Electron Configurations
... Electron Configurations • Need to Know: • Period numbers of periodic table are the energy levels (n) of the orbitals • Regions of periodic table where ...
... Electron Configurations • Need to Know: • Period numbers of periodic table are the energy levels (n) of the orbitals • Regions of periodic table where ...
Atomic Theory and Structure Notes
... 4 Postulates of Theory: 1) all matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible. 2) All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties 3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different elements 4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms ...
... 4 Postulates of Theory: 1) all matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible. 2) All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties 3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different elements 4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms ...
Science Homework week 2
... 6. What information would you use to distinguish between atoms of different elements? The numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons. 7. Use an example to identify the smallest unit of an element. 8 a. Dalton proposed his atomic theory in 1808. Outline the theory. All matter is composed of atoms, A ...
... 6. What information would you use to distinguish between atoms of different elements? The numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons. 7. Use an example to identify the smallest unit of an element. 8 a. Dalton proposed his atomic theory in 1808. Outline the theory. All matter is composed of atoms, A ...
The Atom: Idea to Theory
... – Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element Mullis ...
... – Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element Mullis ...
document
... The fourth and fifth periods each contains 18 electrons. The sixth period contains 32 electrons The seventh period, incomplete yet, ...
... The fourth and fifth periods each contains 18 electrons. The sixth period contains 32 electrons The seventh period, incomplete yet, ...
Worksheet: Development of Atomic Theory
... True-False: place a "+" in the blank if the statement is true, and a "O" in the blank if the statement is false. 1. Dalton's atomic theory stated: a. atoms are indivisible. b. all atoms of the same element are alike. c. atoms unite in small, whole number ratios to form compounds. ...
... True-False: place a "+" in the blank if the statement is true, and a "O" in the blank if the statement is false. 1. Dalton's atomic theory stated: a. atoms are indivisible. b. all atoms of the same element are alike. c. atoms unite in small, whole number ratios to form compounds. ...
CHM134 General Chemistry I Semester Review – Dr. Steel This list
... 21. If n = 3, what are the allowed quantum numbers for l? 22. What element has the ground state electron configuration: [Ar]4s13d5? 23. What element has the ground state electron configuration: [Kr]5s2? 24. What is the maximum number of electrons permitted in a d sublevel? 25. Green light has a wave ...
... 21. If n = 3, what are the allowed quantum numbers for l? 22. What element has the ground state electron configuration: [Ar]4s13d5? 23. What element has the ground state electron configuration: [Kr]5s2? 24. What is the maximum number of electrons permitted in a d sublevel? 25. Green light has a wave ...
The Atom
... metals and nonmetals On the metal/nonmetal barrier Have some physical properties of metals but some chemical properties of nonmetals Semiconductors Si, ...
... metals and nonmetals On the metal/nonmetal barrier Have some physical properties of metals but some chemical properties of nonmetals Semiconductors Si, ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an element determine how the element will change when it react ...
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an element determine how the element will change when it react ...
chem 1 TIFF new.indd
... As we just saw, the atomic number tells how many protons the atom contains. In an atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, so this number is also the number of electrons in an atom. For example, the smallest element is hydrogen. It has an atomic number of 1, which means it has onl ...
... As we just saw, the atomic number tells how many protons the atom contains. In an atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, so this number is also the number of electrons in an atom. For example, the smallest element is hydrogen. It has an atomic number of 1, which means it has onl ...
Atomic Structure - Pleasantville High School
... Most particles passed through. So, atoms are mostly empty. Some positive -particles deflected or bounced back! Thus, a “nucleus” is positive & holds most of an atom’s mass. ...
... Most particles passed through. So, atoms are mostly empty. Some positive -particles deflected or bounced back! Thus, a “nucleus” is positive & holds most of an atom’s mass. ...
The Atom - TeacherWeb
... Neutrons maintain stability. If you change the number of neutrons, you have an ISOTOPE. ...
... Neutrons maintain stability. If you change the number of neutrons, you have an ISOTOPE. ...
Radioactive Reactions
... • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
... • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
Elements and Atoms
... • Elements are the building blocks of all matter. • The periodic table is a list of all of the elements that can build matter. It’s a little like the alphabet of chemistry. • The periodic table tells us several things… ...
... • Elements are the building blocks of all matter. • The periodic table is a list of all of the elements that can build matter. It’s a little like the alphabet of chemistry. • The periodic table tells us several things… ...
A Student want to prepare 250mL of .10 M NaCl solution
... – Liters of solution (concentration) – Gas (Ideal gas law) ...
... – Liters of solution (concentration) – Gas (Ideal gas law) ...
Document
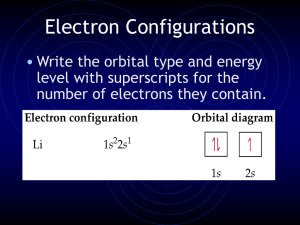
... like Sc: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1 skips energy change in orbital energies higher orbitals have lower energy i.e., 4s is lower than 3d shows gap in periodic table electron energy level order: 1s2s2p3s3p4s3d4p5s4d5p6s4f5d6p7s5f6d7p6f7d increasing energy ...
... like Sc: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1 skips energy change in orbital energies higher orbitals have lower energy i.e., 4s is lower than 3d shows gap in periodic table electron energy level order: 1s2s2p3s3p4s3d4p5s4d5p6s4f5d6p7s5f6d7p6f7d increasing energy ...
Bohr`s Atomic Model Quiz
... 2. Which describes the orbits of the electrons according to the Bohr model? a) The orbits are highly elliptical. b) Electrons cannot move between orbits. c) The orbits are at fixed distances from the nucleus. d) Electrons continually radiate energy as they orbit the nucleus. ...
... 2. Which describes the orbits of the electrons according to the Bohr model? a) The orbits are highly elliptical. b) Electrons cannot move between orbits. c) The orbits are at fixed distances from the nucleus. d) Electrons continually radiate energy as they orbit the nucleus. ...
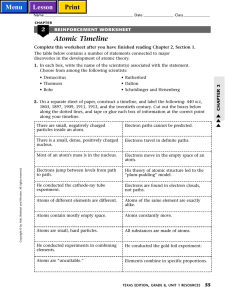
Atomic Timeline
... along the dotted lines, and tape or glue each box of information at the correct point along your timeline. There are small, negatively charged particles inside an atom. 1897 (Thomson) There is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 1911 (Rutherford) ...
... along the dotted lines, and tape or glue each box of information at the correct point along your timeline. There are small, negatively charged particles inside an atom. 1897 (Thomson) There is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 1911 (Rutherford) ...
oxidation number
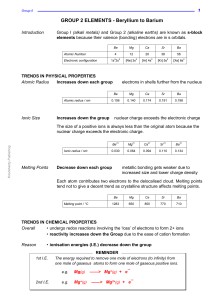
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
Ch. 4-7 Review Answers pg. 3-7
... 7) What are the three possible energy states of the atom and how does the atom go between these states? Ground (lowest energy state); excited (electron(s) in higher energy state than ground); ionized (electron removed from atom) 8) Who predicted the spectral lines of hydrogen? Bohr Why didn’t his pr ...
... 7) What are the three possible energy states of the atom and how does the atom go between these states? Ground (lowest energy state); excited (electron(s) in higher energy state than ground); ionized (electron removed from atom) 8) Who predicted the spectral lines of hydrogen? Bohr Why didn’t his pr ...
Atomic Structure
... Definition : Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons; Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. ...
... Definition : Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons; Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. ...