Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... periodic table (shaded in different colors in this chart) correspond to different types of orbitals. ...
... periodic table (shaded in different colors in this chart) correspond to different types of orbitals. ...
C 4 The Atomic Theory
... them C, D, and E. As it turned out, for the same amount of nitrogen, D always required twice as much oxygen as C does. Similarly, E always required exactly four times as much oxygen as C does. Once again, Dalton noticed that small whole numbers (2 and 4) seemed to be the rule. Dalton used his experi ...
... them C, D, and E. As it turned out, for the same amount of nitrogen, D always required twice as much oxygen as C does. Similarly, E always required exactly four times as much oxygen as C does. Once again, Dalton noticed that small whole numbers (2 and 4) seemed to be the rule. Dalton used his experi ...
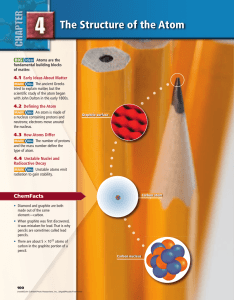
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... Conservation of mass Recall from Chapter 3 that the law of conservation of mass states that mass is conserved in any process, such as a chemical reaction. Dalton’s atomic theory easily explains that the conservation of mass in chemical reactions is the result of the separation, combination, or rearr ...
... Conservation of mass Recall from Chapter 3 that the law of conservation of mass states that mass is conserved in any process, such as a chemical reaction. Dalton’s atomic theory easily explains that the conservation of mass in chemical reactions is the result of the separation, combination, or rearr ...
rate of chemical reaction and chemical equilibrium
... water and releases chloride ion bound to central platinum metal. The reaction is represented as Pt(NH3)2Cl2 + H2O Pt(NH3)2Cl+ + Cl Here the conc. of cisplatin decreases with lapse of time but conc. of Cl increases. ...
... water and releases chloride ion bound to central platinum metal. The reaction is represented as Pt(NH3)2Cl2 + H2O Pt(NH3)2Cl+ + Cl Here the conc. of cisplatin decreases with lapse of time but conc. of Cl increases. ...
INTRODUCTION The HSAB concept is an acronym for `hard and soft
... species which are big, have low charge states and are strongly polarizable. HSAB theory is also useful in predicting the products of metathesis reactions Theory The gist of this theory is that soft acids react faster and form stronger bonds with soft bases, whereas hard acids react faster and form s ...
... species which are big, have low charge states and are strongly polarizable. HSAB theory is also useful in predicting the products of metathesis reactions Theory The gist of this theory is that soft acids react faster and form stronger bonds with soft bases, whereas hard acids react faster and form s ...
Chapter 2 slides
... The first draft of the periodic table was developed between 1879 and 1871, and published by Dmitri Mendeleev. Note that this was before the subatomic particles were discovered, so it was not based on atomic number. The 63 known elements were arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass, and ...
... The first draft of the periodic table was developed between 1879 and 1871, and published by Dmitri Mendeleev. Note that this was before the subatomic particles were discovered, so it was not based on atomic number. The 63 known elements were arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass, and ...
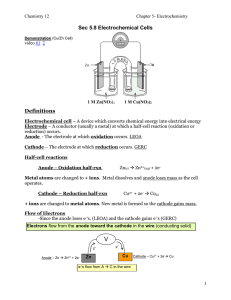
Sec 5.8 - 5.11 notes
... All are written as reductions (GERC) Their reverse would be oxidations (LEOA) The half rxn which is lower on the table will be a stronger reducing agent therefore it will be oxidized = anode The half-rxn which is higher on the table will be a weaker reducing agent , therefore it will be reduced = ca ...
... All are written as reductions (GERC) Their reverse would be oxidations (LEOA) The half rxn which is lower on the table will be a stronger reducing agent therefore it will be oxidized = anode The half-rxn which is higher on the table will be a weaker reducing agent , therefore it will be reduced = ca ...
ppt - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... However: many reactions approach a state of equilibrium Equilibrium – condition of a chemical reaction in which chemical change ceases and no further change occurs spontaneously Equilibrium – a dynamic equilibrium between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. At Equilibrium: ...
... However: many reactions approach a state of equilibrium Equilibrium – condition of a chemical reaction in which chemical change ceases and no further change occurs spontaneously Equilibrium – a dynamic equilibrium between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. At Equilibrium: ...
Document
... The Modern Model – also called Electron Cloud Model or Orbital Model or Wave Mechanical Model – This model says it is impossible to know exactly where an electron is at any given time. Electrons are in regions of space called orbitals. You will learn more about this model & the scientists that contr ...
... The Modern Model – also called Electron Cloud Model or Orbital Model or Wave Mechanical Model – This model says it is impossible to know exactly where an electron is at any given time. Electrons are in regions of space called orbitals. You will learn more about this model & the scientists that contr ...
Shedding Light on Atoms Episode 8: Ionic Bonding
... of the Periodic Table react in a similar kind of way, since they have the same number of outer shell electrons. Let’s look at how some of the atoms of the Group 1 elements react with chlorine atoms starting with Na, the one we’re familiar with. Since the electron configuration of sodium is 2, 8, 1, ...
... of the Periodic Table react in a similar kind of way, since they have the same number of outer shell electrons. Let’s look at how some of the atoms of the Group 1 elements react with chlorine atoms starting with Na, the one we’re familiar with. Since the electron configuration of sodium is 2, 8, 1, ...
4.1 Studying Atoms
... Rutherford’s Atomic Theory Thomson’s model did not explain all of the evidence from Rutherford's experiment. Rutherford proposed a new model. • The positive charge of an atom is not evenly spread throughout the atom. • Positive charge is concentrated in a very small, central area. • The nucleus of t ...
... Rutherford’s Atomic Theory Thomson’s model did not explain all of the evidence from Rutherford's experiment. Rutherford proposed a new model. • The positive charge of an atom is not evenly spread throughout the atom. • Positive charge is concentrated in a very small, central area. • The nucleus of t ...
- Angelo State University
... • If the total mass of a sample of small objects is known, and the average mass of each small object is known, the number of objects in the sample can be determined. ...
... • If the total mass of a sample of small objects is known, and the average mass of each small object is known, the number of objects in the sample can be determined. ...
Atomic Structure
... An unwanted side effect of this medicine is that it can cause the patient to have ‘wind’ (too much gas in the intestine). The equation below represents the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid (the acid present in the stomach). CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) →CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g ...
... An unwanted side effect of this medicine is that it can cause the patient to have ‘wind’ (too much gas in the intestine). The equation below represents the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid (the acid present in the stomach). CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) →CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g ...
C - Thierry Karsenti
... The module, Physical Chemistry 2, focuses on five (5) areas of physical chemistry important to many aspects of our lives: solutions, colloids, phase equilibrium, electrochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Solutions are often necessary to facilitate many chemical reactions in life processes or industry ...
... The module, Physical Chemistry 2, focuses on five (5) areas of physical chemistry important to many aspects of our lives: solutions, colloids, phase equilibrium, electrochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Solutions are often necessary to facilitate many chemical reactions in life processes or industry ...
Atomic Structure-pdf
... periodic table (shaded in different colors in this chart) correspond to different types of orbitals. ...
... periodic table (shaded in different colors in this chart) correspond to different types of orbitals. ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... periodic table (shaded in different colors in this chart) correspond to different types of orbitals. ...
... periodic table (shaded in different colors in this chart) correspond to different types of orbitals. ...
Physical Chemistry 2.pdf
... electrochemical reactions. Many substances exist in more than one physical state, the most common being solid, liquid and gas. Each of the phases has significantly different physical properties. Knowledge of electrochemistry allows us understand certain biological processes. Rusting of iron, bleachi ...
... electrochemical reactions. Many substances exist in more than one physical state, the most common being solid, liquid and gas. Each of the phases has significantly different physical properties. Knowledge of electrochemistry allows us understand certain biological processes. Rusting of iron, bleachi ...
Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Bond Enthalpy (BE) and Enthalpy changes in reactions Imagine a reaction proceeding by breaking all bonds in the reactants and then using the gaseous atoms to form all the bonds in the products. ...
... Bond Enthalpy (BE) and Enthalpy changes in reactions Imagine a reaction proceeding by breaking all bonds in the reactants and then using the gaseous atoms to form all the bonds in the products. ...
Test 8 Review
... depends on the balance between the drive toward greater stability (reduced potential ΔG = ΔH – TΔS energy); and the drive toward less organization (increased entropy). The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) predicts whether or not a reaction is spontaneous. It is the difference between the energy change ...
... depends on the balance between the drive toward greater stability (reduced potential ΔG = ΔH – TΔS energy); and the drive toward less organization (increased entropy). The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) predicts whether or not a reaction is spontaneous. It is the difference between the energy change ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 16
... 16.8 Free Energy and Equilibrium -equilibrium point occurs at the lowest value of free energy available to the reaction system -when the system has reached equilibrium, the system has reached minimum free energy or the free energy of the reactants is equal to the free energy of the products ( G = ...
... 16.8 Free Energy and Equilibrium -equilibrium point occurs at the lowest value of free energy available to the reaction system -when the system has reached equilibrium, the system has reached minimum free energy or the free energy of the reactants is equal to the free energy of the products ( G = ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... Because Dalton thought atoms were the smallest particles of matter, he envisioned them as solid, hard spheres, like billiard (pool) balls, so he used wooden balls to model them. Three of his model atoms are pictured in the Figure 1.2. Do you see the holes in the balls? Dalton added these so the mode ...
... Because Dalton thought atoms were the smallest particles of matter, he envisioned them as solid, hard spheres, like billiard (pool) balls, so he used wooden balls to model them. Three of his model atoms are pictured in the Figure 1.2. Do you see the holes in the balls? Dalton added these so the mode ...
The effect of confinement on chemical reactions
... ethanol to produce ethyl acetate, CH3COOH + C2H5OH $ C2H5OOCCH3 + H2O, is a common industrial process in the synthesis of organic solvents. There is experimental evidence [16] that when this reaction is carried out in porous materials, the selectivity towards ethyl acetate depends on the adsorbent u ...
... ethanol to produce ethyl acetate, CH3COOH + C2H5OH $ C2H5OOCCH3 + H2O, is a common industrial process in the synthesis of organic solvents. There is experimental evidence [16] that when this reaction is carried out in porous materials, the selectivity towards ethyl acetate depends on the adsorbent u ...
Fall 2012
... 47. (5 pts) Nitrogen and phosphorus are in the same group, so you would expect them to exhibit similar chemical properties. NCl3, PCl3, and PCl5 are all stable compounds that are easily synthesized in the lab. However, NCl5 has never been synthesized or observed. Why would phosphorus form two compou ...
... 47. (5 pts) Nitrogen and phosphorus are in the same group, so you would expect them to exhibit similar chemical properties. NCl3, PCl3, and PCl5 are all stable compounds that are easily synthesized in the lab. However, NCl5 has never been synthesized or observed. Why would phosphorus form two compou ...
Chemistry
... "Father of Modern Chemistry". fundamental contributions to chemistry were a result of a conscious effort to fit all experiments into the framework of a single theory. He established the consistent use of the chemical balance, used oxygen to overthrow the phlogiston theory, and developed a new system ...
... "Father of Modern Chemistry". fundamental contributions to chemistry were a result of a conscious effort to fit all experiments into the framework of a single theory. He established the consistent use of the chemical balance, used oxygen to overthrow the phlogiston theory, and developed a new system ...
Ch 4 Student.pptx
... If the actual yield for the previous problem was 10.5 g, calculate the percent yield. The theoretical yield that we calculated was 13.6 g. If the actual yield is 3.16 g then percent yield is ...
... If the actual yield for the previous problem was 10.5 g, calculate the percent yield. The theoretical yield that we calculated was 13.6 g. If the actual yield is 3.16 g then percent yield is ...