A) Directly proportional to square of effective nuclear charges (B) Inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge (C) Inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge (D) Directly proportional to effective nuclear charge. ...
1.02 x 10 = 3 mol lit 3.4 x 10
... Ostwald’s dilution law. “The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is directly proportional to the square root of its dilution or inversely proportional to the square root of its concentration. ...
... Ostwald’s dilution law. “The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is directly proportional to the square root of its dilution or inversely proportional to the square root of its concentration. ...
File
... Let the electrodes have a potential difference applied to them (about 10 kV). The electrode connected to the negative terminal is known as the cathode and the terminal connected to the positive terminal is known as the anode. As the discharge tube is evacuated, measure the pressure inside in terms o ...
... Let the electrodes have a potential difference applied to them (about 10 kV). The electrode connected to the negative terminal is known as the cathode and the terminal connected to the positive terminal is known as the anode. As the discharge tube is evacuated, measure the pressure inside in terms o ...
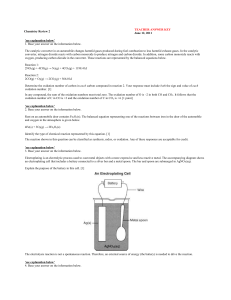
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... 'see explanation below' 24. Base your answer on the information below. Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brothe ...
... 'see explanation below' 24. Base your answer on the information below. Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brothe ...
3/23/2014 1 8 Chemical Equations Chapter Outline Chemical
... Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of magnesium hydroxide and phosphoric acid to form magnesium phosphate and water. 3. Balance the equation. 3 Mg(OH)2 + 2 H3PO4 ...
... Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of magnesium hydroxide and phosphoric acid to form magnesium phosphate and water. 3. Balance the equation. 3 Mg(OH)2 + 2 H3PO4 ...
jyvaskla2 - School of Chemistry
... additive, but do not look very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au ...
... additive, but do not look very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au ...
No Slide Title
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
Document
... • How much Al,Ca,Na,K (“sialic components”) is in the mantle ? • 11 elements of interest: O,Mg,Si,Fe,Ni,Al,Ca,S,Na,K,P ...
... • How much Al,Ca,Na,K (“sialic components”) is in the mantle ? • 11 elements of interest: O,Mg,Si,Fe,Ni,Al,Ca,S,Na,K,P ...
Chapter 8
... Note: If polyatomic ions do not change, they can be balanced as a “unit”. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Note: If polyatomic ions do not change, they can be balanced as a “unit”. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Summer Work: Independent Packet: Basics Of Atomic Structure
... e.g) Ca2+ is an ion. It has an unequal number of protons and electrons. The charge of +2 indicates that it has 2 more protons (or 2 more + charges) relative to its atom (Ca0) because 2 electrons (or 2 negative charges) have been removed/lost [Ca2+ is the oxidized form of the element calcium] ...
... e.g) Ca2+ is an ion. It has an unequal number of protons and electrons. The charge of +2 indicates that it has 2 more protons (or 2 more + charges) relative to its atom (Ca0) because 2 electrons (or 2 negative charges) have been removed/lost [Ca2+ is the oxidized form of the element calcium] ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • Compounds containing C, H and O are routinely analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
... • Compounds containing C, H and O are routinely analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
8 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
... For proposal B only the slow step is critical in determining the dependence of the rate constant on the temperature. The complexation step is very stable which explains the negative activation energy. For proposal B: k = A e-EB / RT = A e+83.60/RT which decreases with increasing T THE COMPETITION PR ...
... For proposal B only the slow step is critical in determining the dependence of the rate constant on the temperature. The complexation step is very stable which explains the negative activation energy. For proposal B: k = A e-EB / RT = A e+83.60/RT which decreases with increasing T THE COMPETITION PR ...
chapter4-bur.2917051..
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
Chapter 3 PPt
... Subatomic Particles, continued Rutherford Discovers the Nucleus, continued • Rutherford reasoned that only a very concentrated positive charge in a tiny space within the gold atom could possibly repel the fast-moving, alpha particles enough to reverse the alpha particles’ direction. • Rutherford als ...
... Subatomic Particles, continued Rutherford Discovers the Nucleus, continued • Rutherford reasoned that only a very concentrated positive charge in a tiny space within the gold atom could possibly repel the fast-moving, alpha particles enough to reverse the alpha particles’ direction. • Rutherford als ...
ch03 - Atoms and Elements
... Atomic mass is the • weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element • number on the periodic table below the chemical symbol with two decimal places ...
... Atomic mass is the • weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element • number on the periodic table below the chemical symbol with two decimal places ...