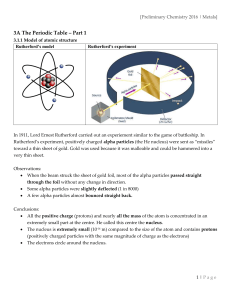
The Periodic Table
... ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
... ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
The Periodic Table
... ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
... ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
Periodic Relationships Among the Elements
... which it is formed. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. ...
... which it is formed. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. ...
Episode 7 - The Periodic Table
... 2. What are some examples of physical properties? 3. How many elements are on the modern periodic table? _____ How many of these can be found in nature? ______ 4. Why do the symbols for some elements (such as iron) seem to have no relationship to their name? 5. What is meant by the atomic and mass n ...
... 2. What are some examples of physical properties? 3. How many elements are on the modern periodic table? _____ How many of these can be found in nature? ______ 4. Why do the symbols for some elements (such as iron) seem to have no relationship to their name? 5. What is meant by the atomic and mass n ...
The Periodic Table - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 2. What are some examples of physical properties? 3. How many elements are on the modern periodic table? _____ How many of these can be found in nature? ______ 4. Why do the symbols for some elements (such as iron) seem to have no relationship to their name? 5. What is meant by the atomic and mass n ...
... 2. What are some examples of physical properties? 3. How many elements are on the modern periodic table? _____ How many of these can be found in nature? ______ 4. Why do the symbols for some elements (such as iron) seem to have no relationship to their name? 5. What is meant by the atomic and mass n ...
are smaller than their respective atoms.
... 1) Metals- high luster, good conductors, ductile, malleable, most are solid at room temp (except Hg is liquid) 2)Nonmetals- low luster, poor conductors, very brittle, various states of matter at room temperature (ex: S is solid, O is gas, Br is liquid) 3) Semi-Conductors - sit on stair-step line met ...
... 1) Metals- high luster, good conductors, ductile, malleable, most are solid at room temp (except Hg is liquid) 2)Nonmetals- low luster, poor conductors, very brittle, various states of matter at room temperature (ex: S is solid, O is gas, Br is liquid) 3) Semi-Conductors - sit on stair-step line met ...
CHAPTER 5, THE PERIODIC LAW Section 1, History of the Periodic
... By 1860, more than 60 elements had been discovered. FYI, there was no method for accurately determining an element’s atomic mass or the number of atoms of an element in a particular chemical compound. In 1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published his periodic table of elements in which elements with similar ...
... By 1860, more than 60 elements had been discovered. FYI, there was no method for accurately determining an element’s atomic mass or the number of atoms of an element in a particular chemical compound. In 1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published his periodic table of elements in which elements with similar ...
Physical Science
... Until 1750, scientists had identified only 17 elements, mainly metals, such as copper and iron. As the number of known elements grew, so did the need to organize them into groups based on their properties. In 1789, Antoine Lavoisier grouped the known elements into categories he called metals, nonmet ...
... Until 1750, scientists had identified only 17 elements, mainly metals, such as copper and iron. As the number of known elements grew, so did the need to organize them into groups based on their properties. In 1789, Antoine Lavoisier grouped the known elements into categories he called metals, nonmet ...
Organizing the Elements (Use pages 500
... atom? Which part of the atom may vary in number? How is the periodic table organized today? number of protons; proton; neutron; by atomic number 8. What does the square of each element on the periodic table contain? Why is the atomic mass for most elements listed as a whole number and a decimal frac ...
... atom? Which part of the atom may vary in number? How is the periodic table organized today? number of protons; proton; neutron; by atomic number 8. What does the square of each element on the periodic table contain? Why is the atomic mass for most elements listed as a whole number and a decimal frac ...
Periodic Properties
... • 3. This number is the atomic number. • The period number indicates how many energy levels (rings) each atom has. ...
... • 3. This number is the atomic number. • The period number indicates how many energy levels (rings) each atom has. ...
Concepts
... electron is in a higher energy level and unstable. Electrons in excited states will eventually fall back down to the ground state. 8. When an electron falls from a higher to a lower energy level, energy is released in the form of light of a specific color called a photon. ...
... electron is in a higher energy level and unstable. Electrons in excited states will eventually fall back down to the ground state. 8. When an electron falls from a higher to a lower energy level, energy is released in the form of light of a specific color called a photon. ...
Describe the Periodic Table
... Atomic Symbol: 0The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). 0 These symbols are used every where in the world 0 Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
... Atomic Symbol: 0The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). 0 These symbols are used every where in the world 0 Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... When elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. The way properties change from left to right across a period and from top to bottom within a group are called periodic trends. Here is a su ...
... When elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. The way properties change from left to right across a period and from top to bottom within a group are called periodic trends. Here is a su ...
The Periodical Table and chemical properties
... The transition metals, also called the d-block elements, are found in groups 3-12 of the periodic table. These elements make the transition between the representative metals in groups 1 and 2 and the metalloids, representative metals, and nonmetals in groups 13-18. Moreover, it is in this block of e ...
... The transition metals, also called the d-block elements, are found in groups 3-12 of the periodic table. These elements make the transition between the representative metals in groups 1 and 2 and the metalloids, representative metals, and nonmetals in groups 13-18. Moreover, it is in this block of e ...
Trends of the Periodic Table
... – For example, elements in period 4 each have a total of 4 energy levels for electrons ...
... – For example, elements in period 4 each have a total of 4 energy levels for electrons ...
Unit 2 PPT
... All are gases at room temperature He is less dense than air (It “floats” in air) Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe are used in lighting Rn is radioactive All have 8 electrons in the valence shell without forming compounds, so … Considered to be un-reactive (or “inert”) so natural compounds of these elements do n ...
... All are gases at room temperature He is less dense than air (It “floats” in air) Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe are used in lighting Rn is radioactive All have 8 electrons in the valence shell without forming compounds, so … Considered to be un-reactive (or “inert”) so natural compounds of these elements do n ...
Name
... 1. Which of these elements is a MORE reactive nonmetal? 2. Which of these elements has a LOWER ionization energy? 3. Which of these elements has a LOWER electron affinity? 4. Which of these atoms is a BIGGER? 5. Which of these elements has a HIGH ionization energy? 6. Which of these elements is a MO ...
... 1. Which of these elements is a MORE reactive nonmetal? 2. Which of these elements has a LOWER ionization energy? 3. Which of these elements has a LOWER electron affinity? 4. Which of these atoms is a BIGGER? 5. Which of these elements has a HIGH ionization energy? 6. Which of these elements is a MO ...
Chapter 5 – The Periodic Law
... Describe the modern periodic table Explain how the periodic law can be used to predict the physical and chemical properties of elements. Describe how the elements belonging to a group of the periodic table are interrelated in terms of atomic number. Describe the relationship between electrons in orb ...
... Describe the modern periodic table Explain how the periodic law can be used to predict the physical and chemical properties of elements. Describe how the elements belonging to a group of the periodic table are interrelated in terms of atomic number. Describe the relationship between electrons in orb ...
Chapter 12: Chemical Periodicity
... metals) into gold. They were not successful, but they did discover other elements in the process. Scientists began to predict the existence of other elements. Experimentation continued and improved. By 1940 all 90 naturally occurring elements had been discovered. Since then work in nuclear science h ...
... metals) into gold. They were not successful, but they did discover other elements in the process. Scientists began to predict the existence of other elements. Experimentation continued and improved. By 1940 all 90 naturally occurring elements had been discovered. Since then work in nuclear science h ...
Section 5.2 The Modern Periodic Table
... 6. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about a carbon-12 atom. a. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. b. Scientists assigned a mass of 6 atomic mass units to the carbon-12 atom. c. It is used as a standard for comparing the masses of atoms. d. An atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth t ...
... 6. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about a carbon-12 atom. a. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. b. Scientists assigned a mass of 6 atomic mass units to the carbon-12 atom. c. It is used as a standard for comparing the masses of atoms. d. An atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth t ...
Section 5.2 The Modern Periodic Table
... 6. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about a carbon-12 atom. a. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. b. Scientists assigned a mass of 6 atomic mass units to the carbon-12 atom. c. It is used as a standard for comparing the masses of atoms. d. An atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth t ...
... 6. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about a carbon-12 atom. a. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. b. Scientists assigned a mass of 6 atomic mass units to the carbon-12 atom. c. It is used as a standard for comparing the masses of atoms. d. An atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth t ...
Ch.4 Notes Powerpoint Version
... • Recall that groups 1 and 7 are the most reactive metals and nonmetals. • As we move down group 1, the alkali metals become more reactive- this is because of the trend seen in ionization energy! • As we move down group 7, the halogens become less reactive- this is because of the trend seen in elect ...
... • Recall that groups 1 and 7 are the most reactive metals and nonmetals. • As we move down group 1, the alkali metals become more reactive- this is because of the trend seen in ionization energy! • As we move down group 7, the halogens become less reactive- this is because of the trend seen in elect ...
The Periodic Table
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...