Chap 4 Review with answers
... When scientists wanted to find out what an atom was, they were not able to look directly at what the atom was made of. They had to make inferences from the results of many different experiments. It was like trying to describe a picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small portions vis ...
... When scientists wanted to find out what an atom was, they were not able to look directly at what the atom was made of. They had to make inferences from the results of many different experiments. It was like trying to describe a picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small portions vis ...
Atomic
... • Electrons are much smaller than protons (2000 times smaller). • Electrons move around the nucleus very quickly. Scientists have found that it is not possible to determine the exact position of any single electron in an atom because they are moving too fast. This is why we picture electrons as a cl ...
... • Electrons are much smaller than protons (2000 times smaller). • Electrons move around the nucleus very quickly. Scientists have found that it is not possible to determine the exact position of any single electron in an atom because they are moving too fast. This is why we picture electrons as a cl ...
Density
... increase in reactivity left and down. • Nonmetals become more reactive up and to the right. • Most reactive metal is? Fr • Most reactive nonmetal is?F ...
... increase in reactivity left and down. • Nonmetals become more reactive up and to the right. • Most reactive metal is? Fr • Most reactive nonmetal is?F ...
Study Guide Chapters 4
... Explain what makes elements and isotopes different from each other and the same Construct and understand chemical (shorthand) notation for isotopes of elements ...
... Explain what makes elements and isotopes different from each other and the same Construct and understand chemical (shorthand) notation for isotopes of elements ...
Chem 111 Summer 2003 Exam I Whelan Some Useful And Not So
... Metal, Non Metal, Halide, Noble Gas, Alkali Metal, Alkali Earth Metal, Transition Metal, Lanthanide or Actinide. ...
... Metal, Non Metal, Halide, Noble Gas, Alkali Metal, Alkali Earth Metal, Transition Metal, Lanthanide or Actinide. ...
Chapter 10 - MrsDoughertys
... I will post a pdf of the overhead notes on the wiki this afternoon. For now, make sure you copy what I write so that if you have questions you can come see me. ...
... I will post a pdf of the overhead notes on the wiki this afternoon. For now, make sure you copy what I write so that if you have questions you can come see me. ...
Match the person / institution with the concept / discovery
... containing positive protons and neutral neutrons. The behavior of each electron is described in terms of probabilities that are used to identify a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron of that energy. b. Negative electrons are found outside a small, dense, massi ...
... containing positive protons and neutral neutrons. The behavior of each electron is described in terms of probabilities that are used to identify a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron of that energy. b. Negative electrons are found outside a small, dense, massi ...
SPS1: Students will investigate our current understanding of the
... Just as matter is conserved, so is energy. The law of conservation of _ENERGY__ states that energy, like matter, cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be changed from one form of energy to another. Energy takes many forms in the world around us. Each form of energy can be converted to and fro ...
... Just as matter is conserved, so is energy. The law of conservation of _ENERGY__ states that energy, like matter, cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be changed from one form of energy to another. Energy takes many forms in the world around us. Each form of energy can be converted to and fro ...
word doc (perfect formatting)
... 1) Represents an atom that is in an excited state 2) Represents an atom that is a noble gas 3) Represents an atom that is a transition metal 4) Represents an atom of an alkali earth metal Questions 5-8 refer to the following descriptions of bonding in different types of solids. a) Lattice of positiv ...
... 1) Represents an atom that is in an excited state 2) Represents an atom that is a noble gas 3) Represents an atom that is a transition metal 4) Represents an atom of an alkali earth metal Questions 5-8 refer to the following descriptions of bonding in different types of solids. a) Lattice of positiv ...
α C =
... Radioactive decay chains The product of disintegration may also be unstable (daughter nuclide) and undergoes further changes. It is possible for a nucleus to undergo a whole series of changes, resulting in radioactive decay chains. There are three natural decay chains: radium, actinium and thorium. ...
... Radioactive decay chains The product of disintegration may also be unstable (daughter nuclide) and undergoes further changes. It is possible for a nucleus to undergo a whole series of changes, resulting in radioactive decay chains. There are three natural decay chains: radium, actinium and thorium. ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... 5. Atomic MASS NUMBER is TOTAL number of _____________ plus ______________ in the NUCLEUS of a specific ATOM a. (e.g.) silver [__] (period 5; group 11) proton count = ____; neutron count = 61 = _____ u argon [__] (period 3; group 18) proton count = ____; neutron count = 22 = _____ u arsenic [__] ( ...
... 5. Atomic MASS NUMBER is TOTAL number of _____________ plus ______________ in the NUCLEUS of a specific ATOM a. (e.g.) silver [__] (period 5; group 11) proton count = ____; neutron count = 61 = _____ u argon [__] (period 3; group 18) proton count = ____; neutron count = 22 = _____ u arsenic [__] ( ...
AS specification - word format File
... existence of quantum shells and the group to which the element belongs ii an understanding that the first ionization energy of successive elements provides evidence for electron sub-shells f describe the shapes of electron density plots (or maps) for s and p orbitals g predict the electronic structu ...
... existence of quantum shells and the group to which the element belongs ii an understanding that the first ionization energy of successive elements provides evidence for electron sub-shells f describe the shapes of electron density plots (or maps) for s and p orbitals g predict the electronic structu ...
Atomic - My CCSD
... If you lose an electron you have a positive ion. Magnesium (Mg) can loose 2 electrons making it a positive ionwritten as:Mg2+ O will gain 2 electrons making it a negative ion. It is written as ...
... If you lose an electron you have a positive ion. Magnesium (Mg) can loose 2 electrons making it a positive ionwritten as:Mg2+ O will gain 2 electrons making it a negative ion. It is written as ...
The Begenius School of Atom Model Drawing
... while the red dot around the outside represents an instance of the electron. Imagine, as the electron moves it leaves a trace of where it was. This collection of traces quickly begins to resemble a cloud. ...
... while the red dot around the outside represents an instance of the electron. Imagine, as the electron moves it leaves a trace of where it was. This collection of traces quickly begins to resemble a cloud. ...
chemical reaction
... (aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water, exists as ions) ↓ - a precipitate has formed ...
... (aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water, exists as ions) ↓ - a precipitate has formed ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
Erin Connors 12/14/10 Chemistry Mrs. Galfunt Atomic Structure
... 8. The atomic 3 is the # of _______ 9. The atomic # is _______ to each element 10. The mass # is the # of ____________ 11. ______________ is the general name for the 2 particles found in the nucleus (_______ & _______) 12. The mass # is written to the ______________ corner of an element’s __________ ...
... 8. The atomic 3 is the # of _______ 9. The atomic # is _______ to each element 10. The mass # is the # of ____________ 11. ______________ is the general name for the 2 particles found in the nucleus (_______ & _______) 12. The mass # is written to the ______________ corner of an element’s __________ ...
The Atom - South Dade Senior High
... • JJ Thompson discovered one day that he two separate samples of neon gas, the same element, but they had different masses, how could this be? • The answer again is isotopes, if the number of neutrons is different the mass will be as well. ...
... • JJ Thompson discovered one day that he two separate samples of neon gas, the same element, but they had different masses, how could this be? • The answer again is isotopes, if the number of neutrons is different the mass will be as well. ...
atoms.
... that make them up. • Nanotechnology (making products that are atom-size) is being used to make microsubmarines which will eventually be able to travel in our bodies to detect health problems. ...
... that make them up. • Nanotechnology (making products that are atom-size) is being used to make microsubmarines which will eventually be able to travel in our bodies to detect health problems. ...
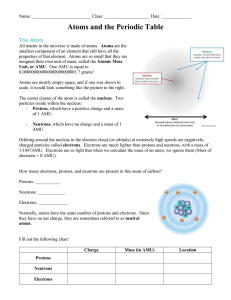
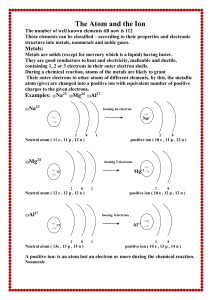
The Atom and the Ion
... liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells. Nonmetals atoms are likely to gain el ...
... liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells. Nonmetals atoms are likely to gain el ...
BS5-Ch 2.
... the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. • cements the idea that atoms react as complete (whole) particles. • chemical formulas indicate whole numbers of atoms- not fractions ...
... the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. • cements the idea that atoms react as complete (whole) particles. • chemical formulas indicate whole numbers of atoms- not fractions ...
Atoms
... • if you know the mass number and the atomic number you can calculate the neutrons. Mass Number – Atomic Number = Neutrons ***An element’s average atomic mass refers to the weighted average of all the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element! *** Atomic Masses The mass of a si ...
... • if you know the mass number and the atomic number you can calculate the neutrons. Mass Number – Atomic Number = Neutrons ***An element’s average atomic mass refers to the weighted average of all the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element! *** Atomic Masses The mass of a si ...
ATOMIC THEORY Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory
... 1808 based on the following: • Democritus’ atom • Law of conservation of mass • Law of definite proportions • Law of multiple proportions ...
... 1808 based on the following: • Democritus’ atom • Law of conservation of mass • Law of definite proportions • Law of multiple proportions ...
Matter and Atoms Notes
... Atoms are everywhere and make up everything (including what we breathe and empty spaces)! Weird that we (and our coffins) break down when we die (don’t actually disappear-atoms that make us up go help other things like plants grow). We can’t destroy atoms…mind blown (or make them). Weird that everyt ...
... Atoms are everywhere and make up everything (including what we breathe and empty spaces)! Weird that we (and our coffins) break down when we die (don’t actually disappear-atoms that make us up go help other things like plants grow). We can’t destroy atoms…mind blown (or make them). Weird that everyt ...
Chapter 4
... All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg2+. All sulfates are soluble except those containing ...
... All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg2+. All sulfates are soluble except those containing ...