1 - Hobbs Freshman High School
... 8. The positively charged particles found in an atom are called (electrons, neutrons, nuclei, protons) 9. Where is most of the mass of an atom located? (in the energy levels, in the electron cloud, inside the nucleus, evenly distributed throughout the atom) 10. Which of the following statements best ...
... 8. The positively charged particles found in an atom are called (electrons, neutrons, nuclei, protons) 9. Where is most of the mass of an atom located? (in the energy levels, in the electron cloud, inside the nucleus, evenly distributed throughout the atom) 10. Which of the following statements best ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY
... **A Brief Note on the Antineutrino: As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the elect ...
... **A Brief Note on the Antineutrino: As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the elect ...
chemical bonds. - Dr. Gerry Cronin
... • Electrons are very small and light (mass about 1/2000th that of proton or neutron), often represented as a “planet” orbiting the “sun” (atomic nucleus). In reality, they are found in a “cloud” of probability. This concept, however, made even Einstein’s head hurt – we can use the planets-orbiting-t ...
... • Electrons are very small and light (mass about 1/2000th that of proton or neutron), often represented as a “planet” orbiting the “sun” (atomic nucleus). In reality, they are found in a “cloud” of probability. This concept, however, made even Einstein’s head hurt – we can use the planets-orbiting-t ...
Atomic Models
... the great Madame Curie, produced a beam of particles that could go through almost anything And James Chadwick determined this beam was not affected by a magnetic field (no charge!) Neutrons were given credit ...
... the great Madame Curie, produced a beam of particles that could go through almost anything And James Chadwick determined this beam was not affected by a magnetic field (no charge!) Neutrons were given credit ...
Chemistry I - Net Start Class
... 3. A solid, silver-colored metallic element is combined with a light green, gaseous element, producing a powdery white solid product. What type of substance was the reactant? 4. A solid, pure, green substance was heated and yielded a white gas and a purple solid. The material that was heated was wha ...
... 3. A solid, silver-colored metallic element is combined with a light green, gaseous element, producing a powdery white solid product. What type of substance was the reactant? 4. A solid, pure, green substance was heated and yielded a white gas and a purple solid. The material that was heated was wha ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... 65. The reaction Mg(s) + 2HCI(aq) H2(g) + MgCl2(aq) is a a) composition reaction b) decomposition reaction. c) single-replacement reaction. d) double-replacement reaction. 66. The reaction Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(S) + 2KNO3(aq) is a a) double-replacement reaction. b) synthesis reaction. c) d ...
... 65. The reaction Mg(s) + 2HCI(aq) H2(g) + MgCl2(aq) is a a) composition reaction b) decomposition reaction. c) single-replacement reaction. d) double-replacement reaction. 66. The reaction Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(S) + 2KNO3(aq) is a a) double-replacement reaction. b) synthesis reaction. c) d ...
3.1.1 Fundamental Particles Introduction - Chemistry
... • The smallest positive rays were present when hydrogen was the initial gas. • This smallest positive particle was eventually named the PROTON by Rutherford in 1914 ...
... • The smallest positive rays were present when hydrogen was the initial gas. • This smallest positive particle was eventually named the PROTON by Rutherford in 1914 ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature ...
... At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature ...
Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory
... 15. Refer back to the note “In Search for a Model for Matter: 2400 Years of Atomic Theory”. Two of the statements made by Dalton in his atomic model are incorrect. Which two statements are incorrect, and why? Dalton believed that all atoms of an element are identical. This is untrue. Most atoms h ...
... 15. Refer back to the note “In Search for a Model for Matter: 2400 Years of Atomic Theory”. Two of the statements made by Dalton in his atomic model are incorrect. Which two statements are incorrect, and why? Dalton believed that all atoms of an element are identical. This is untrue. Most atoms h ...
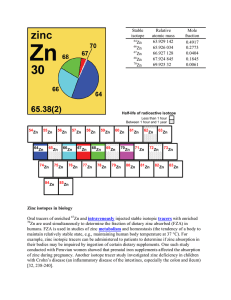
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
Example of calculating average atomic mass
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
FirstSemesterReviewHonors
... 4. How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)? 5. Be able to do the electron configuration for a given atom. 6. According to the aufbau principle, how many electrons may occupy an orbital? Chapter 6 1. Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass, and used the arrangem ...
... 4. How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)? 5. Be able to do the electron configuration for a given atom. 6. According to the aufbau principle, how many electrons may occupy an orbital? Chapter 6 1. Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass, and used the arrangem ...
Unit 3.2 worksheet 4 atomic model of matter
... Tips and tricks! Hope I help :)) Video Rating: / 5. Click Here - Movie Star Planet. Hi i am writing u to ask what is the state requirments while growing for person medical needs. what will make it completely legal where if visited by the law i wanna. Getting Started. USATestprep is very user-friendl ...
... Tips and tricks! Hope I help :)) Video Rating: / 5. Click Here - Movie Star Planet. Hi i am writing u to ask what is the state requirments while growing for person medical needs. what will make it completely legal where if visited by the law i wanna. Getting Started. USATestprep is very user-friendl ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... Some observations on the series Lead (Pb) is above H, so is Al. But these metals are not attacked by 6M HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable b ...
... Some observations on the series Lead (Pb) is above H, so is Al. But these metals are not attacked by 6M HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable b ...
File
... CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM Atoms are composed of electrons in a cloud around a positive nucleus. ...
... CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM Atoms are composed of electrons in a cloud around a positive nucleus. ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure 101 Week 13 2
... What fundamental factors determine the size of an atom? November 2011 ...
... What fundamental factors determine the size of an atom? November 2011 ...
Trend #1 atomic mass
... There are 7 trends on the periodic table that we will follow. Using your periodic table, answer all of the questions in the packet. Think hard. The periodic table has 18 groups that go UP and DOWN. The rows that go across left to right are called the PERIODS. Similar elements are found in GROUPS. El ...
... There are 7 trends on the periodic table that we will follow. Using your periodic table, answer all of the questions in the packet. Think hard. The periodic table has 18 groups that go UP and DOWN. The rows that go across left to right are called the PERIODS. Similar elements are found in GROUPS. El ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... He determined the actual charge of an electron. His experimental setup and technique was so good that the charge he measured almost 100 years ago is within 1% of the currently accepted value. ...
... He determined the actual charge of an electron. His experimental setup and technique was so good that the charge he measured almost 100 years ago is within 1% of the currently accepted value. ...
File
... The normal atom (also called a stable atom) has three main parts (or particles) that we are concerned with; protons, neutrons, and electrons. A fourth part, the nucleus, is often referred to but we are not focusing on it as much as we are on protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus is the centr ...
... The normal atom (also called a stable atom) has three main parts (or particles) that we are concerned with; protons, neutrons, and electrons. A fourth part, the nucleus, is often referred to but we are not focusing on it as much as we are on protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus is the centr ...
Atomic and Nuclear Physics Atomic structure
... The current model of atomic structure was not undestood until the 20th century. ● 1808 - John Dalton – new idea - the matter is made of atoms (tiny indivisible spheres) ● 1897 – J. J. Thomson discovered that all matter ...
... The current model of atomic structure was not undestood until the 20th century. ● 1808 - John Dalton – new idea - the matter is made of atoms (tiny indivisible spheres) ● 1897 – J. J. Thomson discovered that all matter ...