CIR Newsletter July 2016 - The University of Edinburgh
... research could also lead to new treatments for sepsis, where a body-wide immune response causes life-threatening tissue damage. The compounds called alpha defensins are part of the body’s first line of defence against infection. They help to stop bacteria and other infectious agents from reproducing ...
... research could also lead to new treatments for sepsis, where a body-wide immune response causes life-threatening tissue damage. The compounds called alpha defensins are part of the body’s first line of defence against infection. They help to stop bacteria and other infectious agents from reproducing ...
Immunity to protozoa and worms
... The development of immunity is a complex process arising from the interactions of many different kinds of cells over a period of time. Effects are often local ad many cell types secreting several different mediators may be present at sites of immune rejection. Moreover, the processes involved in con ...
... The development of immunity is a complex process arising from the interactions of many different kinds of cells over a period of time. Effects are often local ad many cell types secreting several different mediators may be present at sites of immune rejection. Moreover, the processes involved in con ...
Activated B cells
... For the passing of the Immunology exam the minimum of 51 points (out of 100) should be collected on condition that the 50% of points plus one (minimally 36) has been reached in the final test Note: If the student collected less than 15 points in colloqium (i.e. 50%), he/she must perform better than ...
... For the passing of the Immunology exam the minimum of 51 points (out of 100) should be collected on condition that the 50% of points plus one (minimally 36) has been reached in the final test Note: If the student collected less than 15 points in colloqium (i.e. 50%), he/she must perform better than ...
The Lymphatic System and Immunity
... Most B cells do not respond to antigens without stimulation from (1) . This process begins when a B cell takes in the same kind of (2) that stimulated the helper T cell. The antigen is processed by the B cell and presented to the helper T cell using a(n) (3) . There is also costimulation involving ( ...
... Most B cells do not respond to antigens without stimulation from (1) . This process begins when a B cell takes in the same kind of (2) that stimulated the helper T cell. The antigen is processed by the B cell and presented to the helper T cell using a(n) (3) . There is also costimulation involving ( ...
What are hypersensitivities?
... What characteristics are shared by all hypersensitivies? Immune responses: Primary (sensitization) response Secondary (activation) response Abnormal (hyper-) response to antigens (allergens) Symptoms: localized or systemic Onset can be: Early, Late or Chronic ...
... What characteristics are shared by all hypersensitivies? Immune responses: Primary (sensitization) response Secondary (activation) response Abnormal (hyper-) response to antigens (allergens) Symptoms: localized or systemic Onset can be: Early, Late or Chronic ...
BIO CEO Presentation - Trillium Therapeutics Inc.
... Mouse SIRPaFc treatment: 0.2, 1 or 5 mg/kg IP 3x/wk for 4 wks, starting 21d after engraftment Mouse (NOD) SIRPαFc binds both human and mouse CD47 (antigen sink effect) ...
... Mouse SIRPaFc treatment: 0.2, 1 or 5 mg/kg IP 3x/wk for 4 wks, starting 21d after engraftment Mouse (NOD) SIRPαFc binds both human and mouse CD47 (antigen sink effect) ...
Inflammatory response: 1. Vascular reaction 2. Cellular reaction
... - most common mechanism; “immediate transient response” - histamine, bradykinin, LTs, substance P bind to their receptors intracellular signaling pathways contraction of cytoskeletal proteins (myosin) contraction of endothelial cells separation of intercellular junctions - IL-1, TNF, IFN-γ ...
... - most common mechanism; “immediate transient response” - histamine, bradykinin, LTs, substance P bind to their receptors intracellular signaling pathways contraction of cytoskeletal proteins (myosin) contraction of endothelial cells separation of intercellular junctions - IL-1, TNF, IFN-γ ...
0018
... Th1 response protected mice against L. major infection.11 Handman et al mentioned that prophylactic DNA vaccination shifted the T cellderived cytokine environment with an increase in the INF-gamma-producing Th1 type cells.12 Cabrera et al showed that by using live Mycobacterium bovis BCG and heated ...
... Th1 response protected mice against L. major infection.11 Handman et al mentioned that prophylactic DNA vaccination shifted the T cellderived cytokine environment with an increase in the INF-gamma-producing Th1 type cells.12 Cabrera et al showed that by using live Mycobacterium bovis BCG and heated ...
Uvod u imunski sistem - University of Belgrade
... - first: in the 5th week - second: in the 9th week - third: in the 13th week ...
... - first: in the 5th week - second: in the 9th week - third: in the 13th week ...
Safe Immunoguard Leaf Leaf .pmd - sbpl
... The ability of birds to fight against infections and disease is determined by its capability to invade pathogens. The body protects itself against foreign materials such as virus and bacteria through its immune system. Immune system triggers the action of lymphocytes i.e white blood cells (WBC) or m ...
... The ability of birds to fight against infections and disease is determined by its capability to invade pathogens. The body protects itself against foreign materials such as virus and bacteria through its immune system. Immune system triggers the action of lymphocytes i.e white blood cells (WBC) or m ...
CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE IN VITRO
... (From the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Melbourne, Victoria 3050, Australia) (Received for publication 21 March 1972) The combined use of in vitro culture techniques together with efficient cell separation methods have revealed that macrophages are essential participants in th ...
... (From the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Melbourne, Victoria 3050, Australia) (Received for publication 21 March 1972) The combined use of in vitro culture techniques together with efficient cell separation methods have revealed that macrophages are essential participants in th ...
Evasion of innate immunity by parasitic protozoa
... David Sacks and Alan Sher Parasitic protozoa are a major cause of global infectious disease. These eukaryotic pathogens have evolved with the vertebrate immune system and typically produce long-lasting chronic infections. A critical step in their host interaction is the evasion of innate immune defe ...
... David Sacks and Alan Sher Parasitic protozoa are a major cause of global infectious disease. These eukaryotic pathogens have evolved with the vertebrate immune system and typically produce long-lasting chronic infections. A critical step in their host interaction is the evasion of innate immune defe ...
Macrophages in Kidney Injury and Repair
... chemokines, a major role for Mφs is their capacity for phagocytosis (46). In addition to invading microbes, Mφs scavenge aged erythrocytes, dying leukocytes, cellular debris, pathological matrix, and ICs (47). In all these circumstances, phagocytic clearance can occur without cellular activation and ...
... chemokines, a major role for Mφs is their capacity for phagocytosis (46). In addition to invading microbes, Mφs scavenge aged erythrocytes, dying leukocytes, cellular debris, pathological matrix, and ICs (47). In all these circumstances, phagocytic clearance can occur without cellular activation and ...
Early steps regulating proliferation and activation in macrophages Ester Sánchez Tilló 2006
... environment, macrophages stop their proliferation program and acquire effectors functions. LPS activates macrophages to increase the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, IL-8 and to up-regulate NOS2 expression, which play important roles in the immune response (Marc ...
... environment, macrophages stop their proliferation program and acquire effectors functions. LPS activates macrophages to increase the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, IL-8 and to up-regulate NOS2 expression, which play important roles in the immune response (Marc ...
Immune modulation of some autoimmune diseases: the critical role
... All these populations are in homeostasis that includes a well-preserved equilibrium among granulopoiesis, bone marrow storage and release, intravascular transit, and destruction [14]. Therefore, after the neutrophil production, development and storage in the bone marrow, its releasing includes a tra ...
... All these populations are in homeostasis that includes a well-preserved equilibrium among granulopoiesis, bone marrow storage and release, intravascular transit, and destruction [14]. Therefore, after the neutrophil production, development and storage in the bone marrow, its releasing includes a tra ...
lec1-host parasite r..
... sweet and urine. It destroys the cell wall of bacteria. Interferons(IFN): C-reactive protein (CRP): Measure of inflammation produced in liver in response to inflammatory chemicals. ...
... sweet and urine. It destroys the cell wall of bacteria. Interferons(IFN): C-reactive protein (CRP): Measure of inflammation produced in liver in response to inflammatory chemicals. ...
Review Set Unit 2, Lesson 1 *The Immune System*
... pathogens as they come in contact with the body’s surface. • B. T cells and B cells attach themselves to antigens, gradually absorbing each antigen until it is no longer a threat to the body. • C. When a body is exposed to a certain pathogen, T cells and B cells remember that pathogen and produce an ...
... pathogens as they come in contact with the body’s surface. • B. T cells and B cells attach themselves to antigens, gradually absorbing each antigen until it is no longer a threat to the body. • C. When a body is exposed to a certain pathogen, T cells and B cells remember that pathogen and produce an ...
Cell-mediated immunity in pigeon breeders' lung:... removal from antigen exposure
... Although the pathogenesis of extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) has been considered to be an immune complex mediated tissue injury, current opinion considers that EAA reflects a local cell-mediated immune response [1-3]. Antigen is deposited in the lung and precipitating antibodies are present in t ...
... Although the pathogenesis of extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) has been considered to be an immune complex mediated tissue injury, current opinion considers that EAA reflects a local cell-mediated immune response [1-3]. Antigen is deposited in the lung and precipitating antibodies are present in t ...
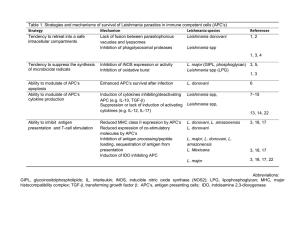
Table 1. Strategies and mechanisms of survival of Leishmania
... 12. Bermudez LE Covaro G, Remington J: Infection of murine macrophages with Toxoplasma gondii is associated with the release of transforming growth factor β and downregulation of expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61:4126– ...
... 12. Bermudez LE Covaro G, Remington J: Infection of murine macrophages with Toxoplasma gondii is associated with the release of transforming growth factor β and downregulation of expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61:4126– ...
Immune Physiology
... • Activate complement proteins • Agglutination reaction (antibodies sticks antigen-bearing cells together) • Agglutination “tags” pathogenic cells so they’re recognized & destroyed by phagocytes. ...
... • Activate complement proteins • Agglutination reaction (antibodies sticks antigen-bearing cells together) • Agglutination “tags” pathogenic cells so they’re recognized & destroyed by phagocytes. ...
Rheumatoid arthritis and myasthenia gravis as examples of
... must consist of a series of chemical elements which act as a code. ...
... must consist of a series of chemical elements which act as a code. ...
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the retina in acquired immune
... population of TNF-a-positive cells had processes terminating at endothelial cells, suggesting the end-feet processes of astrocytes (Fig. 6B). In two patients (2 and 3), the population of TNF-a-reactive cells consisted of parallel elongated cells, spanning the inner retina, and suggesting Miiller cel ...
... population of TNF-a-positive cells had processes terminating at endothelial cells, suggesting the end-feet processes of astrocytes (Fig. 6B). In two patients (2 and 3), the population of TNF-a-reactive cells consisted of parallel elongated cells, spanning the inner retina, and suggesting Miiller cel ...
Pathophysiological implications between chronic inflammation and
... activation of NADPH oxidase in the pancreas. This acts as a buffer to cellular oxidative stress because NADPH accepts electrons. In turn, the NADPH system activates TRX reductase, which reduces TRX, producing a bond with TxNIP. The ultimate effect is NLRP3 activation with consequent production and m ...
... activation of NADPH oxidase in the pancreas. This acts as a buffer to cellular oxidative stress because NADPH accepts electrons. In turn, the NADPH system activates TRX reductase, which reduces TRX, producing a bond with TxNIP. The ultimate effect is NLRP3 activation with consequent production and m ...
Applicability of laser scanning cytometry to study paediatric alveolar macrophages H.J. Bunn
... Applicability of laser scanning cytometry to study paediatric alveolar macrophages. H.J. Bunn, G. Woltmann, J. Grigg. #ERS Journals Ltd 2002. ABSTRACT: Laser scanning cytometry (LSC) generates quantitative information on immune receptor expression from cells cytocentrifuged onto a microscope slide. ...
... Applicability of laser scanning cytometry to study paediatric alveolar macrophages. H.J. Bunn, G. Woltmann, J. Grigg. #ERS Journals Ltd 2002. ABSTRACT: Laser scanning cytometry (LSC) generates quantitative information on immune receptor expression from cells cytocentrifuged onto a microscope slide. ...
Macrophages, pathology and parasite persistence in
... Although a low dose model of infection has recently been established, most studies on the early immune response to L. donovani and L. infantum have employed high dose (107) inoculation of amastigotes. Under these conditions, there are a few indications that initiation of immune responses to this par ...
... Although a low dose model of infection has recently been established, most studies on the early immune response to L. donovani and L. infantum have employed high dose (107) inoculation of amastigotes. Under these conditions, there are a few indications that initiation of immune responses to this par ...
Macrophage

Macrophages (Greek: big eaters, from makros ""large"" + phagein ""eat""; abbr. MΦ) are a type of white blood cell that engulfs and digests cellular debris, foreign substances, microbes, cancer cells, and anything else that does not have the types of proteins specific to the surface of healthy body cells on its surface in a process called phagocytosis. Macrophages were first discovered by Élie Metchnikoff, a Russian bacteriologist, in 1884. They are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They play a critical role in non-specific defense (innate immunity), and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune cells such as lymphocytes. In humans, dysfunctional macrophages cause severe diseases such as chronic granulomatous disease that result in frequent infections.Beyond increasing inflammation and stimulating the immune system, macrophages also play an important anti-inflammatory role and can decrease immune reactions through the release of cytokines. Macrophages that encourage inflammation are called M1 macrophages, whereas those that decrease inflammation and encourage tissue repair are called M2 macrophages. This difference is reflected in their metabolism, M1 macrophages have the unique ability to metabolize arginine to the ""killer"" molecule nitric oxide, whereas M2 macrophages have the unique ability to metabolize arginine to the ""repair"" molecule ornithine.Human macrophages are about 21 micrometres (0.00083 in) in diameter and are produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. They can be identified using flow cytometry or immunohistochemical staining by their specific expression of proteins such as CD14, CD40, CD11b, CD64, F4/80 (mice)/EMR1 (human), lysozyme M, MAC-1/MAC-3 and CD68.