THE ATOM - A COMPUTER GUIDED LESSON
... 1. Write out the Atomic Molecular Theory of Matter. 2. How can scientists know so much about atoms when they are so small that they cannot see them? 3. What is Indirect Evidence? 4. What is a model? 5. Scientists have been making models of atoms for a long time. Can a model ever be changed? Explain ...
... 1. Write out the Atomic Molecular Theory of Matter. 2. How can scientists know so much about atoms when they are so small that they cannot see them? 3. What is Indirect Evidence? 4. What is a model? 5. Scientists have been making models of atoms for a long time. Can a model ever be changed? Explain ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Mini quiz
... c. the number of neutrons in the nucleus. b. the electric charge of the nucleus. d. atomic mass. 2. Atoms of elements that are in the same group have the same number of a. protons. c. valence electrons. b. neutrons. d. protons and neutrons. 3. Oxygen’s atomic number is 8. This means that an oxygen a ...
... c. the number of neutrons in the nucleus. b. the electric charge of the nucleus. d. atomic mass. 2. Atoms of elements that are in the same group have the same number of a. protons. c. valence electrons. b. neutrons. d. protons and neutrons. 3. Oxygen’s atomic number is 8. This means that an oxygen a ...
Atomic Number
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
Chapter 3, Section One - Bismarck Public Schools
... –Atoms make up elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and helium. •Check out your periodic table! –Atoms are the smallest part of an element that still has all the same properties of an element. What is an Atom? •Today, scientists believe the following about atoms…. •All elements are composed of atoms. ...
... –Atoms make up elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and helium. •Check out your periodic table! –Atoms are the smallest part of an element that still has all the same properties of an element. What is an Atom? •Today, scientists believe the following about atoms…. •All elements are composed of atoms. ...
Workshop Tutorials for Introductory Physics Solutions to QI2: Atomic
... the quantum theory. Bohr incorporated the quantum theory into Rutherford’s model, which solved a lot of the problems and explained not only why atoms show spectra, but predicted where the lines for hydrogen would be. Unfortunately it didn’t work very well for bigger atoms. The currently accepted mod ...
... the quantum theory. Bohr incorporated the quantum theory into Rutherford’s model, which solved a lot of the problems and explained not only why atoms show spectra, but predicted where the lines for hydrogen would be. Unfortunately it didn’t work very well for bigger atoms. The currently accepted mod ...
Atoms and isotopes MS
... Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. 2Na + 2T2O 2NaOT + T2; Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. If H is used instead of T in any of the equations [3 max]. Accept any other suitable equation for both parts. ...
... Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. 2Na + 2T2O 2NaOT + T2; Correct formulas [1], balancing of correct equation [1]. If H is used instead of T in any of the equations [3 max]. Accept any other suitable equation for both parts. ...
Word
... the quantum theory. Bohr incorporated the quantum theory into Rutherford’s model, which solved a lot of the problems and explained not only why atoms show spectra, but predicted where the lines for hydrogen would be. Unfortunately it didn’t work very well for bigger atoms. The currently accepted mod ...
... the quantum theory. Bohr incorporated the quantum theory into Rutherford’s model, which solved a lot of the problems and explained not only why atoms show spectra, but predicted where the lines for hydrogen would be. Unfortunately it didn’t work very well for bigger atoms. The currently accepted mod ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
What is an isotope?
... What is an isotope? Number of protons for an atom of a specific element never changes. Number of neutrons can change. Two atoms with equal protons but different neutrons are called isotopes of each other. All atoms in existence are isotopes! Some isotopes are just more common than others. ...
... What is an isotope? Number of protons for an atom of a specific element never changes. Number of neutrons can change. Two atoms with equal protons but different neutrons are called isotopes of each other. All atoms in existence are isotopes! Some isotopes are just more common than others. ...
ch. 4 atoms outline notes
... 4.1 The Development of Atomic Theory Key Ideas: (1) Who came up with the first theory of atoms? (2) What did Dalton add to the atomic theory? (3) How did Thompson discover the electron? (4) What is Rutherford’s atomic model? Key Terms: electron , proton, nucleus, law of definite proportions Why it M ...
... 4.1 The Development of Atomic Theory Key Ideas: (1) Who came up with the first theory of atoms? (2) What did Dalton add to the atomic theory? (3) How did Thompson discover the electron? (4) What is Rutherford’s atomic model? Key Terms: electron , proton, nucleus, law of definite proportions Why it M ...
Chem 152 Chapter 4
... As you heat a substance, its particle move faster (greater kinetic energy). Particles in the gas phase are moving the fastest. Liquid phase particles move with less energy than the gas phase. Solid phase particles are the slowest but they also have movement. (vibrations). ...
... As you heat a substance, its particle move faster (greater kinetic energy). Particles in the gas phase are moving the fastest. Liquid phase particles move with less energy than the gas phase. Solid phase particles are the slowest but they also have movement. (vibrations). ...
Chemistrypart107
... electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. • The valence shell can have 1 to 8 electrons in it depending on its place on the periodic table. Elements to the left have 1 and elements to the right have 8. ...
... electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. • The valence shell can have 1 to 8 electrons in it depending on its place on the periodic table. Elements to the left have 1 and elements to the right have 8. ...
Postulates of Dalton`s atomic theory - Chemwiki
... According to Dalton, the atoms of same element are similar in all respects. However, atoms of some elements vary in their masses and densities. These atoms of different masses are called isotopes. For example, chlorine has two isotopes with mass numbers 35 and 37. Dalton also claimed that atoms of d ...
... According to Dalton, the atoms of same element are similar in all respects. However, atoms of some elements vary in their masses and densities. These atoms of different masses are called isotopes. For example, chlorine has two isotopes with mass numbers 35 and 37. Dalton also claimed that atoms of d ...
Atomic Theory - Wallingford-Swarthmore School District
... • Located outside of the nucleus in rings or energy levels called atomic clouds • Their mass is so small that it is usually considered zero. • It takes more than 1,800 electrons to equal the mass of one proton. • However electrons occupy most of an atoms volume. ...
... • Located outside of the nucleus in rings or energy levels called atomic clouds • Their mass is so small that it is usually considered zero. • It takes more than 1,800 electrons to equal the mass of one proton. • However electrons occupy most of an atoms volume. ...
ch04_sec3_as - LCMR School District
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
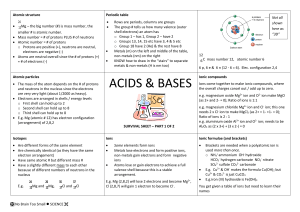
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
Section 3: Modern Atomic Theory Atoms Section 3
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
Elements, Compounds and Chemical Reactions
... element has an element cube that gives information about the element. The symbol is the short name for the element. Notice that for an element, there is only ONE capital letter! Sometime the chemical symbol doesn’t look like it comes from the name of the element. This happens when the symbol comes f ...
... element has an element cube that gives information about the element. The symbol is the short name for the element. Notice that for an element, there is only ONE capital letter! Sometime the chemical symbol doesn’t look like it comes from the name of the element. This happens when the symbol comes f ...
3.2 Notes
... Scientists have identified 109 different __________________________________ o 90 types are found in ____________________________ o Remaining 19 are _____________________________________________ o Represented by a _____________________________________________ ...
... Scientists have identified 109 different __________________________________ o 90 types are found in ____________________________ o Remaining 19 are _____________________________________________ o Represented by a _____________________________________________ ...
Atomic Structure
... 1. What evidence supports your conclusion about the type of item contained in the box? 2. What kinds of things can you do to determine the contents of your box if you had access to other kinds of observational tools? 3. Since you cannot see what is inside, how can you be 100% sure of its contents? ...
... 1. What evidence supports your conclusion about the type of item contained in the box? 2. What kinds of things can you do to determine the contents of your box if you had access to other kinds of observational tools? 3. Since you cannot see what is inside, how can you be 100% sure of its contents? ...
Unit 4 Slide Show
... He was able to support his ideas through experimentation, and his work revolutionized scientists’ concept of matter and its smallest building block, the atom. Dalton’s theory has two flaws: ...
... He was able to support his ideas through experimentation, and his work revolutionized scientists’ concept of matter and its smallest building block, the atom. Dalton’s theory has two flaws: ...
File - MrAllanScienceGFC
... the presence of a negatively charged particle. Used a fluorescent screen in CRT to measure deflection of beam Found that all particles in the beam had same charge and mass Proved that the beam, using magnets, was negatively charged particles called Electrons ...
... the presence of a negatively charged particle. Used a fluorescent screen in CRT to measure deflection of beam Found that all particles in the beam had same charge and mass Proved that the beam, using magnets, was negatively charged particles called Electrons ...
Atomic History and Structure PowerPoint
... the atoms of an element. Discuss what the mass number represents concerning the atoms of an element. Determine the electronic structure for elements 1-20 on the Periodic Table. ...
... the atoms of an element. Discuss what the mass number represents concerning the atoms of an element. Determine the electronic structure for elements 1-20 on the Periodic Table. ...