* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Hobbs Freshman High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
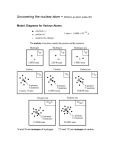
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Unit Review 1. Who proposed the idea that an atom was a uniformly solid sphere, much like a billiard ball? (Rutherford, Dalton, Thompson, Bohr) 2. The negatively charged particles found in an atom are called (electrons, neutrons, nuclei, protons). 3. The periodic table indicates that the atomic number of silver (Ag) is (47, 61,107.868, 108). 4. How many electrons are necessary to completely fill the first energy level of an atom? (2, 6, 8, 18) 5. Valence electrons are located in (the atom’s outermost energy level, all the energy levels of an atom, the atom’s nucleus, none of the above) 6. What is the maximum number of electrons the second energy level can hold? (2, 4, 8, 18) 7. According to the present theory of atomic structure, the nucleus of an atom is composed of which of the following? (electrons only, neutrons and electrons, protons and electrons, protons and neutrons) 8. The positively charged particles found in an atom are called (electrons, neutrons, nuclei, protons) 9. Where is most of the mass of an atom located? (in the energy levels, in the electron cloud, inside the nucleus, evenly distributed throughout the atom) 10. Which of the following statements best describes the Bohr model of an atom? (the nucleus contains almost all of the mass of an atom and the electrons move in orbits outside the nucleus, the positive charge is spread throughout the atom making up its mass and the electrons are plugged into the positive charge, the atom is a small indivisible particle that differs for different elements, the neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom and the protons and electrons move around the nucleus) 11. In an experiment Rutherford bombarded gold foil with high-speed positively charges particles and found, that while most of the particles passed through this foil, a few bounced back. In terms of atomic structure, which of the following statements explains this observation? (The atom is mostly empty space and has a small dense nucleus, the electrons keep out other atoms, the electrons repel the positively charged particles, the atom is a solid sphere much like a billiard ball) 12. An atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. What is the distribution of the electrons in the first three energy levels? (2, 6, 9, or 2,7,8 or 2,8,7 or 8,2,7). 13. The atomic number of an element refers to the number of? (neutrons, protons, neutrons and protons, protons and electrons) 14. Which of the following are the correct chemical symbols for Magnesium, Carbon Chlorine and Phosphorus? (Mg, Cb, Ch, Po or M, C, Cl, Ph or Mg, C, Cl, P or Ma, Ca, Ch, Pr) 15. The members of the halogen family (F, Cl, Br, I and At) have atoms containing how many electrons in their outer energy level? (1, 7, 14, 17) 16. A vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called? (a family, an order, a period, a series) 17. The elements of a period are listed consecutively in order of increasing (atomic mass, atomic number, isotope number, mass number) 18. The notation 178O, the superscript refers to the (atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, valence electrons) 19. The elements of a family generally have the same? (mass for isotopes, number of neutrons, number of protons, number of valence electrons) 20. The number of neutrons in an atom can be found by (adding the atomic number to the mass number, adding the mass number to the number of electrons, subtracting the atomic number from the mass number, subtracting the mass number from the atomic number) Questions 21 and 22 refer to an atom having a mass number of 28 and an atomic number of 13. 21. How many electrons are present in the atom? (13, 15, 28, 41) 22. The number of neutrons present in the atom is (3, 14, 15, 28) 23. A neutral aluminum atom, with a mass number of 27, contains 3 valence electrons in the third energy level. How many electrons, protons, neutrons does the atom contain? 5 electrons, 13 protons, 14 neutrons 11 electrons, 13 protons, 27 neutrons 13 electrons, 13 protons, 14 neutrons 14 electrons, 14 protons, 13 neutrons 24. An atom of which of the following elements contains 27 electrons, 27 protons, and 33 neutrons? (As-33, Co-60, Fr-87, Xe 54) 25. In which of the following ways are isotopes of an element the same? (in atomic number, in atomic mass, in mass number, in number of neutrons) 26. Helium, a nonmetal, is a (good conductor of electricity, solid, poor conductor of heat, lustrous substance) 27. The mass of one proton is equal to (one atomic mass unit- amu, the mass of one electron, one gram, the mass of one carbon atom) 28. The atomic mass of an element is (#of protons and electrons; # protons and neutrons; an average of the mass of an electron, proton, and neutron; an average of the mass numbers of the naturally occurring isotopes) 29. The periodic table indicates that the atomic mass of Gold (Au), is (79, 118,196.97, 175.97) 30. Which of the following is a nonmetal? (Lead, Sodium, Titanium, Lithium, Fluorine) 31. In the isotope 92238U,the subscript 92 refers to the (atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, valence electron, number of neutrons). 32. A horizontal row on the periodic table is called? (a family, an order, a period, a column) 33. Which group reacts readily with the alkali metals to form salts? (halogens, noble gases, inert group, alkaline earth metals, rare earth metals). 34. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? (Family IIA, Group 2, Group 1, Both A and B) 35. Which of the following describes the alkali metals? (2 valence electrons, sometimes found in a free state, never found in a free state, noble or inert, dark red in color) 36. The mass of one electron equals (1 AMU, 1 gram, 1 atomic number, an insignificant amount) 37. List the energy levels of an atom from the inside to the outside. (J, K, L, M or K, L, M, N or N, M, L, K or L, M, N, O or M, N,O ,K). 38. Which of the following best describes the Group VIIIA elements? (2 valence electrons, sometimes found in a free state, never found in a free state, noble or inert, form salts). 39. A metalloid has properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. Which elements would be metalloids? (Si, Ge, Sb or Ni, Ag, Hg or Kr, Xe, Rn, or Li, Na, K or H, Li, Na). 40. The word atom comes from the Greek word meaning what? (proton, infinite, small, indivisible, smallest part). 41. The outermost energy level (except for the K level) can hold a maximum of how many electrons? (8, 2, 16, 18, 32) Answer the following on your own paper. 1. Draw a Bohr model for the element Potassium 2. List the properties of metals and nonmetals. 3. Describe Dalton’s, Thomson’s, and Bohr’s atomic models. 4. Describe the organization of the periodic table. 5. Discuss the relationship between the terms atomic weight (mass), mass number, and isotope.