Contributions to Atomic Theory - VCC Library
... the following people: Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr, or Schrodinger. 1) Electrons can possess only certain specified energies. 2) All atoms of a given element have the same size, shape and mass. 3) I discovered the electron. 4) I discovered the neutron. 5) Electrons travel around the n ...
... the following people: Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr, or Schrodinger. 1) Electrons can possess only certain specified energies. 2) All atoms of a given element have the same size, shape and mass. 3) I discovered the electron. 4) I discovered the neutron. 5) Electrons travel around the n ...
Radioactive Decay Laws
... Hahn and Strassmann repeated the experiment numerous times and were never able to isolate the ‘radium’ from barium. They reported their results as follows: "As chemists, we must actually say the new particles do not behave like radium but, in fact, like barium; as nuclear physicists, we cannot make ...
... Hahn and Strassmann repeated the experiment numerous times and were never able to isolate the ‘radium’ from barium. They reported their results as follows: "As chemists, we must actually say the new particles do not behave like radium but, in fact, like barium; as nuclear physicists, we cannot make ...
Chapter 2
... Mass of electron = 1/1800 the mass of a proton or neutron Atomic mass number is a superscript to the left of the symbol ...
... Mass of electron = 1/1800 the mass of a proton or neutron Atomic mass number is a superscript to the left of the symbol ...
- Google Sites
... 13. Atomic mass unit is based on carbon having a mass of 12 amu. 1 amu = 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12. 14. Isotopes are two atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Therefore they have different masses. 15. Average atomic mass – weighted aver ...
... 13. Atomic mass unit is based on carbon having a mass of 12 amu. 1 amu = 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12. 14. Isotopes are two atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Therefore they have different masses. 15. Average atomic mass – weighted aver ...
atomic number - Teacher Pages
... ability to conduct electricity. – Some metalloids are used to make semiconductors. Semiconductors are substances that under some conditions can carry electricity, and under other conditions cannot. Semiconductors are used to make computer chips, transistors, and lasers. ...
... ability to conduct electricity. – Some metalloids are used to make semiconductors. Semiconductors are substances that under some conditions can carry electricity, and under other conditions cannot. Semiconductors are used to make computer chips, transistors, and lasers. ...
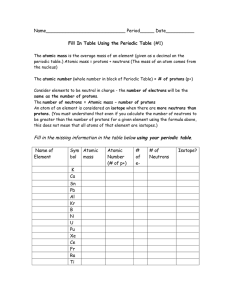
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
john dalton - sced350akdeniz
... compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped ...
... compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped ...
CW07 Electron Structure of the Atom Click HERE for Puzzle Click
... oscillating waves (7.1; 2WWS) A description of the distribution of electrons in an atom's sublevels (7.3; 2WWS) The size of the anion is ___ than the atom from which it was formed (7.7) Can hold only 2 electrons (7.3) The smallest packet of energy of a specific type of radiation (7.1) In writing the ...
... oscillating waves (7.1; 2WWS) A description of the distribution of electrons in an atom's sublevels (7.3; 2WWS) The size of the anion is ___ than the atom from which it was formed (7.7) Can hold only 2 electrons (7.3) The smallest packet of energy of a specific type of radiation (7.1) In writing the ...
Chapter 5/6 Notes
... Dimitri Mendeleev – published the first real periodic table in 1869 - Based upon chemical and physical properties - Listed elements in order of increasing atomic mass - Left spaces for undiscovered elements ...
... Dimitri Mendeleev – published the first real periodic table in 1869 - Based upon chemical and physical properties - Listed elements in order of increasing atomic mass - Left spaces for undiscovered elements ...
Notes on Atomic Theory
... protons and neutrons are about same size electrons are much smaller nuclear force- when particles in the nucleus get very close, they have a strong attraction ...
... protons and neutrons are about same size electrons are much smaller nuclear force- when particles in the nucleus get very close, they have a strong attraction ...
theory
... atoms in simple, whole-number ratios. • In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but not created or destroyed. ...
... atoms in simple, whole-number ratios. • In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but not created or destroyed. ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... d) alpha and beta, but not gamma 24. Which elements did Mendeleev leave spaces for in 14. A high energy form of light ...
... d) alpha and beta, but not gamma 24. Which elements did Mendeleev leave spaces for in 14. A high energy form of light ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 x = 12.3 g Cd 1.3 2.24845 ×12 u
... Silver and gold are in the same periodic table group as copper, so they might well be expected to occur together in nature, because of their similar properties and tendencies to form similar compounds. ...
... Silver and gold are in the same periodic table group as copper, so they might well be expected to occur together in nature, because of their similar properties and tendencies to form similar compounds. ...
Document
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
Topic 3 – Atoms and the Periodic Table – Learning Outcomes
... us the electron arrangement for all the elements. We are just interested in the first 20 in standard grade and we can use this information on page 1 to draw target diagrams for the first 20 elements. Elements in the same group have the same number of outer electrons e.g. lithium, sodium, potassium e ...
... us the electron arrangement for all the elements. We are just interested in the first 20 in standard grade and we can use this information on page 1 to draw target diagrams for the first 20 elements. Elements in the same group have the same number of outer electrons e.g. lithium, sodium, potassium e ...
Summary: History of Models of the Atom
... Bohr developed an explanation of atomic structure that underlies the regularities of the periodic table of elements. His atomic model had atoms built up of successive orbital shells of electrons. The electrons moved in spherical orbits at fixed distances from the nucleus. The electron cloud model is ...
... Bohr developed an explanation of atomic structure that underlies the regularities of the periodic table of elements. His atomic model had atoms built up of successive orbital shells of electrons. The electrons moved in spherical orbits at fixed distances from the nucleus. The electron cloud model is ...
PS.Ch6.Test.95
... d) alpha and beta, but not gamma 24. Which elements did Mendeleev leave spaces for in 14. A high energy form of light ...
... d) alpha and beta, but not gamma 24. Which elements did Mendeleev leave spaces for in 14. A high energy form of light ...
Assignment
... worked well in explaining the behaviour of simple atoms such as hydrogen, that contained few electrons, but it did not explain the more complex atoms. ...
... worked well in explaining the behaviour of simple atoms such as hydrogen, that contained few electrons, but it did not explain the more complex atoms. ...
Review for Exam 1
... CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know The difference between ionic and covalent bonds Define cations and anions Predict cation/anion charge using the octet rule or group number Familiar with metals with multiple potential charges (do not need to memorize) Determine ionic compound formulas from th ...
... CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know The difference between ionic and covalent bonds Define cations and anions Predict cation/anion charge using the octet rule or group number Familiar with metals with multiple potential charges (do not need to memorize) Determine ionic compound formulas from th ...