
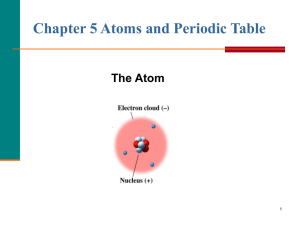
The Atom
... Rutherford’s model for the atom was appealing. It was simple. It was based on the well known electric force. It was consistent with all known experimental evidence. It had one flaw however that led to its demise but opened up a grand new era in physics. We know from Maxwell’s equations that an accel ...
... Rutherford’s model for the atom was appealing. It was simple. It was based on the well known electric force. It was consistent with all known experimental evidence. It had one flaw however that led to its demise but opened up a grand new era in physics. We know from Maxwell’s equations that an accel ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the information below. In the early 1800s, John Dalton proposed an atomic theory that was based on experimental observations made by several scientists. Three concepts of Dalto ...
... may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the information below. In the early 1800s, John Dalton proposed an atomic theory that was based on experimental observations made by several scientists. Three concepts of Dalto ...
Basic Chemistry – Terminology and Reactions
... A radical is a group of atoms of the same or different elements that behaves as a single unit with a positive or negative charge. VALENCY The valency of an atom or ion is the number of electrons it shares, loses or gains in a chemical reaction to become stable i.e. the number of bonds it forms w ...
... A radical is a group of atoms of the same or different elements that behaves as a single unit with a positive or negative charge. VALENCY The valency of an atom or ion is the number of electrons it shares, loses or gains in a chemical reaction to become stable i.e. the number of bonds it forms w ...
Unit 10 Student Packet PS and FRQs
... Later, after searching in vain for a positively charged particle nearly the same size as an electron, Rutherford’s experiments led him to the fact that the positively charged particle he was searching for, eventually named the proton, is 1840 times more massive than the electron even though it carri ...
... Later, after searching in vain for a positively charged particle nearly the same size as an electron, Rutherford’s experiments led him to the fact that the positively charged particle he was searching for, eventually named the proton, is 1840 times more massive than the electron even though it carri ...
23.32 KB - KFUPM Resources v3
... electrons fall from higher energy levels to lower energy levels. the atoms condense from a gas to a liquid. electrons jump from lower energy levels to higher energy levels. they melt to form a liquid. electrons move in their circular orbit. ...
... electrons fall from higher energy levels to lower energy levels. the atoms condense from a gas to a liquid. electrons jump from lower energy levels to higher energy levels. they melt to form a liquid. electrons move in their circular orbit. ...
ch2 - sscyr11chemistry
... Atoms are electrically neutral. The positive charge on one proton balances the negative charge on one electron. Therefore, for electrical neutrality, there must be equal numbers of protons and electrons. Q26. Using the element bromine as an example, explain why elements are best identified by their ...
... Atoms are electrically neutral. The positive charge on one proton balances the negative charge on one electron. Therefore, for electrical neutrality, there must be equal numbers of protons and electrons. Q26. Using the element bromine as an example, explain why elements are best identified by their ...
CHAPTER 4 TEST
... a.The nucleus is made of protons and neutrons and has a negative charge. b.The nucleus is made of protons and neutrons and has a positive charge. c.The nucleus is made of electrons and has a positive charge. d.The nucleus is made of electrons and has a negative charge. _____17. An element’s atomic n ...
... a.The nucleus is made of protons and neutrons and has a negative charge. b.The nucleus is made of protons and neutrons and has a positive charge. c.The nucleus is made of electrons and has a positive charge. d.The nucleus is made of electrons and has a negative charge. _____17. An element’s atomic n ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... *Atoms of the same substance are exactly alike, atoms of different atoms are different. *Atoms join with other atoms of other substances to make new substances. Dalton's theory was proved wrong when new information was discovered and Dalton's theory could not explain it. The atomic theory has evolve ...
... *Atoms of the same substance are exactly alike, atoms of different atoms are different. *Atoms join with other atoms of other substances to make new substances. Dalton's theory was proved wrong when new information was discovered and Dalton's theory could not explain it. The atomic theory has evolve ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Powerpoint
... Commonly used graphite and platinum electrodes are inert and have no effect on the preference of ion discharge. But some may. • Mercury electrode(汞電極) If graphite or platinum electrodes are used in the electrolysis of concentrated NaCl solution, only H+ is discharged at the cathode. But if mercury e ...
... Commonly used graphite and platinum electrodes are inert and have no effect on the preference of ion discharge. But some may. • Mercury electrode(汞電極) If graphite or platinum electrodes are used in the electrolysis of concentrated NaCl solution, only H+ is discharged at the cathode. But if mercury e ...
internal geodynamics - Ninova
... charges were of the atoms of individual elements in the periodic table of Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (1834-1907). Mendeleev and his predecessors who attempted to find a sort of periodic relationship between successive elements, used atomic weights. The concept of atomic weight had been introduced by ...
... charges were of the atoms of individual elements in the periodic table of Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (1834-1907). Mendeleev and his predecessors who attempted to find a sort of periodic relationship between successive elements, used atomic weights. The concept of atomic weight had been introduced by ...
Energy - Winona State University
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation Change in enthalpy that accompanies the formation of one mole of substance from its elements, with all substances in their standard states. ...
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation Change in enthalpy that accompanies the formation of one mole of substance from its elements, with all substances in their standard states. ...
C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
Ionic bonding
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
C2 revision slides V3 + questions + MS
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
Ionic bonding - Animated Science
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
... • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and elec ...
atom
... these shells helps reveal how an atom reacts chemically, that is, how it combines with other atoms to form molecules. Because a neutral atom has the same number of electrons in orbit as protons in the nucleus, the number of protons ultimately determines the chemical behavior of an atom. The number o ...
... these shells helps reveal how an atom reacts chemically, that is, how it combines with other atoms to form molecules. Because a neutral atom has the same number of electrons in orbit as protons in the nucleus, the number of protons ultimately determines the chemical behavior of an atom. The number o ...
Sample Pages
... 3. All atoms of a given element are distinct from all atoms of any other element. The mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of one element are different from the mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of any other element. 4. Chemical compounds form when atoms combine in whole-n ...
... 3. All atoms of a given element are distinct from all atoms of any other element. The mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of one element are different from the mass, size, and chemical properties of the atoms of any other element. 4. Chemical compounds form when atoms combine in whole-n ...
Types of reactions: redox reactions
... A redox reaction is one involving oxidation and reduction, where there is always a change in the oxidation numbers of the elements involved. ...
... A redox reaction is one involving oxidation and reduction, where there is always a change in the oxidation numbers of the elements involved. ...
Chapter 4 powerpoint
... the Bohr model to show the number of electrons in each orbit around the nucleus. • Why: Bohr was trying to show why the negative electrons were not sucked into the nucleus of the atom. ...
... the Bohr model to show the number of electrons in each orbit around the nucleus. • Why: Bohr was trying to show why the negative electrons were not sucked into the nucleus of the atom. ...
Chemistry Chapter 4 (Due October 24) [Test
... c. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged. d. Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. ____ 38. Why do chemists use relative masses of atoms compared to a reference isotope rather than the actual masses of the atoms? a. The actual mass of an electron is very large compared to the actual ...
... c. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged. d. Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. ____ 38. Why do chemists use relative masses of atoms compared to a reference isotope rather than the actual masses of the atoms? a. The actual mass of an electron is very large compared to the actual ...
General Concepts
... If you are not given this symbol with the mass number, you can still determine the mass number for the most abundant isotopic form for that atom. For example, if you look on the periodic table for Carbon, you will see a value underneath its symbol - the RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS of 12.011. This mass is ...
... If you are not given this symbol with the mass number, you can still determine the mass number for the most abundant isotopic form for that atom. For example, if you look on the periodic table for Carbon, you will see a value underneath its symbol - the RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS of 12.011. This mass is ...













![C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000092833_1-97fb33725e7f1ef12029ed42751d3dca-300x300.png)








