Recherches sur la théorie des quanta
... Postulate of Stationary States : the Hydrogen atom can exist, without radiating energy, in any one of a discrete set of orbits of fixed energy Frequency Postulate : the Hydrogen atom can emit or absorb a quantity of energy only when the electron changes from one stationary state into another. This a ...
... Postulate of Stationary States : the Hydrogen atom can exist, without radiating energy, in any one of a discrete set of orbits of fixed energy Frequency Postulate : the Hydrogen atom can emit or absorb a quantity of energy only when the electron changes from one stationary state into another. This a ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Introduction Modern concept of an
... Democritus studied the nature of matter and the constituents of all the substances. In 1808 John Dalton put forward atomic theory to explain the laws of chemical combination. According to him, an atom is the smallest unit of matter which takes part in a chemical reaction. He considered that atoms ar ...
... Democritus studied the nature of matter and the constituents of all the substances. In 1808 John Dalton put forward atomic theory to explain the laws of chemical combination. According to him, an atom is the smallest unit of matter which takes part in a chemical reaction. He considered that atoms ar ...
Chem Unit2 template - Region 7 Professional Development
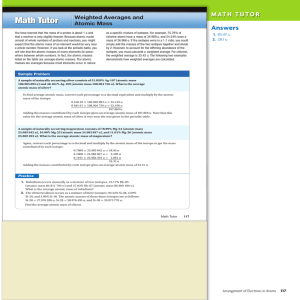
... • Identify isotope using mass number and atomic number and relate to number of protons, neutrons and electrons. • Differentiate average atomic mass of an element from the actual isotopic mass and mass number of specific isotopes. (Use example calculations to determine average atomic mass of atoms fr ...
... • Identify isotope using mass number and atomic number and relate to number of protons, neutrons and electrons. • Differentiate average atomic mass of an element from the actual isotopic mass and mass number of specific isotopes. (Use example calculations to determine average atomic mass of atoms fr ...
Chapter 4 Review Answers
... • An orbital, a three-dimensional region around the nucleus, shows the region in space where an electron is most likely to be found. • The four quantum numbers that describe the properties of electrons in atomic orbitals are the principal quantum number, the angular momentum quantum number, the magn ...
... • An orbital, a three-dimensional region around the nucleus, shows the region in space where an electron is most likely to be found. • The four quantum numbers that describe the properties of electrons in atomic orbitals are the principal quantum number, the angular momentum quantum number, the magn ...
AQA C2 revision book
... held together by strong forces called covalent bonds, but there are only very weak forces between the molecules. This means: 1) They have low melting and boiling points (many are liquids or gases). 2) They tend to be soft and/or have little strength. 3) They do not conduct electricity Simple molecul ...
... held together by strong forces called covalent bonds, but there are only very weak forces between the molecules. This means: 1) They have low melting and boiling points (many are liquids or gases). 2) They tend to be soft and/or have little strength. 3) They do not conduct electricity Simple molecul ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 1) Chemical reactivity and ...
... descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 1) Chemical reactivity and ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.2 - reich
... • ___Mg + _2_HCl ___ H2+ __ MgCl2 • Notice: Mg is elemental on the left side, and Hydrogen is elemental on the right side. • The single lone element was displaced by a different lone element. ...
... • ___Mg + _2_HCl ___ H2+ __ MgCl2 • Notice: Mg is elemental on the left side, and Hydrogen is elemental on the right side. • The single lone element was displaced by a different lone element. ...
110 exam i material
... Metric metric conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English english conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English metric conversion factors are measured numbers and have a finite number of signi ...
... Metric metric conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English english conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English metric conversion factors are measured numbers and have a finite number of signi ...
presentation1-elements-atoms-and-isotopes
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their chemical reactions. This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. The uncharged neutrons make little difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and dens ...
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their chemical reactions. This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. The uncharged neutrons make little difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and dens ...
Name: _ Date: Period: ______ Page: ______ Atomic Structure and
... Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) was digging potatoes in a field in his native country of New Zealand when he received a letter from J. J. Thomson, informing him that he had been accepted as Thomson’s student at Cambridge University. Rutherford was honored to be selected to join this prestigious group ...
... Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) was digging potatoes in a field in his native country of New Zealand when he received a letter from J. J. Thomson, informing him that he had been accepted as Thomson’s student at Cambridge University. Rutherford was honored to be selected to join this prestigious group ...
BERKELEY HEIGHTS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... technology in developing the models of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr. (5.2 B/1-3; 5.6 A/1; 5.6 A/8; 8.2 A/3) 15. Apply the concepts of radioisotopes, fusion, fission and nuclear decay to understand a half-life, including how to predict the age of a fossil and determine nuclear waste hazards. ...
... technology in developing the models of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr. (5.2 B/1-3; 5.6 A/1; 5.6 A/8; 8.2 A/3) 15. Apply the concepts of radioisotopes, fusion, fission and nuclear decay to understand a half-life, including how to predict the age of a fossil and determine nuclear waste hazards. ...
The Chemistry of Life
... atoms of the same element combine it is called a molecule of that element. For example: two atoms of oxygen combine to form a molecule of oxygen gas O2. If two or more different atoms combine, they are said to form molecules of a compound. For example two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of ...
... atoms of the same element combine it is called a molecule of that element. For example: two atoms of oxygen combine to form a molecule of oxygen gas O2. If two or more different atoms combine, they are said to form molecules of a compound. For example two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of ...
Multivalent Ionic Compounds
... For positive ions, one electron dot is removed from the valence shell for each positive charge of the ion. For negative ions, one electron dot is added to each valence shell for each negative charge of the ion. Square brackets are placed around each ion to indicate transfer of electrons ...
... For positive ions, one electron dot is removed from the valence shell for each positive charge of the ion. For negative ions, one electron dot is added to each valence shell for each negative charge of the ion. Square brackets are placed around each ion to indicate transfer of electrons ...
Document
... This is indeed the mode of decay observed for carbon-14. (b) Xenon has an atomic number of 54. Thus, xenon-118 has 54 protons and 118 – 54 = 64 neutrons, giving it a neutron-to-proton ratio of According to Figure 21.2, stable nuclei in this region of the belt of stability have higher neutron-to-prot ...
... This is indeed the mode of decay observed for carbon-14. (b) Xenon has an atomic number of 54. Thus, xenon-118 has 54 protons and 118 – 54 = 64 neutrons, giving it a neutron-to-proton ratio of According to Figure 21.2, stable nuclei in this region of the belt of stability have higher neutron-to-prot ...
Oxidation
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers 1) The sum of the oxidation numbers will always equal the particle’s charge 2) The oxidation number for a neutral atom is always zero 3) Oxidation numbers for non–VOS metals depend on their group 4) Oxidation numbers for VOS metals are found based on anion 5) O ...
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers 1) The sum of the oxidation numbers will always equal the particle’s charge 2) The oxidation number for a neutral atom is always zero 3) Oxidation numbers for non–VOS metals depend on their group 4) Oxidation numbers for VOS metals are found based on anion 5) O ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... the reactants and products of a chemical reaction by their symbols or formulas Notice that the formula equation does not give information about the amounts of reactants and products. A formula equation meets two of the three requirements for a correct chemical equation; it represents facts and sho ...
... the reactants and products of a chemical reaction by their symbols or formulas Notice that the formula equation does not give information about the amounts of reactants and products. A formula equation meets two of the three requirements for a correct chemical equation; it represents facts and sho ...
Chapter 3
... 37. molecules consist of the same element with different numbers of atoms and chemical structure are called … A. ions. B. neutrons. C. allotropes. D. isotopes. 38. An atom of the isotope 16S-31 consists of how many protons, neutrons, and electrons? (p = proton, n = neutron, e = electron) A. 15 p, 1 ...
... 37. molecules consist of the same element with different numbers of atoms and chemical structure are called … A. ions. B. neutrons. C. allotropes. D. isotopes. 38. An atom of the isotope 16S-31 consists of how many protons, neutrons, and electrons? (p = proton, n = neutron, e = electron) A. 15 p, 1 ...
Unit 11: The Mole
... MOLAR MASS The molar mass of an element is the mass in grams of one mole of any pure substance. ...
... MOLAR MASS The molar mass of an element is the mass in grams of one mole of any pure substance. ...
Practice Exam 3
... ____ 24. All of the following statements concerning nuclei are true EXCEPT a. only hydrogen-1 and helium-3 have more protons than neutrons. b. from He to Ca, stable nuclei have roughly equal numbers of protons and neutrons. c. isotopes with a low neutron to proton ratio always decay by alpha particl ...
... ____ 24. All of the following statements concerning nuclei are true EXCEPT a. only hydrogen-1 and helium-3 have more protons than neutrons. b. from He to Ca, stable nuclei have roughly equal numbers of protons and neutrons. c. isotopes with a low neutron to proton ratio always decay by alpha particl ...
Determination of the Atomic Weight of Magnesium CHEM 101
... the balance. Other potential sources of experimental uncertainty are: the reaction might not be complete; if not enough time was allowed for total oxidation, less than complete oxidation of the magnesium might have, in part, reacted with nitrogen in the air (incorrect reaction); the magnesium oxide ...
... the balance. Other potential sources of experimental uncertainty are: the reaction might not be complete; if not enough time was allowed for total oxidation, less than complete oxidation of the magnesium might have, in part, reacted with nitrogen in the air (incorrect reaction); the magnesium oxide ...
File - Mr. J`s Chemistry 4U
... B- A list of elements where the most active element is placed at the top. C- A list of elements where the least active element is placed at the bottom. D- A list of elements arranged where each element listed can, in a chemical reaction, replace the elements listed below it but cannot replace the el ...
... B- A list of elements where the most active element is placed at the top. C- A list of elements where the least active element is placed at the bottom. D- A list of elements arranged where each element listed can, in a chemical reaction, replace the elements listed below it but cannot replace the el ...
Unit Review III
... __ 14) Which of the following particles has the smallest mass? a) proton b) neutron c) alpha particle d) electron __ 15) A pure substance whose atoms have all the same atomic number is a) a compound b) an element c) a radical d) a mixture __ 16) An atom containing 9 protons, 10 neutrons and 9 elect ...
... __ 14) Which of the following particles has the smallest mass? a) proton b) neutron c) alpha particle d) electron __ 15) A pure substance whose atoms have all the same atomic number is a) a compound b) an element c) a radical d) a mixture __ 16) An atom containing 9 protons, 10 neutrons and 9 elect ...