Counting Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... •Masses of atoms expressed in grams are very small. For example, an atom of oxygen-16 has a mass of 2.657 x 10-23 g. •For simplicity, scientists use the atomic mass unit (amu) to express the mass of atoms. 1 amu is 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. •The atomic mass of any nuclide is determined by c ...
... •Masses of atoms expressed in grams are very small. For example, an atom of oxygen-16 has a mass of 2.657 x 10-23 g. •For simplicity, scientists use the atomic mass unit (amu) to express the mass of atoms. 1 amu is 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. •The atomic mass of any nuclide is determined by c ...
atom
... Discovery of the Electron J. J. Thomson used an apparatus similar to the one shown on the next slide, a cathode ray tube. He discovered that the particles that make up the cathode ray are negative and are part of all matter. This finding is illustrated on the following slides. As a result, Thomson ...
... Discovery of the Electron J. J. Thomson used an apparatus similar to the one shown on the next slide, a cathode ray tube. He discovered that the particles that make up the cathode ray are negative and are part of all matter. This finding is illustrated on the following slides. As a result, Thomson ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... Democritus was an ancient Greek philosopher who lived from 460 - 370 B.C. What did Democritus conclude about cutting matter in half? There was a limit to how far you could divide matter. You would eventually end up with a piece of matter that could not be cut. ...
... Democritus was an ancient Greek philosopher who lived from 460 - 370 B.C. What did Democritus conclude about cutting matter in half? There was a limit to how far you could divide matter. You would eventually end up with a piece of matter that could not be cut. ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... Democritus was an ancient Greek philosopher who lived from 460 - 370 B.C. What did Democritus conclude about cutting matter in half? There was a limit to how far you could divide matter. You would eventually end up with a piece of matter that could not be cut. ...
... Democritus was an ancient Greek philosopher who lived from 460 - 370 B.C. What did Democritus conclude about cutting matter in half? There was a limit to how far you could divide matter. You would eventually end up with a piece of matter that could not be cut. ...
普通化学 (全英文) 教学大纲
... 2.1.Atomic structure, Isotope 2.2.The periodic table (a).Main groups, metals and non-metals (b).s-block, p-block, d-block elements 2.3.Electron cloud and Atomic orbitals 2.4.Electron configurations (a).4 quantum numbers: n, l, m, ms (b).Pictures of the orbitals: s, px, py, pz (c).How to fill electro ...
... 2.1.Atomic structure, Isotope 2.2.The periodic table (a).Main groups, metals and non-metals (b).s-block, p-block, d-block elements 2.3.Electron cloud and Atomic orbitals 2.4.Electron configurations (a).4 quantum numbers: n, l, m, ms (b).Pictures of the orbitals: s, px, py, pz (c).How to fill electro ...
iClicker PARTICIPATION Question: Development of the Modern
... 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
... 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
Lecture - 1
... neutrons). Such elements are called Isotopes, the lightest of them being 21D (Deuterium) and 31T (Tritium) being the isotopes of 11H (Hydrogen) as shown in ...
... neutrons). Such elements are called Isotopes, the lightest of them being 21D (Deuterium) and 31T (Tritium) being the isotopes of 11H (Hydrogen) as shown in ...
Unit 6 Regents Level
... i) Electrons may _______________________ and temporarily move to a _____________ energy level. (1) This could be due to _____________________________________________ (2) This unstable state is called the ______________________________ ii) After the electron quickly returns to the ___________________ ...
... i) Electrons may _______________________ and temporarily move to a _____________ energy level. (1) This could be due to _____________________________________________ (2) This unstable state is called the ______________________________ ii) After the electron quickly returns to the ___________________ ...
Atomic Structure Atomic Structure
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, each of which is uniquely essential to the structure and function of the atom. The core of the atom is the nucleus, which consists of protons and neutrons. Most of the mass of an atom (about 99.9 percent) is in the nucleus, even though the nucl ...
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, each of which is uniquely essential to the structure and function of the atom. The core of the atom is the nucleus, which consists of protons and neutrons. Most of the mass of an atom (about 99.9 percent) is in the nucleus, even though the nucl ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
Chapter 2
... of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing ...
... of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing ...
Atomic Mass - MrKanesSciencePage
... Mass Number and Atomic Mass • Atomic Mass - The average mass of all the different isotopes of an element. (Usually not a whole number) • Mass Number – The sum of the number of protons and neutrons. It is usually equal to the rounded atomic mass and is always expressed as a whole number. ...
... Mass Number and Atomic Mass • Atomic Mass - The average mass of all the different isotopes of an element. (Usually not a whole number) • Mass Number – The sum of the number of protons and neutrons. It is usually equal to the rounded atomic mass and is always expressed as a whole number. ...
File
... atomic emission spectra; Bohr model of the hydrogen atom including explanation of H line spectrum and orbits, electron cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts o ...
... atomic emission spectra; Bohr model of the hydrogen atom including explanation of H line spectrum and orbits, electron cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts o ...
Preview Sample 1
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
Simple View of Atomic Structure - Chemwiki
... The atomic number is the number of protons (9); the mass number counts protons + neutrons (19). If there are 9 protons, there must be 10 neutrons adding up to a total of 19 nucleons in the atom. The atomic number is tied to the position of the element in the periodic table; the number of protons the ...
... The atomic number is the number of protons (9); the mass number counts protons + neutrons (19). If there are 9 protons, there must be 10 neutrons adding up to a total of 19 nucleons in the atom. The atomic number is tied to the position of the element in the periodic table; the number of protons the ...
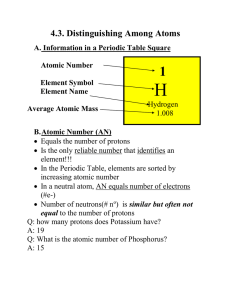
Notes 4.3 filled in
... B. Atomic Number (AN) Equals the number of protons Is the only reliable number that identifies an element!!! In the Periodic Table, elements are sorted by increasing atomic number In a neutral atom, AN equals number of electrons (#e-) Number of neutrons(# no) is similar but often not equal ...
... B. Atomic Number (AN) Equals the number of protons Is the only reliable number that identifies an element!!! In the Periodic Table, elements are sorted by increasing atomic number In a neutral atom, AN equals number of electrons (#e-) Number of neutrons(# no) is similar but often not equal ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... 1. Balance the different types of atoms one at a time 2. First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. (start with the largest ...
... 1. Balance the different types of atoms one at a time 2. First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. (start with the largest ...
Development of Atomic Theory Paragraph
... in his law of __(3)__, that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Then __(4)__ proposed, in his law of __(5)__, that the ratio of the masses of elements in any given compound is always the same. The law of __(6)__, proposed soon after, states that the masses of one element that combine with a fixed ...
... in his law of __(3)__, that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Then __(4)__ proposed, in his law of __(5)__, that the ratio of the masses of elements in any given compound is always the same. The law of __(6)__, proposed soon after, states that the masses of one element that combine with a fixed ...
Odd Number of Electrons
... 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend to be chemically unreactive. 5. Units are measured in kJ/mo1 6. A mol is a che ...
... 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend to be chemically unreactive. 5. Units are measured in kJ/mo1 6. A mol is a che ...
Introductory Chemistry Test Review
... 25. In the laboratory, potassium chlorate will decompose when heated to form potassium chloride and oxygen gas according to the following equation. Calculate how much oxygen in grams is produced when 35.0 grams of potassium chlorate decomposes. 2 KClO3(s) ...
... 25. In the laboratory, potassium chlorate will decompose when heated to form potassium chloride and oxygen gas according to the following equation. Calculate how much oxygen in grams is produced when 35.0 grams of potassium chlorate decomposes. 2 KClO3(s) ...
Chemistry I Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... D. Rutherford’s model did not place electrons in energy levels, while Bohr’s model did. E. Rutherford’s model showed the atom to consist of low density positively charged matter with tiny negatively charged particles embedded in it, while Bohr’s model showed the nucleus consisting of protons and neu ...
... D. Rutherford’s model did not place electrons in energy levels, while Bohr’s model did. E. Rutherford’s model showed the atom to consist of low density positively charged matter with tiny negatively charged particles embedded in it, while Bohr’s model showed the nucleus consisting of protons and neu ...