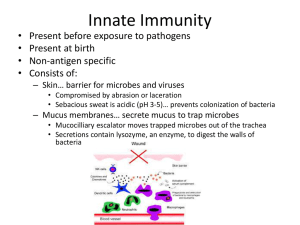
(Innate) Immunity Lecture
... TollToll-like receptors Mast cells & histamine Chemical mediators ...
... TollToll-like receptors Mast cells & histamine Chemical mediators ...
Unit 8 Seminar
... human reactions to infections. This project will allow you to trace pathogens through the infection cycle and human response to the infection. Project requirements: Refer to Table 1.1 and answer the following questions for EACH organism listed above. Word requirements are outlined for each question ...
... human reactions to infections. This project will allow you to trace pathogens through the infection cycle and human response to the infection. Project requirements: Refer to Table 1.1 and answer the following questions for EACH organism listed above. Word requirements are outlined for each question ...
Immune System - Iowa State University
... 3)Saliva and tears contains ______________ which is an enzyme that digests bacterial cell walls. 4) Innate immune system defenses include________________, which are most often __________________, which resides in _____________to prevent infections. 5) Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can b ...
... 3)Saliva and tears contains ______________ which is an enzyme that digests bacterial cell walls. 4) Innate immune system defenses include________________, which are most often __________________, which resides in _____________to prevent infections. 5) Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can b ...
Nonspecific Defenses
... • Mast cells: a type of white blood cell in tissues, cause capillaries to dilate and become more permeable • Some inflammatory responses trigger fever, the onset being controlled by the brain • The fever serves to inhibit the growth of some microorganisms, promotes accelerated tissue repair, stimula ...
... • Mast cells: a type of white blood cell in tissues, cause capillaries to dilate and become more permeable • Some inflammatory responses trigger fever, the onset being controlled by the brain • The fever serves to inhibit the growth of some microorganisms, promotes accelerated tissue repair, stimula ...
NON-SPECIFIC IMMUNE RESPONSE CHAPTER 16 Overview of the Defense
... sequences, LPS of gram-neg ( triggers TLR on monocytes and macrophages and causes cell to produce chemokines (cytokine for chemotaxis) to attract other phagocytes to site ...
... sequences, LPS of gram-neg ( triggers TLR on monocytes and macrophages and causes cell to produce chemokines (cytokine for chemotaxis) to attract other phagocytes to site ...
Tan1
... The complement system is a set of plasma proteins that act together to attack extracellular forms of pathogens. It was first discovered as an effector arm of the antibody response, but complement can also be activated early in infection in the absence of antibodies; complement first evolved as part ...
... The complement system is a set of plasma proteins that act together to attack extracellular forms of pathogens. It was first discovered as an effector arm of the antibody response, but complement can also be activated early in infection in the absence of antibodies; complement first evolved as part ...
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... • Once engulfed the phagocyte fuses a lysosome to the vacuole containing the bacteria • Some bacteria evade phagocytes by hiding surface recognition via a capsule • Types: ...
... • Once engulfed the phagocyte fuses a lysosome to the vacuole containing the bacteria • Some bacteria evade phagocytes by hiding surface recognition via a capsule • Types: ...
Study Guide 11 - Innate Immunity
... a. Toll‐like receptors – surface receptors that allow cells to “see” molecules that signify the presence of microorganisms or viruses b. Pattern recognition ...
... a. Toll‐like receptors – surface receptors that allow cells to “see” molecules that signify the presence of microorganisms or viruses b. Pattern recognition ...
Wounds: Care and Treatment
... • The efficient and orderly processes lost and the wounds are locked in to the state of chronic inflammation and fibrosis. • This is associated with abundant neutrophil infiltration, reactive oxygen species and district in enzymes. ...
... • The efficient and orderly processes lost and the wounds are locked in to the state of chronic inflammation and fibrosis. • This is associated with abundant neutrophil infiltration, reactive oxygen species and district in enzymes. ...
Chronic inflammation
... foreign bodies, or autoimmune Monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells, IFN-γ and other cytokines, GFs, hydrolytic enzymes Delayed ( months or years) Tissue destruction, fibrosis ...
... foreign bodies, or autoimmune Monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells, IFN-γ and other cytokines, GFs, hydrolytic enzymes Delayed ( months or years) Tissue destruction, fibrosis ...
2. Cell-mediated immunity
... Key Concepts in Monocytic Phagocytes in Immune Defense-I 1. Macrophages differentiate from circulating blood monocytes. 2. Macrophages are very heterogeneous in cellular activities, and may play positive or negative roles in immune defense and tissue homeostasis. 3. Tissue (Resident) & recruited ma ...
... Key Concepts in Monocytic Phagocytes in Immune Defense-I 1. Macrophages differentiate from circulating blood monocytes. 2. Macrophages are very heterogeneous in cellular activities, and may play positive or negative roles in immune defense and tissue homeostasis. 3. Tissue (Resident) & recruited ma ...
Suggested Answers for Case Study, Chapter 16, Mechanisms of
... Macrophages are a component of innate immunity and are responsible for the phagocytosis of microbes and processing of antigen. When working with T lymphocytes, macrophages can act as antigen-presenting cells. After ingesting the microbe, digestive enzymes break down antigen into small peptides and c ...
... Macrophages are a component of innate immunity and are responsible for the phagocytosis of microbes and processing of antigen. When working with T lymphocytes, macrophages can act as antigen-presenting cells. After ingesting the microbe, digestive enzymes break down antigen into small peptides and c ...
Monocyte - Macrophage Biology Symposium - Meakins
... macrophage ontogeny, genomics, immune function to exchange the latest research advances in this field. By integrating the ontogeny/genomic/metabolomics and the role of monocytes/macrophages in host immunity during this symposium, we expect to explore the therapeutic potential of these cells in the t ...
... macrophage ontogeny, genomics, immune function to exchange the latest research advances in this field. By integrating the ontogeny/genomic/metabolomics and the role of monocytes/macrophages in host immunity during this symposium, we expect to explore the therapeutic potential of these cells in the t ...
L04 Pathophysiology Inflammastion
... In acute inflammation the dominant players cell is neutrophils , if it was an inflammatory allergic reaction (mast cell ,acenocell , play a significant role in addition to neutrophils ) In chronic inflammation we are talking mostly about macrophages (the dominant player ) but also neutrophils •Macro ...
... In acute inflammation the dominant players cell is neutrophils , if it was an inflammatory allergic reaction (mast cell ,acenocell , play a significant role in addition to neutrophils ) In chronic inflammation we are talking mostly about macrophages (the dominant player ) but also neutrophils •Macro ...
lec1
... a- Attraction by chemotactic substances (microbes, damaged tissues) b- Attachment by receptors on surfaces of phagocytes ...
... a- Attraction by chemotactic substances (microbes, damaged tissues) b- Attachment by receptors on surfaces of phagocytes ...
Lymphatic System - University of Baghdad
... • Phagocytes include neutrophils and macrophages. • Three phases of phagocytosis include chemotaxis, adherence, and ingestion. i). Chemotaxis: means movement of phagocytic cells toward certain substances (such as microbial products and activated complement proteins). ii). Adherance: the cell membran ...
... • Phagocytes include neutrophils and macrophages. • Three phases of phagocytosis include chemotaxis, adherence, and ingestion. i). Chemotaxis: means movement of phagocytic cells toward certain substances (such as microbial products and activated complement proteins). ii). Adherance: the cell membran ...
Immune System
... cell but diffuses to nearby cells and inhibits viral reproduction there -Host specific-not virus specific -Inteferon may act against cancer since some may be induced by viruses one kind mobilizes natural killer cells-destroys tumor cells may change malignant cell membranes- make them less likely to ...
... cell but diffuses to nearby cells and inhibits viral reproduction there -Host specific-not virus specific -Inteferon may act against cancer since some may be induced by viruses one kind mobilizes natural killer cells-destroys tumor cells may change malignant cell membranes- make them less likely to ...
File
... Homeostasis Maintenance of a constant internal body environment. Innate Front line, first responding side of the immune system Adaptive Second line, specialized arm of the immune system Macrophages example of a first line defense immune cell, very phagocytic in nature. Pathogen infectious agent Hemo ...
... Homeostasis Maintenance of a constant internal body environment. Innate Front line, first responding side of the immune system Adaptive Second line, specialized arm of the immune system Macrophages example of a first line defense immune cell, very phagocytic in nature. Pathogen infectious agent Hemo ...
... iii) Monocytes (~6% of WBC): found in blood, recruited to site of injury within 4-6 hrs, Monocytes develop into the following three cell types: Macrophages: found in tissues near blood vessels. Tissue specific forms, e.g. Kupffer cells in the liver, microglial cells in the central nervous system Den ...
THE IMMUNE RESPONSE AGAINST INTRACELLULAR BACTERIA
... Evasion of immune mechanisms by intracellular bacteria Inhibition of phagolysosome formation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Legionella pneumophilia Scavenging of reactive oxigen intermediates Mycobacterium leprae (phenolic glycolipid) ...
... Evasion of immune mechanisms by intracellular bacteria Inhibition of phagolysosome formation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Legionella pneumophilia Scavenging of reactive oxigen intermediates Mycobacterium leprae (phenolic glycolipid) ...
Morphologic Patterns of Acute Inflammation
... • Influx of other cell types via cytokines • Fibroblast proliferation • Angiogenesis Arsenal of mediators make them ...
... • Influx of other cell types via cytokines • Fibroblast proliferation • Angiogenesis Arsenal of mediators make them ...
AHCC - Pulse Nutritional
... have shown that AHCC can significantly enhance the function of certain white blood cells including: • Natural (NK) cells, the body’s first line of defense* • Dendritic Cells, which initiate adaptive immune response* • T-Cells, which provide back-up for NK cells* • Macrophages, which clean up cellula ...
... have shown that AHCC can significantly enhance the function of certain white blood cells including: • Natural (NK) cells, the body’s first line of defense* • Dendritic Cells, which initiate adaptive immune response* • T-Cells, which provide back-up for NK cells* • Macrophages, which clean up cellula ...
4A Worksheet 1) Intrinsic Defense Systems include the ______
... 4) Innate immune system defenses include________________, which are most often __________________, which resides in _____________to prevent infections. 5) Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can be killed before activation of the immune system by__________ __________ ______, which release ___ ...
... 4) Innate immune system defenses include________________, which are most often __________________, which resides in _____________to prevent infections. 5) Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can be killed before activation of the immune system by__________ __________ ______, which release ___ ...
Immunology Review
... produce cytokines to attract other phagocytic cells and make blood vessels leaky, may present antigen to stimulate T cell activation (adaptive) Dendritic cells: innate immune cell, may be phagocytic and may present antigen to simulate T cell ...
... produce cytokines to attract other phagocytic cells and make blood vessels leaky, may present antigen to stimulate T cell activation (adaptive) Dendritic cells: innate immune cell, may be phagocytic and may present antigen to simulate T cell ...
Macrophage

Macrophages (Greek: big eaters, from makros ""large"" + phagein ""eat""; abbr. MΦ) are a type of white blood cell that engulfs and digests cellular debris, foreign substances, microbes, cancer cells, and anything else that does not have the types of proteins specific to the surface of healthy body cells on its surface in a process called phagocytosis. Macrophages were first discovered by Élie Metchnikoff, a Russian bacteriologist, in 1884. They are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They play a critical role in non-specific defense (innate immunity), and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune cells such as lymphocytes. In humans, dysfunctional macrophages cause severe diseases such as chronic granulomatous disease that result in frequent infections.Beyond increasing inflammation and stimulating the immune system, macrophages also play an important anti-inflammatory role and can decrease immune reactions through the release of cytokines. Macrophages that encourage inflammation are called M1 macrophages, whereas those that decrease inflammation and encourage tissue repair are called M2 macrophages. This difference is reflected in their metabolism, M1 macrophages have the unique ability to metabolize arginine to the ""killer"" molecule nitric oxide, whereas M2 macrophages have the unique ability to metabolize arginine to the ""repair"" molecule ornithine.Human macrophages are about 21 micrometres (0.00083 in) in diameter and are produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. They can be identified using flow cytometry or immunohistochemical staining by their specific expression of proteins such as CD14, CD40, CD11b, CD64, F4/80 (mice)/EMR1 (human), lysozyme M, MAC-1/MAC-3 and CD68.