Interaction of Radiation with Matter
... atoms. Unstable atoms differ from stable atoms because they have an excess of energy or mass or both. Unstable atoms are said to be radioactive. In order to reach stability, these atoms give off, or emit, the excess energy or mass. These emissions are called radiation. ...
... atoms. Unstable atoms differ from stable atoms because they have an excess of energy or mass or both. Unstable atoms are said to be radioactive. In order to reach stability, these atoms give off, or emit, the excess energy or mass. These emissions are called radiation. ...
Document
... Organic chemistry is the study of the chemistry of carbon compounds. Over 16 million carbon containing compounds are known and 90% of the new compounds discovered or synthesized are also organic or carbon containing. All of the biomolecules essential to life such as nucleic acids, amino acids, carbo ...
... Organic chemistry is the study of the chemistry of carbon compounds. Over 16 million carbon containing compounds are known and 90% of the new compounds discovered or synthesized are also organic or carbon containing. All of the biomolecules essential to life such as nucleic acids, amino acids, carbo ...
Chemical Reactions - Johnston County Schools
... Substances other than hydrocarbons can also combust. However, you may not be able to tell whether it’s combustion from the chemical equation alone. Remember that combustion must have O2 as a reactant and must release (exothermic) heat and light energy. Reactions with O2.mov ...
... Substances other than hydrocarbons can also combust. However, you may not be able to tell whether it’s combustion from the chemical equation alone. Remember that combustion must have O2 as a reactant and must release (exothermic) heat and light energy. Reactions with O2.mov ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... • Planck’s Quantization of Energy (1900) According to Max Planck, when solids are heated, they emit electromagnetic radiation over a wide range of wavelengths. He proposed that an atom could emit or absorb energy only in discrete quantities, like small packages, and quantum is the smallest quantity ...
... • Planck’s Quantization of Energy (1900) According to Max Planck, when solids are heated, they emit electromagnetic radiation over a wide range of wavelengths. He proposed that an atom could emit or absorb energy only in discrete quantities, like small packages, and quantum is the smallest quantity ...
6 • Structure of the Atom The Subatomic Particles (1 of 8) 6
... The 33 is the mass number which is the mass of one of the isotopes. This mass is due to the protons and neutrons. The number of neutrons is the mass number - the atomic number. 33 - 16 = 17 neutrons. Since the charge is 2-, there are 2 more electrons than protons. In this case, there are 18 electron ...
... The 33 is the mass number which is the mass of one of the isotopes. This mass is due to the protons and neutrons. The number of neutrons is the mass number - the atomic number. 33 - 16 = 17 neutrons. Since the charge is 2-, there are 2 more electrons than protons. In this case, there are 18 electron ...
§2 Atomic Structure , A website that gives a good summary of this
... Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons (and electrons) but have different numbers of neutrons, common isotope of carbon, C-12, has 6 protons in its nucleus and also 6 neutrons while the rarer C-14 contains 6 The chemical properties of isotopes are very similar due to the equal number ...
... Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons (and electrons) but have different numbers of neutrons, common isotope of carbon, C-12, has 6 protons in its nucleus and also 6 neutrons while the rarer C-14 contains 6 The chemical properties of isotopes are very similar due to the equal number ...
Chemistry Unit 3
... an element is the number of protons an element has. Located above the symbol of the element The number of protons determines the identity of the element. Each element has a different atomic number ...
... an element is the number of protons an element has. Located above the symbol of the element The number of protons determines the identity of the element. Each element has a different atomic number ...
Reference Tables - Regents to 2011
... b) State, in terms of the number of electron shells, why the radius of a strontium atom in the ground state is larger than the radius of a magnesium atom in the ground state. ...
... b) State, in terms of the number of electron shells, why the radius of a strontium atom in the ground state is larger than the radius of a magnesium atom in the ground state. ...
02_Lecture_Presentation
... of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
... of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... oxygen, a combustion reaction results. The combustion reaction may also be an example of an earlier type such as 2Mg + O2 2MgO. The combustion reaction may be burning of a fuel. ...
... oxygen, a combustion reaction results. The combustion reaction may also be an example of an earlier type such as 2Mg + O2 2MgO. The combustion reaction may be burning of a fuel. ...
atom n
... atom n. A unit of matter, the smallest unit of an element, consisting of a dense, central, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a system of electrons, equal in number to the number of nuclear protons, the entire structure having an approximate diameter of 10-8 centimeter and characteristically r ...
... atom n. A unit of matter, the smallest unit of an element, consisting of a dense, central, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a system of electrons, equal in number to the number of nuclear protons, the entire structure having an approximate diameter of 10-8 centimeter and characteristically r ...
Chemistry Standard Outline
... SC3 Students will use the modern atomic theory to explain the characteristics of atoms. SC3a. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, and position of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. SC3c. Explain the relationship of the proton number to the element’s identity. SC3d. Explain the ...
... SC3 Students will use the modern atomic theory to explain the characteristics of atoms. SC3a. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, and position of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. SC3c. Explain the relationship of the proton number to the element’s identity. SC3d. Explain the ...
Manohar, Nathan J. - California State Science Fair
... energy was found to be -5.70 Rydbergs. The helium atom computation was considerably more complicated than the one for the hydrogen atom because there are two electrons in this atom. The Li+ ion also is a two electron system. The energy of this ion was found to be -14.4453 Rydbergs. Conclusions/Discu ...
... energy was found to be -5.70 Rydbergs. The helium atom computation was considerably more complicated than the one for the hydrogen atom because there are two electrons in this atom. The Li+ ion also is a two electron system. The energy of this ion was found to be -14.4453 Rydbergs. Conclusions/Discu ...
If each orbital contains two electrons, the second energy level can
... second energy levels are filled to capacity by the ten electrons of neon, which has two electrons in the first and eight electrons in the second energy level. Element 11, sodium (Na), has two electrons in the first energy level and eight electrons in the second energy level, with the remaining elect ...
... second energy levels are filled to capacity by the ten electrons of neon, which has two electrons in the first and eight electrons in the second energy level. Element 11, sodium (Na), has two electrons in the first energy level and eight electrons in the second energy level, with the remaining elect ...
File
... _____ 6. If two or more compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element that is combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This statement is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. conservation ...
... _____ 6. If two or more compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element that is combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This statement is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. conservation ...
Unit 01 Qual Chem
... Law of Conservation of Energy = energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Only transferred. ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy = energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Only transferred. ...
In-Class Exam - Fayetteville State University
... Note: Answer 33 questions only. Leave three questions of your choice unmarked. Mark your answers on SCANTRON provided. Each correct answer is worth 3 points. ...
... Note: Answer 33 questions only. Leave three questions of your choice unmarked. Mark your answers on SCANTRON provided. Each correct answer is worth 3 points. ...
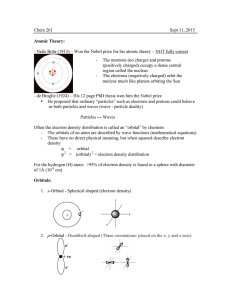
Chem 261 Sept 11, 2015 Atomic Theory:
... - de Broglie (1924) – His 12 page PhD thesis won him the Nobel prize • He proposed that ordinary “particles” such as electrons and protons could behave as both particles and waves (wave - particle duality) Particles ↔ Waves Often the electron density distribution is called an “orbital” by chemists - ...
... - de Broglie (1924) – His 12 page PhD thesis won him the Nobel prize • He proposed that ordinary “particles” such as electrons and protons could behave as both particles and waves (wave - particle duality) Particles ↔ Waves Often the electron density distribution is called an “orbital” by chemists - ...
Many-electron atoms
... With K and Ca, successive electrons go into the 4s orbital, and Ca has the electronic configuration [Ar]4s2. At this point, the pattern changes. To a first approximation, the 10 electrons for the next 10 elements (Sc to Zn) enter the 3d orbitals, giving Zn the electronic configuration 4s23d10. Ther ...
... With K and Ca, successive electrons go into the 4s orbital, and Ca has the electronic configuration [Ar]4s2. At this point, the pattern changes. To a first approximation, the 10 electrons for the next 10 elements (Sc to Zn) enter the 3d orbitals, giving Zn the electronic configuration 4s23d10. Ther ...
Atomic - Ms. Dawkins
... • Electrons are much smaller than protons (2000 times smaller). • Electrons move around the nucleus very quickly. Scientists have found that it is not possible to determine the exact position of any single electron in an atom because they are moving too fast. This is why we picture electrons as a cl ...
... • Electrons are much smaller than protons (2000 times smaller). • Electrons move around the nucleus very quickly. Scientists have found that it is not possible to determine the exact position of any single electron in an atom because they are moving too fast. This is why we picture electrons as a cl ...