Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
Development of the Atomic Theory
... supports your answer? Are new elements formed in a chemical reaction? ...
... supports your answer? Are new elements formed in a chemical reaction? ...
Chap 11 Sect 1 Notes Atomic Theory
... •Atom is composed of electrons surrounded by a “soup” of positive charge to balance the electron’s negative charge, like negativelycharged “plums” surrounded by ...
... •Atom is composed of electrons surrounded by a “soup” of positive charge to balance the electron’s negative charge, like negativelycharged “plums” surrounded by ...
Periodicity PowerPoint
... • The valence electrons (outer e-) in atoms are those shared/transferred to form bonds between atoms. • The number of valence electrons will affect the type(s) of bonds an atom can form with a specific element. • The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined from the electron configur ...
... • The valence electrons (outer e-) in atoms are those shared/transferred to form bonds between atoms. • The number of valence electrons will affect the type(s) of bonds an atom can form with a specific element. • The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined from the electron configur ...
MYP Chemistry: Final Review
... Define the terms electronegativity, ionization energy, atomic radius. Describe their trends on the periodic table. Electronegativity: tendency for and atom to gain an electron; ionization energy: energy required to remove an electron from an atom; atomic radius: size of atom; Electronegativity and ...
... Define the terms electronegativity, ionization energy, atomic radius. Describe their trends on the periodic table. Electronegativity: tendency for and atom to gain an electron; ionization energy: energy required to remove an electron from an atom; atomic radius: size of atom; Electronegativity and ...
Document
... 38) Elements that are shiny conductive solids at room temperature are likely to be classified as which of the following? a) metals b) nonmetals c) inert gases ...
... 38) Elements that are shiny conductive solids at room temperature are likely to be classified as which of the following? a) metals b) nonmetals c) inert gases ...
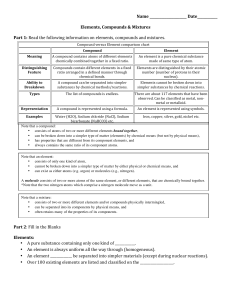
Compound vs Element chart
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
Matter on Earth and in the universe is made of atoms that have
... 10. What gives an atom its identity? What do we call this number? Where do we find this number on the periodic table? If an atom with no charge has 12 protons, how many electrons will it have? Atomic identity is determined by the number of protons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The at ...
... 10. What gives an atom its identity? What do we call this number? Where do we find this number on the periodic table? If an atom with no charge has 12 protons, how many electrons will it have? Atomic identity is determined by the number of protons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The at ...
Page 201 - ClassZone
... about the nucleus. The energy keeps the negative electron from falling into the positive nucleus. We also know that electrons with similar amounts of energy are grouped together in shells. Each shell can hold only a certain number of electrons that have about the same energy. An electron may jump fr ...
... about the nucleus. The energy keeps the negative electron from falling into the positive nucleus. We also know that electrons with similar amounts of energy are grouped together in shells. Each shell can hold only a certain number of electrons that have about the same energy. An electron may jump fr ...
Chemistry Review Answers
... Metalloids- A nonmetallic element, such as arsenic, that has some of the chemical properties of a metal. A nonmetallic element, such as carbon, that can form an alloy with metals. Halogens- Any of a group of five chemically related nonmetallic elements including fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, ...
... Metalloids- A nonmetallic element, such as arsenic, that has some of the chemical properties of a metal. A nonmetallic element, such as carbon, that can form an alloy with metals. Halogens- Any of a group of five chemically related nonmetallic elements including fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, ...
Chapter 18: Atoms and Elements
... Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. ...
... Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. ...
Section 2A
... electrons, it acquires an electrical charge. ! If it loses electrons, it becomes more positive, and this is called a cation. (positive charge) ! If it gains electrons, it becomes more negative, and this is called an anion. (negative charge) ...
... electrons, it acquires an electrical charge. ! If it loses electrons, it becomes more positive, and this is called a cation. (positive charge) ! If it gains electrons, it becomes more negative, and this is called an anion. (negative charge) ...
The atom
... particles called atoms 2. Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions 3. All atoms of a given element are identical 4. Atoms chemically combine in definite whole-number ratios to form compounds 5. Atoms of different elements have different masses ...
... particles called atoms 2. Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions 3. All atoms of a given element are identical 4. Atoms chemically combine in definite whole-number ratios to form compounds 5. Atoms of different elements have different masses ...
Developing Ideas about Matter
... In groups of 5, you will become “experts” on a particular model of the atom You must teach the concept in a way to answer the questions on the worksheet and be useful to your fellow classmates You will teach your classmates about the topic so be comfortable with it! ...
... In groups of 5, you will become “experts” on a particular model of the atom You must teach the concept in a way to answer the questions on the worksheet and be useful to your fellow classmates You will teach your classmates about the topic so be comfortable with it! ...
Study Guide Answer Key
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other ...
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other ...
1 Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of
... 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of the Atom An _____________ is the smallest particle of an element that retains it identity in a chemical reaction. The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. - 370 B.C) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus believed that atoms were ind ...
... 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of the Atom An _____________ is the smallest particle of an element that retains it identity in a chemical reaction. The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. - 370 B.C) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus believed that atoms were ind ...
A`r ji r/ Ii
... Z?7) 12. Suppose the length of a piece of string is measured to be 33.45 cm. Calculate the percent error if the string is ...
... Z?7) 12. Suppose the length of a piece of string is measured to be 33.45 cm. Calculate the percent error if the string is ...
SOL Essential Knowledge
... producing) and endothermic (heat absorbing). 4. Reaction rates/kinetics are affected by activation energy, catalysis, and the degree of randomness (entropy). 5. Catalysts decrease the amount of activation energy needed. 6. Reactions can occur in two directions spontaneously. 7. LeChatelier's Princip ...
... producing) and endothermic (heat absorbing). 4. Reaction rates/kinetics are affected by activation energy, catalysis, and the degree of randomness (entropy). 5. Catalysts decrease the amount of activation energy needed. 6. Reactions can occur in two directions spontaneously. 7. LeChatelier's Princip ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... The “staircase” at the right part of MPT divides metals from non-metals. Everything left of the staircase is a metal (includes the weird transition element rows outside and below the MPT), everything right of is non-metals. Few borderline cases are referred to as metalloids (semiconductors!!!!). All ...
... The “staircase” at the right part of MPT divides metals from non-metals. Everything left of the staircase is a metal (includes the weird transition element rows outside and below the MPT), everything right of is non-metals. Few borderline cases are referred to as metalloids (semiconductors!!!!). All ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... • the more an element reacts with other substances, the greater the activity is. • Metals: the greater the activity, the greater it loses electrons (to form cations) • Non-metals: the greater the activity, the greater it gains electrons (to form anions) • Activity series: a list of which elements a ...
... • the more an element reacts with other substances, the greater the activity is. • Metals: the greater the activity, the greater it loses electrons (to form cations) • Non-metals: the greater the activity, the greater it gains electrons (to form anions) • Activity series: a list of which elements a ...