Element Symbol
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
Inside the Atom connections to the lower secondary (KS3
... • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics related content in the KS3 curriculum is taught in the chemi ...
... • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics related content in the KS3 curriculum is taught in the chemi ...
File
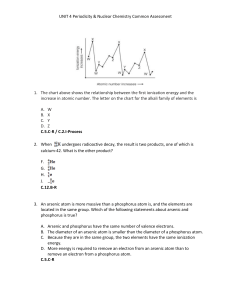
... Which of the following does this equation represent? F. Decomposition reaction G. Physical change H. Radiation decay J. Synthesis reaction C.12.B-R 13. In which group are the particles arranged in order of decreasing mass? A. alpha, beta, neutron B. alpha, neutron, beta C. neutron, beta, alpha D. ne ...
... Which of the following does this equation represent? F. Decomposition reaction G. Physical change H. Radiation decay J. Synthesis reaction C.12.B-R 13. In which group are the particles arranged in order of decreasing mass? A. alpha, beta, neutron B. alpha, neutron, beta C. neutron, beta, alpha D. ne ...
Chapter 5
... Beta Decay The emission of an electron from the nucleus and the transformation of the atom into a different element with the next higher atomic # is the result. ...
... Beta Decay The emission of an electron from the nucleus and the transformation of the atom into a different element with the next higher atomic # is the result. ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... 2. What was Dalton’s 5 part atomic theory of matter and his model of the atom? a. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, which cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. b. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. c. Atoms of diff ...
... 2. What was Dalton’s 5 part atomic theory of matter and his model of the atom? a. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, which cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. b. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. c. Atoms of diff ...
Extension 18.2: Isotopes
... Normally, isotopes of elements do not have separate names the way hydrogen does. For example, we might speak about different isotopes of carbon. We could speak of three of the isotopes of carbon, the elements with Z = 6 and 6, 7, or 8 neutrons in the nucleus, as carbon-12 ...
... Normally, isotopes of elements do not have separate names the way hydrogen does. For example, we might speak about different isotopes of carbon. We could speak of three of the isotopes of carbon, the elements with Z = 6 and 6, 7, or 8 neutrons in the nucleus, as carbon-12 ...
Atomic Structure Timeline
... • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
... • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
Learning Outcomes for Chemical Reactions and
... • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction
... 6. Drawing Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams a) Find the element on the periodic table b) The atomic # = # of p’s = # of e’s c) Find the atomic mass on the periodic table (round off to the nearest whole #) d) # of n’s = atomic mass – # of p’s e) Draw the nucleus as a circle with the # of p’s and n’s inside ...
... 6. Drawing Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams a) Find the element on the periodic table b) The atomic # = # of p’s = # of e’s c) Find the atomic mass on the periodic table (round off to the nearest whole #) d) # of n’s = atomic mass – # of p’s e) Draw the nucleus as a circle with the # of p’s and n’s inside ...
Atom Timeline PPT
... • On your Atomic Structure Timeline quiz, you will be expected to… – draw the atomic models – match scientists to their experiments and discoveries – place the models in chronological order ...
... • On your Atomic Structure Timeline quiz, you will be expected to… – draw the atomic models – match scientists to their experiments and discoveries – place the models in chronological order ...
Material presented
... – absorb energy by excitation of electrons to higher energy levels – release energy by relaxation of electrons to lower energy levels ...
... – absorb energy by excitation of electrons to higher energy levels – release energy by relaxation of electrons to lower energy levels ...
Historical Development of Quantum Mechanics
... Energy Shell Atomic Model (explains the emission and absorption spectrums of different elements) – realized his early model as incomplete and limited Werner Heisenberg (1924) – Uncertainty Principle (one cannot be certain of the position and momentum of an electron – the act of observing changes its ...
... Energy Shell Atomic Model (explains the emission and absorption spectrums of different elements) – realized his early model as incomplete and limited Werner Heisenberg (1924) – Uncertainty Principle (one cannot be certain of the position and momentum of an electron – the act of observing changes its ...
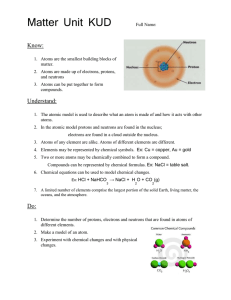
Matter Unit KUD
... Understand: 1. The atomic model is used to describe what an atom is made of and how it acts with other atoms. 2. In the atomic model protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus; electrons are found in a cloud outside the nucleus. 3. Atoms of any element are alike. Atoms of different elements are d ...
... Understand: 1. The atomic model is used to describe what an atom is made of and how it acts with other atoms. 2. In the atomic model protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus; electrons are found in a cloud outside the nucleus. 3. Atoms of any element are alike. Atoms of different elements are d ...
Periodic Table - Ralph C. Mahar
... The electron configuration for calcium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 The configuration for an ion of calcium would be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 Ca2+ This is isoelectronic to (has the same electron configuration as) an Argon atom. ...
... The electron configuration for calcium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 The configuration for an ion of calcium would be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 Ca2+ This is isoelectronic to (has the same electron configuration as) an Argon atom. ...
Six Weeks Review PPT
... Democritus, 460 BC – proposes particles so small they can not be destroyed or divided, and describes them as “atomos” (uncuttable) John Dalton, early 1800’s - first to use “atom”; proposes that atoms of the same element are identical, and atoms of different elements have different weights/masses; So ...
... Democritus, 460 BC – proposes particles so small they can not be destroyed or divided, and describes them as “atomos” (uncuttable) John Dalton, early 1800’s - first to use “atom”; proposes that atoms of the same element are identical, and atoms of different elements have different weights/masses; So ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
Topic one midterm review
... – If the “Plum Pudding” model was correct then the α particles would pass through the foil with just a few being slightly ...
... – If the “Plum Pudding” model was correct then the α particles would pass through the foil with just a few being slightly ...