FREE Sample Here
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 9. group – ionization energy decreases going down due to increasing number of energy levels, which are shielding the increasing nuclear charge, resulting in less attraction for the valence electrons period – ionization energy increases moving right due to increasing nuclear charge, while the number ...
... 9. group – ionization energy decreases going down due to increasing number of energy levels, which are shielding the increasing nuclear charge, resulting in less attraction for the valence electrons period – ionization energy increases moving right due to increasing nuclear charge, while the number ...
name chemistry final review
... What does Boyle’s Law state? Its formula? What 2 factors must be held constant for this law to be true? Pressure and volume are inversely related to each other when temperature and the number of m ...
... What does Boyle’s Law state? Its formula? What 2 factors must be held constant for this law to be true? Pressure and volume are inversely related to each other when temperature and the number of m ...
Chemistry I Accelerated StudyGuideline
... 3. Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers 4. Radiation consisting of a high speed Helium nuclei 5. Center of the atom 6. Subatomic particle with no charge 7. Element with a mass number of 19.0 8. A mass __________________, a device used to determine atomic masses. (If you can’t ...
... 3. Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers 4. Radiation consisting of a high speed Helium nuclei 5. Center of the atom 6. Subatomic particle with no charge 7. Element with a mass number of 19.0 8. A mass __________________, a device used to determine atomic masses. (If you can’t ...
A) electrons B) neutrons C) positrons D) protons 1. According to the
... C) most of the atom is empty space ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus ® the atom is a hard sphere D) most of the atom is empty space ® the atom is a hard sphere ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus Which electron configuration represents the electrons in an atom of Ga in ...
... C) most of the atom is empty space ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus ® the atom is a hard sphere D) most of the atom is empty space ® the atom is a hard sphere ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus Which electron configuration represents the electrons in an atom of Ga in ...
Test 1
... Einstein's Law of Relativity that no object with mass can travel at the speed of light. Dalton's Atomic Theory that matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. ...
... Einstein's Law of Relativity that no object with mass can travel at the speed of light. Dalton's Atomic Theory that matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... • 4. The formula can tell us what atoms a compound is made of but does not reveal how they are connected. ...
... • 4. The formula can tell us what atoms a compound is made of but does not reveal how they are connected. ...
Kimya
... • All other masses are measured relative to this carbon-12 standard. For example, suppose we do an experiment and find that the isotope bromine-81 has a mass that is 6.743 times that of carbon-12. Then the mass of bromine-81 would be given by ...
... • All other masses are measured relative to this carbon-12 standard. For example, suppose we do an experiment and find that the isotope bromine-81 has a mass that is 6.743 times that of carbon-12. Then the mass of bromine-81 would be given by ...
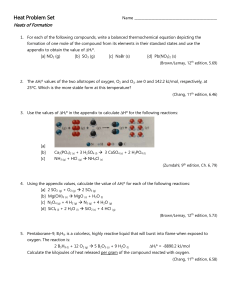
Heats of Formation WS
... [a] Write a balanced chemical equation for the combustion of 1 mol of C8H18. [b] Write a balanced equation for the formation of C8H18 from its elements. [c] By using the information in this problem and appendix data, calculate the ∆Hfº for ...
... [a] Write a balanced chemical equation for the combustion of 1 mol of C8H18. [b] Write a balanced equation for the formation of C8H18 from its elements. [c] By using the information in this problem and appendix data, calculate the ∆Hfº for ...
atomic theory - Scorpion Science with Mrs. Page
... …grew as a series of models that developed from experimental evidence. As more evidence was collected, the theory and models were revised. ...
... …grew as a series of models that developed from experimental evidence. As more evidence was collected, the theory and models were revised. ...
bonding and geometry
... FORCES IN A MOLECULE London Dispersion Forces Electrons are in constant motion around a nucleus At any given time there might be more electrons on one side of an atom than on the other For a split second, the side with more electrons is negative, and the side with less electrons is positive ...
... FORCES IN A MOLECULE London Dispersion Forces Electrons are in constant motion around a nucleus At any given time there might be more electrons on one side of an atom than on the other For a split second, the side with more electrons is negative, and the side with less electrons is positive ...
models_of_the_atom task
... Clouds of mystery Bohr’s sharply defined electron shells have been superseded by fuzzy electron ‘clouds’ which can be seen with an electron microscope. It is now known that electrons behave as waves, as well as like particles. An electron is most likely to be found where the electron ‘cloud’ is dens ...
... Clouds of mystery Bohr’s sharply defined electron shells have been superseded by fuzzy electron ‘clouds’ which can be seen with an electron microscope. It is now known that electrons behave as waves, as well as like particles. An electron is most likely to be found where the electron ‘cloud’ is dens ...
Chapter 4 Greek Idea Thomson`s Model Rutherford`s Model Bohr`s
... move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrodinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom A ...
... move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrodinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom A ...
Chapter 6:Electronic Structure of Atoms
... does not behave like a wave but rather as if it were a stream of tiny energy packets. Each energy packet, called a photon behaves like a tiny particle. • Extending Planck’s quantum theory, Einstein deduced that each photon must have an energy equal to Planck’s constant times the frequency of the lig ...
... does not behave like a wave but rather as if it were a stream of tiny energy packets. Each energy packet, called a photon behaves like a tiny particle. • Extending Planck’s quantum theory, Einstein deduced that each photon must have an energy equal to Planck’s constant times the frequency of the lig ...
Structure of the Atom
... BRIGHT LINE SPECTRA are produced when “electrons in the EXCITED STATE” fall back to lower energy levels of the GROUND STATE. Unlike the continuous spectrum of sunlight, only certain colors will be present in the BRIGHT LINE SPECTRA. The BRIGHT LINE SPECTRUM is like a “fingerprint” of the element tha ...
... BRIGHT LINE SPECTRA are produced when “electrons in the EXCITED STATE” fall back to lower energy levels of the GROUND STATE. Unlike the continuous spectrum of sunlight, only certain colors will be present in the BRIGHT LINE SPECTRA. The BRIGHT LINE SPECTRUM is like a “fingerprint” of the element tha ...
Unit 4 Day 1 Intro to Atom
... The number of protons “defines” the element. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton carbon atoms always contain 6 protons ...
... The number of protons “defines” the element. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton carbon atoms always contain 6 protons ...
Nuclear Physics Sections 10.1-10.7
... • To get to 4 cts/min • 16cts => (t1/2) 8 cts => (t1/2) 4 cts or 2 half-lives • 14C has a half life of 5730 yrs • 2 x 5730 = 11,460 yrs • The scroll is between 11,000 and 12,000 years old. ...
... • To get to 4 cts/min • 16cts => (t1/2) 8 cts => (t1/2) 4 cts or 2 half-lives • 14C has a half life of 5730 yrs • 2 x 5730 = 11,460 yrs • The scroll is between 11,000 and 12,000 years old. ...
Chapter Two:
... Figure 2.7 A Cathode-ray tube. The fast-moving electrons excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the electrodes. The green color in the photo is due to the response of the screen (coated with zinc sulfide) to the electron beam. ...
... Figure 2.7 A Cathode-ray tube. The fast-moving electrons excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the electrodes. The green color in the photo is due to the response of the screen (coated with zinc sulfide) to the electron beam. ...
Chemistry Final Review 2017 1. List a set of elements
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...