File
... 4. The modern model of an atom is called the (electron-cloud/nucleus-orbit) model. 5. Electrons that are close to the nucleus have (more energy/less energy) than electrons that are farther from the nucleus. ...
... 4. The modern model of an atom is called the (electron-cloud/nucleus-orbit) model. 5. Electrons that are close to the nucleus have (more energy/less energy) than electrons that are farther from the nucleus. ...
Chapter 2 – Elements
... order of increasing atomic mass, chemical and physical properties form patterns that repeat at regular intervals. initially he called this law “The Law of Octaves” because properties repeated every eighth element. ...
... order of increasing atomic mass, chemical and physical properties form patterns that repeat at regular intervals. initially he called this law “The Law of Octaves” because properties repeated every eighth element. ...
MrsB-Chemistry
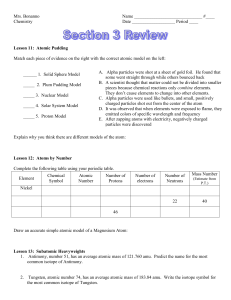
... B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elements. C. Alpha particles were used like bullets, and small, positively charged particles shot out from the center of the at ...
... B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elements. C. Alpha particles were used like bullets, and small, positively charged particles shot out from the center of the at ...
Name Test Review Chapters 4 and 25 Honors Chemistry 1. Fill in
... Discovered the neutron. _______________________________ Created the first atomic theory based on experimental evidence. ___________________________ Discovered the electron. __________________________ Discovered the nucleus. ___________________________ Discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass. ____ ...
... Discovered the neutron. _______________________________ Created the first atomic theory based on experimental evidence. ___________________________ Discovered the electron. __________________________ Discovered the nucleus. ___________________________ Discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass. ____ ...
History of Atomic Theory
... 1. Aufbau Principle: An electron occupies the lowest energy level that can receive it. 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle: No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. • If two electrons have the same n, m, and l values they have to have different spins • Two electrons ...
... 1. Aufbau Principle: An electron occupies the lowest energy level that can receive it. 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle: No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. • If two electrons have the same n, m, and l values they have to have different spins • Two electrons ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... H2SO3 - Sulfurous Acid H2SO4 - Sulfuric Acid The ratio of oxygen in these two compounds is 3 to 4. Ionic bonding When chemical bonds are formed, electrons are shared between atoms or they are transferred from one atom to another to create a positive and negative ion. When chemical bonds are formed ...
... H2SO3 - Sulfurous Acid H2SO4 - Sulfuric Acid The ratio of oxygen in these two compounds is 3 to 4. Ionic bonding When chemical bonds are formed, electrons are shared between atoms or they are transferred from one atom to another to create a positive and negative ion. When chemical bonds are formed ...
chapter 19 - Celina City Schools
... Located inside the electron cloud which immediately surrounds the nucleus (the electron orbits around the nucleus) The mass of an electron is about 1/2000 that of a proton (or 0 amu) e) Electron ____________ The area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely to be found ...
... Located inside the electron cloud which immediately surrounds the nucleus (the electron orbits around the nucleus) The mass of an electron is about 1/2000 that of a proton (or 0 amu) e) Electron ____________ The area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely to be found ...
electron
... abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
... abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
Questions About Atoms and Elements
... c.) The particle that can occur in different numbers in atoms of the same element ______ d.) Held in shells around the nucleus. ______ e.) The negatively-charged particle. ______ f.) The particle with the negligible mass. ______ g.) The number of these particles is found by subtracting the proton nu ...
... c.) The particle that can occur in different numbers in atoms of the same element ______ d.) Held in shells around the nucleus. ______ e.) The negatively-charged particle. ______ f.) The particle with the negligible mass. ______ g.) The number of these particles is found by subtracting the proton nu ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... • Within a period positive ions gradually decrease until Group 5A or 6A negative ion greatly increase then gradually decrease decreases ...
... • Within a period positive ions gradually decrease until Group 5A or 6A negative ion greatly increase then gradually decrease decreases ...
Unit 1: Chapter 3
... a. The horizontal rows are called the periods. There are seven periods. Going across a period from left to right, elements are filling that energy level’s “s & p” orbitals, eventually getting to a full octet at the noble gas. b. The vertical columns are called groups or families. Elements within th ...
... a. The horizontal rows are called the periods. There are seven periods. Going across a period from left to right, elements are filling that energy level’s “s & p” orbitals, eventually getting to a full octet at the noble gas. b. The vertical columns are called groups or families. Elements within th ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Exam Problem. A sample of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is synthesized in the laboratory. It contains 1.50 g of carbon and 2.00 g of oxygen. Another sample of ascorbic acid isolated from citrus fruits contains 9.22 g of carbon. How many grams of oxygen does it contain? a. 12.3 ...
... Exam Problem. A sample of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is synthesized in the laboratory. It contains 1.50 g of carbon and 2.00 g of oxygen. Another sample of ascorbic acid isolated from citrus fruits contains 9.22 g of carbon. How many grams of oxygen does it contain? a. 12.3 ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT AP Chemistry is a
... 4) Similarities in periods: The period corresponds to how many principal energy levels (PEL) the electrons occupy in the atom when in its ground state. Ex. Silicon (Si) and Magnesium (Mg) are in period 3 and have 3 energy levels in which their electrons are ...
... 4) Similarities in periods: The period corresponds to how many principal energy levels (PEL) the electrons occupy in the atom when in its ground state. Ex. Silicon (Si) and Magnesium (Mg) are in period 3 and have 3 energy levels in which their electrons are ...
6th grade review facts
... Potential energy is energy stored in an object. Energy can be stored chemically or based on position. The sun is the original source of all energy. In order to do work, energy is transformed from one form to another. This is the law of conservation of energy. Greenhouse effect is the Earth’s heating ...
... Potential energy is energy stored in an object. Energy can be stored chemically or based on position. The sun is the original source of all energy. In order to do work, energy is transformed from one form to another. This is the law of conservation of energy. Greenhouse effect is the Earth’s heating ...
Facts for Science - Kempsville Middle School
... Potential energy is energy stored in an object. Energy can be stored chemically or based on position. The sun is the original source of all energy. In order to do work, energy is transformed from one form to another. This is the law of conservation of energy. Greenhouse effect is the Earth’s heating ...
... Potential energy is energy stored in an object. Energy can be stored chemically or based on position. The sun is the original source of all energy. In order to do work, energy is transformed from one form to another. This is the law of conservation of energy. Greenhouse effect is the Earth’s heating ...
u3_tqs
... describes the behavior of electrons within atoms 36. Why did Bohr change Rutherford’s model? to include new discoveries about how the energy of an atom changes when it absorbs or emits light 37. What did Bohr propose about electrons? that they are found only in specific circular paths (or orbits) ar ...
... describes the behavior of electrons within atoms 36. Why did Bohr change Rutherford’s model? to include new discoveries about how the energy of an atom changes when it absorbs or emits light 37. What did Bohr propose about electrons? that they are found only in specific circular paths (or orbits) ar ...