
What is Matter?
... outside the nucleus called the electron cloud • Carry a negative (-) charge • Have an insignificant mass compared to protons and neutrons ...
... outside the nucleus called the electron cloud • Carry a negative (-) charge • Have an insignificant mass compared to protons and neutrons ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Elements, Orbitals, and Electron Configurations
... atomic mass of Cu to the correct number of significant figures from the data. [ANS: see periodic chart. (63.5)] ...
... atomic mass of Cu to the correct number of significant figures from the data. [ANS: see periodic chart. (63.5)] ...
Chapter 10: The Atom
... In alpha decay, the nucleus ejects two protons and two neutrons. Beta decay occurs when a neutron in the nucleus splits into a proton and an electron. Gamma decay is not truly a decay reaction in the sense that the nucleus becomes something different. ...
... In alpha decay, the nucleus ejects two protons and two neutrons. Beta decay occurs when a neutron in the nucleus splits into a proton and an electron. Gamma decay is not truly a decay reaction in the sense that the nucleus becomes something different. ...
Ch 4 and Ch 5 Study Guide (ICP) Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... 52. An atom of potassium has a mass number of 39 and an atomic number of 19. It therefore has _______________________ neutrons in its nucleus. 53. When an atom gains or loses energy, _______________________ jump between energy levels. 54. An electron that gains energy enters an excited state and abs ...
... 52. An atom of potassium has a mass number of 39 and an atomic number of 19. It therefore has _______________________ neutrons in its nucleus. 53. When an atom gains or loses energy, _______________________ jump between energy levels. 54. An electron that gains energy enters an excited state and abs ...
atoms - Wappingers Central School
... • An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make the atom _______. ...
... • An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make the atom _______. ...
The Atom
... must have elements. Elements are made of atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
... must have elements. Elements are made of atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
History of the Atom
... In 1803, proposed an Atomic Theory which states: o All substances are made of atoms; atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. o Atoms of the same element are exactly alike o Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances ...
... In 1803, proposed an Atomic Theory which states: o All substances are made of atoms; atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. o Atoms of the same element are exactly alike o Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances ...
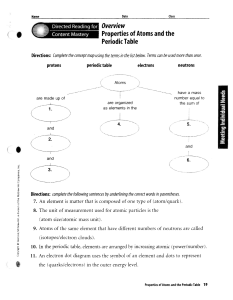
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit), 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ...
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit), 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ...
Chapter+4+Ques Honorst
... 10. Did Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment go as planned? 11. What did Rutherford experiment find about the atom? 12. What is a nucleus? 13. Describe or draw what the new model (Rutherford’s model) looks like: 14. What was Rutherford’s contribution to the Atomic Theory? Chp 4-2 1. What are the three ...
... 10. Did Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment go as planned? 11. What did Rutherford experiment find about the atom? 12. What is a nucleus? 13. Describe or draw what the new model (Rutherford’s model) looks like: 14. What was Rutherford’s contribution to the Atomic Theory? Chp 4-2 1. What are the three ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
Neutron - Piscataway High School
... Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element Atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element Atomic mass unit: one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having 6 protons and 6 neutrons Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucl ...
... Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element Atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element Atomic mass unit: one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having 6 protons and 6 neutrons Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucl ...
Electrons and the Atom PPT
... of electrons, it is said to be filled. Electrons in the outer shell of an atom are known as valence electrons and the shell is the valence shell. The valence electrons are the only electrons involved in forming chemical bonds ...
... of electrons, it is said to be filled. Electrons in the outer shell of an atom are known as valence electrons and the shell is the valence shell. The valence electrons are the only electrons involved in forming chemical bonds ...
Basic Structure of the Atom
... Energy levels closest to nucleus have low energy Energy levels increase in energy with distance from the nucleus Electrons gain and lose energy by moving between energy levels (quantum) ...
... Energy levels closest to nucleus have low energy Energy levels increase in energy with distance from the nucleus Electrons gain and lose energy by moving between energy levels (quantum) ...
Script of atoms video
... # of protons gives identity of the element (atomic number) So what is helium’s atomic number? (fig. 2.3) Protons + Neutrons gives atomic mass So what is the atomic mass of helium? (fig. 2.3) For uncharged (electrically neutral) atoms: # of protons = # of electrons Re-cap Protons and neutrons are in ...
... # of protons gives identity of the element (atomic number) So what is helium’s atomic number? (fig. 2.3) Protons + Neutrons gives atomic mass So what is the atomic mass of helium? (fig. 2.3) For uncharged (electrically neutral) atoms: # of protons = # of electrons Re-cap Protons and neutrons are in ...
Periodic Table Powerpoint
... Elements from different families Not similar properties Last element an inactive gas Reactive – unreactive 7 periods Valance electrons increase from left to right across a period. ...
... Elements from different families Not similar properties Last element an inactive gas Reactive – unreactive 7 periods Valance electrons increase from left to right across a period. ...
Chapter 5
... Charges are of two types: Positive and Negative Unlike charges attract and like charges repel Charges may be transferred by contact or induction The closer two object are, the greater the force of attraction ...
... Charges are of two types: Positive and Negative Unlike charges attract and like charges repel Charges may be transferred by contact or induction The closer two object are, the greater the force of attraction ...
Chapter 3 - mrgoosby
... Discovered the neutron- neutral particle in the nucleus Found this data when he noticed that the gold atoms in the foil had released some mass with no charge ...
... Discovered the neutron- neutral particle in the nucleus Found this data when he noticed that the gold atoms in the foil had released some mass with no charge ...
Section 3
... •Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. •Atoms of different elements can join to form molecules. •His theory was accepted because there was evidence to support it. 4 parts of an atom •Nucleus – is center of an atom that carries a positive charge. It contains both protons & neutrons. The electr ...
... •Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. •Atoms of different elements can join to form molecules. •His theory was accepted because there was evidence to support it. 4 parts of an atom •Nucleus – is center of an atom that carries a positive charge. It contains both protons & neutrons. The electr ...
download
... of atoms, but this discuss will be conducted in terms of single atoms. Ionic bonding occurs between metal atoms and nonmetal atoms. Metals usually have 1, 2, or 3 electrons in their outermost shell. Nonmetals have 5, 6, or 7 electrons in their outer shell. Atoms with outer shells that are only parti ...
... of atoms, but this discuss will be conducted in terms of single atoms. Ionic bonding occurs between metal atoms and nonmetal atoms. Metals usually have 1, 2, or 3 electrons in their outermost shell. Nonmetals have 5, 6, or 7 electrons in their outer shell. Atoms with outer shells that are only parti ...
Lesson 7
... know the mass number, you can also determine the number of neutrons. Isotopes: Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. (ex. Lithium isotope with a mass number of 6 is called lithium-6 or Li-6) Atomic Mass: measured in atomic mass units(u). not whole numbers. The atom ...
... know the mass number, you can also determine the number of neutrons. Isotopes: Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. (ex. Lithium isotope with a mass number of 6 is called lithium-6 or Li-6) Atomic Mass: measured in atomic mass units(u). not whole numbers. The atom ...
Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... Ions- positive or negatively charged atom or groups of atoms (Ca2+, N3-) Isotope- the number of neutrons is changed and the mass number is different from the average atomic mass 24 Rubidium has two naturally occurring isotopes, Rb-85 (84.9118 amu) and Rb-87 (86.9092 amu). If Rubidium has an average ...
... Ions- positive or negatively charged atom or groups of atoms (Ca2+, N3-) Isotope- the number of neutrons is changed and the mass number is different from the average atomic mass 24 Rubidium has two naturally occurring isotopes, Rb-85 (84.9118 amu) and Rb-87 (86.9092 amu). If Rubidium has an average ...






















![Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000860497_1-e3bea510ba504d09bc42d6f5e4936390-300x300.png)