level 11 - Hlubek Piano Studio
... trill: alternation of two notes a second apart supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of the chord progression ii-V or I-V ...
... trill: alternation of two notes a second apart supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of the chord progression ii-V or I-V ...
Strand A - Core Knowledge UK
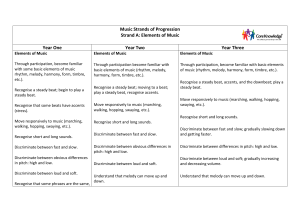
... Sing unaccompanied, accompanied, and in unison. Recognise verse and refrain. Recognise that musical notes have names. Recognise a scale as a series of notes. Sing the C major scale using ‘do re mi’ etc. Review the following notation: Crochet Minim Semi-breve Understand the following notation: ...
... Sing unaccompanied, accompanied, and in unison. Recognise verse and refrain. Recognise that musical notes have names. Recognise a scale as a series of notes. Sing the C major scale using ‘do re mi’ etc. Review the following notation: Crochet Minim Semi-breve Understand the following notation: ...
Psychology of Music Learning
... Also grouping – pitch, timbre, dynamic Also metrical – tension and release Also interpretive – notated duration vs. resulting duration after articulation style is applied ...
... Also grouping – pitch, timbre, dynamic Also metrical – tension and release Also interpretive – notated duration vs. resulting duration after articulation style is applied ...
Jɛnkuno Overview Phrase Duration
... the rapid motion that preceded them. The Jɛnkuno groove arises from this distinctive play between offbeats and onbeats. As is typical of Dagomba dance drumming in quaternary time, accentuation of the fourth pulse within beat one propels the rhythm forward with compelling drive. Meter Although I hav ...
... the rapid motion that preceded them. The Jɛnkuno groove arises from this distinctive play between offbeats and onbeats. As is typical of Dagomba dance drumming in quaternary time, accentuation of the fourth pulse within beat one propels the rhythm forward with compelling drive. Meter Although I hav ...
2014 Orchestra Curriculum Map Orchestra Curriculum Map
... types of orchestral repertoire and literature, plus the review of fundamentals of music and rehearsal technique all help the Orchestra members develop creative, interpretive and appreciative abilities. This group does considerable performing. Participation in all performances is required of all orch ...
... types of orchestral repertoire and literature, plus the review of fundamentals of music and rehearsal technique all help the Orchestra members develop creative, interpretive and appreciative abilities. This group does considerable performing. Participation in all performances is required of all orch ...
Elements of Music
... first movement of multimovement pieces, and is therefore more specifically referred to as sonata-allegro form or firstmovement form. Study of the sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition, and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the ...
... first movement of multimovement pieces, and is therefore more specifically referred to as sonata-allegro form or firstmovement form. Study of the sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition, and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the ...
Freshman Band Scale Checkoff/Final Exam Freshman Band Final
... You will need to know the following information for your band final: Identify the treble (G clef) _____ and the bass (F clef) ________ Name the notes of the treble clef lines (EGBDF) and spaces (FACE) Name the notes of the bass clef lines (GBDFA) and spaces (ACEG) Identify the staff, bar lin ...
... You will need to know the following information for your band final: Identify the treble (G clef) _____ and the bass (F clef) ________ Name the notes of the treble clef lines (EGBDF) and spaces (FACE) Name the notes of the bass clef lines (GBDFA) and spaces (ACEG) Identify the staff, bar lin ...
Musical Terms: Musicians use certain words and phrases (that may
... over time and through different cultures. The Octave is a special kind of interval that has a 2:1 frequency ratio. The two pitches that make up this interval can sound remarkably similar and have been referred to as having the quality of “auditory duplication”. Scales are the way pitches are organiz ...
... over time and through different cultures. The Octave is a special kind of interval that has a 2:1 frequency ratio. The two pitches that make up this interval can sound remarkably similar and have been referred to as having the quality of “auditory duplication”. Scales are the way pitches are organiz ...
Major Key Signatures
... Major Key Signatures Key signatures are symbols representing a scale/key. They tell us which accidentals are used throughout the composition. A key signatures tells a musician the majority of notes that a composer has used in the music. The chart below represents the key signatures for all 15 major ...
... Major Key Signatures Key signatures are symbols representing a scale/key. They tell us which accidentals are used throughout the composition. A key signatures tells a musician the majority of notes that a composer has used in the music. The chart below represents the key signatures for all 15 major ...
Modern Notation for Plainchant
... A dot immediately after a note increases its duration by half, so a dotted half note is equal to three quarter notes. Notes can also be “tied” together to make up a single longer note. And eighth notes can be “barred” together to show how they are grouped together, even if sung separately. ...
... A dot immediately after a note increases its duration by half, so a dotted half note is equal to three quarter notes. Notes can also be “tied” together to make up a single longer note. And eighth notes can be “barred” together to show how they are grouped together, even if sung separately. ...
1 - USC Upstate
... 35. Homophony - layers of musical activity that move at the same rhythm. Melody and accompaniment is a type of homophony 36. Improvisation - spontaneous musical creation. chorus improvisation is the jazz process in which a musician creates new melody on top of a pre-existing chord pattern (such as a ...
... 35. Homophony - layers of musical activity that move at the same rhythm. Melody and accompaniment is a type of homophony 36. Improvisation - spontaneous musical creation. chorus improvisation is the jazz process in which a musician creates new melody on top of a pre-existing chord pattern (such as a ...
laoliuban roeder (modified long abstract)
... metrical profile. By repeating the exact rhythm of beats 1-8, beats 9-16 reinforce the 8 = 3+2+3 structure, and suggest a 16-beat parallel construction, indicated by the two consecutive solid boxes on the top system. The expectations grow so strong as one listens through this group that the sense o ...
... metrical profile. By repeating the exact rhythm of beats 1-8, beats 9-16 reinforce the 8 = 3+2+3 structure, and suggest a 16-beat parallel construction, indicated by the two consecutive solid boxes on the top system. The expectations grow so strong as one listens through this group that the sense o ...
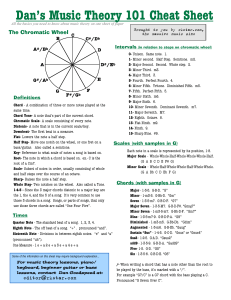
Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet
... the 1, the 4, and the 5 of a song. It’s very common to use those 3 chords in a song. Songs, or parts of songs, that only use those three chords are called “One Four Five”. ...
... the 1, the 4, and the 5 of a song. It’s very common to use those 3 chords in a song. Songs, or parts of songs, that only use those three chords are called “One Four Five”. ...
Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet []
... the 1, the 4, and the 5 of a song. It’s very common to use those 3 chords in a song. Songs, or parts of songs, that only use those three chords are called “One Four Five”. ...
... the 1, the 4, and the 5 of a song. It’s very common to use those 3 chords in a song. Songs, or parts of songs, that only use those three chords are called “One Four Five”. ...
NOTE - Big Lake Schools
... • Lower-pitched notes are written LOWER on the staff. o Higher-pitched notes are written HIGHER. • Sometimes notes are so high or so low they need to be written with LEDGER lines. • Ledger lines are small lines that allow the staff to be EXTENDED . o How many ledger lines can be used? ! AS MANY AS N ...
... • Lower-pitched notes are written LOWER on the staff. o Higher-pitched notes are written HIGHER. • Sometimes notes are so high or so low they need to be written with LEDGER lines. • Ledger lines are small lines that allow the staff to be EXTENDED . o How many ledger lines can be used? ! AS MANY AS N ...
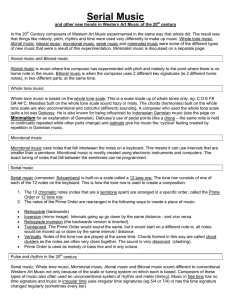
Serial Music - Toot Hill School
... Serial music (composer: Schoenberg) is built on a scale called a 12 tone row. The tone row consists of one of each of the 12 notes on the keyboard. This is how the tone row is used to create a composition: 1. The 12 chromatic notes (notes that are a semitone apart) are arranged in a specific order, ...
... Serial music (composer: Schoenberg) is built on a scale called a 12 tone row. The tone row consists of one of each of the 12 notes on the keyboard. This is how the tone row is used to create a composition: 1. The 12 chromatic notes (notes that are a semitone apart) are arranged in a specific order, ...
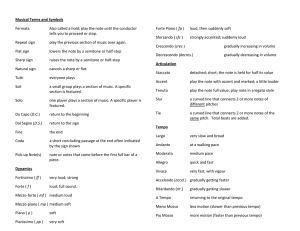
Terms and Symbols
... cut time ( ): 2/2 time (a time signature indicating two half note beats per measure). 8va: play an octave higher or lower than the indicated pitch. loco: back to the original octave after an 8va indication. (Italian for “in its place”.) key signature: the sharp or flat signs placed at the beginning ...
... cut time ( ): 2/2 time (a time signature indicating two half note beats per measure). 8va: play an octave higher or lower than the indicated pitch. loco: back to the original octave after an 8va indication. (Italian for “in its place”.) key signature: the sharp or flat signs placed at the beginning ...
The Mathematics of Music
... Given the fundamental tone the singer is singing, he is able to amplify the overtones simultaneously The result is more than one distinct tone being sung at the same time Let’s listen to a few examples… ...
... Given the fundamental tone the singer is singing, he is able to amplify the overtones simultaneously The result is more than one distinct tone being sung at the same time Let’s listen to a few examples… ...
sign lesson term definition
... natural minor scale with the 6th and 7th raised on the way up and lowered on the way down ...
... natural minor scale with the 6th and 7th raised on the way up and lowered on the way down ...
MU 139 Power Point - Montgomery College
... Harmony: Two or more sounds happening at the same time. Usually as background. Form: Organization or structure of music. Texture: How the musical parts are woven together. Timbre (Tone): The unique individual characteristics of each sound. ...
... Harmony: Two or more sounds happening at the same time. Usually as background. Form: Organization or structure of music. Texture: How the musical parts are woven together. Timbre (Tone): The unique individual characteristics of each sound. ...
Elements of Music Worksheet Name: August 9th, 2011 Fine Arts List
... 19. When notating music, composers have traditionally used ______________words, and their abbreviations, to indicate dynamics. ...
... 19. When notating music, composers have traditionally used ______________words, and their abbreviations, to indicate dynamics. ...
Time signature

The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats (pulses) are to be contained in each bar and which note value is to be given one beat. In a musical score, the time signature appears at the beginning of the piece, as a time symbol or stacked numerals, such as 11px or 34 (read common time and three-four time, respectively), immediately following the key signature or immediately following the clef symbol if the key signature is empty. A mid-score time signature, usually immediately following a barline, indicates a change of meter.There are various types of time signatures, depending on whether the music follows simple rhythms or involves unusual shifting tempos, including: simple (such as 34 or 44), compound (e.g., 98 or 128), complex (e.g., 54 or 78), mixed (e.g., 58 & 38 or 68 & 34), additive (e.g., 3+2+38), fractional (e.g., 2½4), and irrational meters (e.g., 310 or 524).












![Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007752700_2-d39806ec781c16b3e6c991a5c61a970a-300x300.png)