Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory
... When one heats a solid object at a very high temperature, we know that they tend to radiate in different colours. This is the same for any solid object. Scientists used to think that if you increased the temperature or intensity (brightness), you would increase the energy that was being or by th ...
... When one heats a solid object at a very high temperature, we know that they tend to radiate in different colours. This is the same for any solid object. Scientists used to think that if you increased the temperature or intensity (brightness), you would increase the energy that was being or by th ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry of Life
... differ in the number of neutrons – Mass number – sum of protons and neutrons in an atom – Example - ...
... differ in the number of neutrons – Mass number – sum of protons and neutrons in an atom – Example - ...
INTRODUCTION TO GENERAL CHEMISTRY Basic Principles
... The number of neutrons in an atom is equal to the difference between the mass number and the atomic number, or (A 2 Z). For example, if the mass number of a particular boron atom is 12 and the atomic number is 5 (indicating 5 protons in the nucleus), then the number of neutrons is 12 2 5 5 7. Note t ...
... The number of neutrons in an atom is equal to the difference between the mass number and the atomic number, or (A 2 Z). For example, if the mass number of a particular boron atom is 12 and the atomic number is 5 (indicating 5 protons in the nucleus), then the number of neutrons is 12 2 5 5 7. Note t ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have one and only one proton in the nucleus; all atoms of iron have 26 protons in the nucleus. This number of protons is so important to the identity of an atom that it is called the ...
... fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have one and only one proton in the nucleus; all atoms of iron have 26 protons in the nucleus. This number of protons is so important to the identity of an atom that it is called the ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
11/13 atoms powerpoint
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical co ...
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical co ...
Grade 9 Science Unit: Atoms and Elements Topic 4: Periodic Table
... Some metals, such as __________ and ___________, are too ___________ to be used alone for some purposes. Therefore, to make a substance stronger, some metals are often melted and mixed with other melted metal elements. The mixture is cooled to become a solid ____________. A solution of two or more m ...
... Some metals, such as __________ and ___________, are too ___________ to be used alone for some purposes. Therefore, to make a substance stronger, some metals are often melted and mixed with other melted metal elements. The mixture is cooled to become a solid ____________. A solution of two or more m ...
Periodic Table and Electrons
... The names of groups and periods on the periodic chart are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases. Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Peri ...
... The names of groups and periods on the periodic chart are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases. Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Peri ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Calculations showed that the nucleus must contain most of the mass of the atom and must be very small compared to the volume occupied by the atom. The positively charged particle present in the nucleus was called a proton. The nucleus of the hydrogen atom carries one positive charge and is a proton. ...
... Calculations showed that the nucleus must contain most of the mass of the atom and must be very small compared to the volume occupied by the atom. The positively charged particle present in the nucleus was called a proton. The nucleus of the hydrogen atom carries one positive charge and is a proton. ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... Different elements contain different numbers of subatomic particles Hydrogen has 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron Lithium has 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons ...
... Different elements contain different numbers of subatomic particles Hydrogen has 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron Lithium has 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons ...
Nuclear Physics Rutherford`s model of the atom
... Beta positive is where a proton decaying into a neutron and a positron, while also releasing a neutrino, this is exactly opposite to beta negative. (Beta Positive Decay Formula) ...
... Beta positive is where a proton decaying into a neutron and a positron, while also releasing a neutrino, this is exactly opposite to beta negative. (Beta Positive Decay Formula) ...
Day 2 Guided Reading Chapter 4
... around the nucleus. Atomic Orbitals (page 117) 41. T or F An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. 42. An electron model is a good approximation of ________________________________. Use the table to answer questions 43 and 44. ...
... around the nucleus. Atomic Orbitals (page 117) 41. T or F An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. 42. An electron model is a good approximation of ________________________________. Use the table to answer questions 43 and 44. ...
nature of Matter
... H has an atomic number of 1 so, it has only 1 proton in its nucleus and consequently, 1 electron. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Examples: Potassium-39 (19 protons & 20 neutrons) Uranium-235 (92 protons & 143 neutrons) Nitrogen-14 (7 protons ...
... H has an atomic number of 1 so, it has only 1 proton in its nucleus and consequently, 1 electron. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Examples: Potassium-39 (19 protons & 20 neutrons) Uranium-235 (92 protons & 143 neutrons) Nitrogen-14 (7 protons ...
Chapter 3.1 PPT
... the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is ...
... the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is ...
Canyon High School Chemistry
... 33. By which common decay mode does an atom lose the greatest mass? The least? V. Nuclear Stability, Half-Life, Reactions and Health Considerations 34. What force holds protons together in the nucleus? 35. Define Half-Life. How is it useful? 36. A piece of wood found in an ancient burial chamber con ...
... 33. By which common decay mode does an atom lose the greatest mass? The least? V. Nuclear Stability, Half-Life, Reactions and Health Considerations 34. What force holds protons together in the nucleus? 35. Define Half-Life. How is it useful? 36. A piece of wood found in an ancient burial chamber con ...
History of Chemistry
... atoms, which are bits of matter too small to be seen. These atoms CANNOT be further split into smaller portions. • There is a void, which is empty space between atoms. • Atoms are completely solid. • Atoms are homogeneous, with no internal structure. • Atoms are different in ... » 1) ...their sizes ...
... atoms, which are bits of matter too small to be seen. These atoms CANNOT be further split into smaller portions. • There is a void, which is empty space between atoms. • Atoms are completely solid. • Atoms are homogeneous, with no internal structure. • Atoms are different in ... » 1) ...their sizes ...
Atomic terms - ATOMIC NUMBER: The number of protons in the
... 35.45 amu (Natural chlorine is mostly chlorine-35) ...
... 35.45 amu (Natural chlorine is mostly chlorine-35) ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... • He called his theoretical smallest possible piece atomos, meaning “uncuttable” or “can’t be divided. ...
... • He called his theoretical smallest possible piece atomos, meaning “uncuttable” or “can’t be divided. ...
Name
... 7. Which parts of Dalton’s theory are no longer accepted and why? divisible AND 2. atoms of the same element are identical ...
... 7. Which parts of Dalton’s theory are no longer accepted and why? divisible AND 2. atoms of the same element are identical ...
Unit2StudyGuide
... Which two particles have the same mass? What particles make up the nucleus? What particles are NOT in the nucleus? What particles make up the atomic mass? What particles have insignificant mass, but take up most of the space of an atom? Atoms of the same element but have a different mass are _______ ...
... Which two particles have the same mass? What particles make up the nucleus? What particles are NOT in the nucleus? What particles make up the atomic mass? What particles have insignificant mass, but take up most of the space of an atom? Atoms of the same element but have a different mass are _______ ...
1411-Practice Exam 3 (ch6-8)
... Sodium and potassium have similar chemical and physical properties. This is best explained by the fact that both elements A) are active metals. B) are in Period 1 of the periodic table. C) have the same ground-state valence-electron configuration. D) have low relative atomic masses. E) have relative ...
... Sodium and potassium have similar chemical and physical properties. This is best explained by the fact that both elements A) are active metals. B) are in Period 1 of the periodic table. C) have the same ground-state valence-electron configuration. D) have low relative atomic masses. E) have relative ...
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
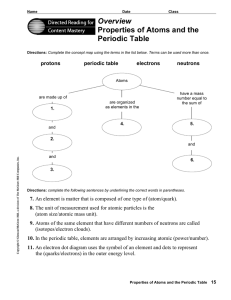
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
Chapter 1 Review Sheet
... 1. element – the most simple form of matter that can’t be broken down by either chemical or physical means 2. compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined 3. atom – the smallest representative part of an element 4. atomic mass unit – the unit used to measure the relative mass of atom ...
... 1. element – the most simple form of matter that can’t be broken down by either chemical or physical means 2. compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined 3. atom – the smallest representative part of an element 4. atomic mass unit – the unit used to measure the relative mass of atom ...