Non-Specific Defenses
... Capsules prevent C activation Surface lipid-carbohydrates prevent MAC formation Enzymatic digestion of C5a ...
... Capsules prevent C activation Surface lipid-carbohydrates prevent MAC formation Enzymatic digestion of C5a ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM and DIseasE
... • Toxins from bacteria trigger the deregulation of the hypothalamus (exogenous pyrogen). Examples are endotoxins (remember them?). • Pyrogen – substance that causes a rise in body temp ...
... • Toxins from bacteria trigger the deregulation of the hypothalamus (exogenous pyrogen). Examples are endotoxins (remember them?). • Pyrogen – substance that causes a rise in body temp ...
Types of White Blood Cells WBCs.
... Granulocytes stay in blood for 4-8 hours and in the tissues 5 days. When there is serious infection their whole life span is shortened to few hours Monocytes stay in the blood for 10-20 hours and then they leave to different tissues where they form tissue macrophages. Tissue macrophages can live ...
... Granulocytes stay in blood for 4-8 hours and in the tissues 5 days. When there is serious infection their whole life span is shortened to few hours Monocytes stay in the blood for 10-20 hours and then they leave to different tissues where they form tissue macrophages. Tissue macrophages can live ...
5 dent inflammation and mucosal immunity
... • Are not present in healthy tissues • Migration elimination of pathogens (enzymes, reactive oxygen intermediates) ...
... • Are not present in healthy tissues • Migration elimination of pathogens (enzymes, reactive oxygen intermediates) ...
PPS - Jacksonville University
... Also I would like to thank Sally and Judy in the Science and Math division office, for signing me out a lab key nearly everyday of the year ...
... Also I would like to thank Sally and Judy in the Science and Math division office, for signing me out a lab key nearly everyday of the year ...
March 2016, Anti-inflammatory role of a natural
... International Conference of the European Association of Fish Pathologists (EAFP) in Gran Canaria, Las Palmas in September 2015, where TargetFish highlights and achievements were discussed, was a great success. The significance of these developments for the aquatic animal health industry and ...
... International Conference of the European Association of Fish Pathologists (EAFP) in Gran Canaria, Las Palmas in September 2015, where TargetFish highlights and achievements were discussed, was a great success. The significance of these developments for the aquatic animal health industry and ...
Lines of Defense - Trinity Christian School
... Localized heat increase the metabolic rate of tissue cells in turn speeding up their defensive responses and repair activities ...
... Localized heat increase the metabolic rate of tissue cells in turn speeding up their defensive responses and repair activities ...
The Inflammatory Response
... reaction and tissue damage from wounds that don’t heal, tumors, heart disease and atherosclerosis …… and……obesity! • Pollen and particles from smoking and pollution can constantly irritate certain tissues • Tissue damage from atherosclerosis, heart disease and wounds that don’t heal can constantly i ...
... reaction and tissue damage from wounds that don’t heal, tumors, heart disease and atherosclerosis …… and……obesity! • Pollen and particles from smoking and pollution can constantly irritate certain tissues • Tissue damage from atherosclerosis, heart disease and wounds that don’t heal can constantly i ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... These chemical mediators activate cell adhesion molecules on endothelial cells. _________________ is the process where neutrophils and monocytes bind to these cell adhesion molecules. When neutrophils bind to these molecules, they are activated and leave the blood vessel by a process called ________ ...
... These chemical mediators activate cell adhesion molecules on endothelial cells. _________________ is the process where neutrophils and monocytes bind to these cell adhesion molecules. When neutrophils bind to these molecules, they are activated and leave the blood vessel by a process called ________ ...
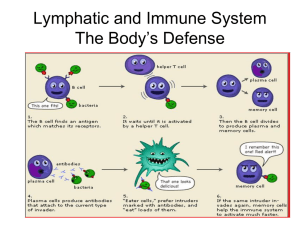
Lymphatic and Immune System
... the body from all types of pathogens • Protective Chemicals – Acid pH of skin secretions toxic to bacteria – Stomach mucosa secretes HCl to kill pathogens that are ingested – Saliva contains lysozyme to kill bacteria – Mucus traps microorganisms in digestive and respiratory pathways ...
... the body from all types of pathogens • Protective Chemicals – Acid pH of skin secretions toxic to bacteria – Stomach mucosa secretes HCl to kill pathogens that are ingested – Saliva contains lysozyme to kill bacteria – Mucus traps microorganisms in digestive and respiratory pathways ...
Foundation Block Lecture Two Natural defense mechanism
... Microbial infections initiate inflammation As bacteria possess an array of pro-inflammatory molecules: e.g. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ...
... Microbial infections initiate inflammation As bacteria possess an array of pro-inflammatory molecules: e.g. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ...
White Blood Cells (WBC`s) or Leukocytes
... macrophages into the inflamed area Along with Neutrophils,Monocytes,enter the tissues. M are low in blood & bone marrow compared with the number of neutrophils( N ). When monocytes enter the tissue they need 8 hours to swell &( several days to weeks) to form lysosomes. ...
... macrophages into the inflamed area Along with Neutrophils,Monocytes,enter the tissues. M are low in blood & bone marrow compared with the number of neutrophils( N ). When monocytes enter the tissue they need 8 hours to swell &( several days to weeks) to form lysosomes. ...
The Immune System - Blue Valley School District
... lysis and death in cellular pathogens • Bound complexes also promote phagocytosis ...
... lysis and death in cellular pathogens • Bound complexes also promote phagocytosis ...
Implantation and Inflammation
... •then the innate immune response begins. •The cells of the immune system determine •“self” from “non-self” by recognizing molecules on the microbe surface. •Macrophages are immune cells (phagocytes) that reside within the tissue. Neutrophils are phagocytes that reside in the blood but can extravasat ...
... •then the innate immune response begins. •The cells of the immune system determine •“self” from “non-self” by recognizing molecules on the microbe surface. •Macrophages are immune cells (phagocytes) that reside within the tissue. Neutrophils are phagocytes that reside in the blood but can extravasat ...
Immunity to infection
... involves a constant battle between the host defenses and the mutant microbes trying to evolve evasive strategies. Specific acquired responses amplify and enhance innate immune mechanisms. Inflammation revisited • Inflammation is a major defensive reaction initiated by infection or tissue injury. The ...
... involves a constant battle between the host defenses and the mutant microbes trying to evolve evasive strategies. Specific acquired responses amplify and enhance innate immune mechanisms. Inflammation revisited • Inflammation is a major defensive reaction initiated by infection or tissue injury. The ...
This new agent could contribute to RA treatment strategies via a new
... anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biological DMARDs, significantly suppress disease activity and joint destruction in RA patients. However, these strategies target only certain patient populations, and thus there is an unmet need for new anti-rheumatic drugs with novel mechanisms of action. Sialic a ...
... anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biological DMARDs, significantly suppress disease activity and joint destruction in RA patients. However, these strategies target only certain patient populations, and thus there is an unmet need for new anti-rheumatic drugs with novel mechanisms of action. Sialic a ...
30_Intracellular bact - parasite BA
... Evasion of immune mechanisms by intracellular bacteria Inhibition of phagolysosome formation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Legionella pneumophila Scavenging of reactive oxigen intermediates Mycobacterium leprae (phenolic glycolipid) ...
... Evasion of immune mechanisms by intracellular bacteria Inhibition of phagolysosome formation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Legionella pneumophila Scavenging of reactive oxigen intermediates Mycobacterium leprae (phenolic glycolipid) ...
Slide 1
... The large amounts of ROS generated during an active infectious inflammatory response would then be responsible for causing greater than normal amounts of DNA damage leading to increased risk for cancer through enhanced rates of DNA damage. In addition, the enhanced production of ROS increases the a ...
... The large amounts of ROS generated during an active infectious inflammatory response would then be responsible for causing greater than normal amounts of DNA damage leading to increased risk for cancer through enhanced rates of DNA damage. In addition, the enhanced production of ROS increases the a ...
328 Comparative evolutionary analysis of IL6 in lagomorphs F
... single individual, but successfully pass between individuals becoming a contagious cancer derived from a single neoplastic cell. Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD) is one such contagious cancer that has emerged in the Tasmanian devil, a carnivorous marsupial endemic to the island of Tasmania. Despit ...
... single individual, but successfully pass between individuals becoming a contagious cancer derived from a single neoplastic cell. Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD) is one such contagious cancer that has emerged in the Tasmanian devil, a carnivorous marsupial endemic to the island of Tasmania. Despit ...
Chronic Inflammation
... Derived from blood monocytes. Various levels of ‘activation’. Functions: ...
... Derived from blood monocytes. Various levels of ‘activation’. Functions: ...
When a person breaks a bone, suffers infection organ damage or
... damaged or killed by the initial trauma release chemicals that in turn cause the death of adjacent cells. While many companies are attempting to develop neuroprotective drugs, Proneuron feels it is unique in taking a cell therapy approach. The therapy will involve taking a sample of a patient's own ...
... damaged or killed by the initial trauma release chemicals that in turn cause the death of adjacent cells. While many companies are attempting to develop neuroprotective drugs, Proneuron feels it is unique in taking a cell therapy approach. The therapy will involve taking a sample of a patient's own ...
irc seminar - MedUni Wien
... presentation by dendritic cell subsets (19982003). In 2004 she joined the department of Molecular Cell Biology and Immunology at the VUMC in Amsterdam. She is an associate professor since 2015. Her group is studying different types of macrophages and DCs that are present in lymphoid organs and how t ...
... presentation by dendritic cell subsets (19982003). In 2004 she joined the department of Molecular Cell Biology and Immunology at the VUMC in Amsterdam. She is an associate professor since 2015. Her group is studying different types of macrophages and DCs that are present in lymphoid organs and how t ...
Macrophage

Macrophages (Greek: big eaters, from makros ""large"" + phagein ""eat""; abbr. MΦ) are a type of white blood cell that engulfs and digests cellular debris, foreign substances, microbes, cancer cells, and anything else that does not have the types of proteins specific to the surface of healthy body cells on its surface in a process called phagocytosis. Macrophages were first discovered by Élie Metchnikoff, a Russian bacteriologist, in 1884. They are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They play a critical role in non-specific defense (innate immunity), and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune cells such as lymphocytes. In humans, dysfunctional macrophages cause severe diseases such as chronic granulomatous disease that result in frequent infections.Beyond increasing inflammation and stimulating the immune system, macrophages also play an important anti-inflammatory role and can decrease immune reactions through the release of cytokines. Macrophages that encourage inflammation are called M1 macrophages, whereas those that decrease inflammation and encourage tissue repair are called M2 macrophages. This difference is reflected in their metabolism, M1 macrophages have the unique ability to metabolize arginine to the ""killer"" molecule nitric oxide, whereas M2 macrophages have the unique ability to metabolize arginine to the ""repair"" molecule ornithine.Human macrophages are about 21 micrometres (0.00083 in) in diameter and are produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. They can be identified using flow cytometry or immunohistochemical staining by their specific expression of proteins such as CD14, CD40, CD11b, CD64, F4/80 (mice)/EMR1 (human), lysozyme M, MAC-1/MAC-3 and CD68.