The Periodic Table
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
File
... - 2 A (or 2) are called the alkaline earth metals - d-block are called transition metals - f-block are called inner-transition metals ...
... - 2 A (or 2) are called the alkaline earth metals - d-block are called transition metals - f-block are called inner-transition metals ...
Ch. 6 SG answers
... b. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are repeating as a result of their atomic number c. Electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves d. The chemical properties of elements can be group according to their periodicity, but physical properties cannot __B___ 4. Which elem ...
... b. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are repeating as a result of their atomic number c. Electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves d. The chemical properties of elements can be group according to their periodicity, but physical properties cannot __B___ 4. Which elem ...
the Periodic Table Regents Review Worksheets with answers.
... atomic radius with increasing atomic number. This may best be explained by the fact that the A. number of protons increases, and the number of shells of electrons remains the same B. number of protons increases, and the number of shells of electrons increases C. number of protons decreases, and the ...
... atomic radius with increasing atomic number. This may best be explained by the fact that the A. number of protons increases, and the number of shells of electrons remains the same B. number of protons increases, and the number of shells of electrons increases C. number of protons decreases, and the ...
Chapter 7.1 Notes
... • One way scientists organized elements in the past was by their atomic mass. • To do this, they had to get the mass of a large chunk of the element and calculate the mass of a single atom. • Because there are isotopes of atoms.. (atoms with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus) the atomic ...
... • One way scientists organized elements in the past was by their atomic mass. • To do this, they had to get the mass of a large chunk of the element and calculate the mass of a single atom. • Because there are isotopes of atoms.. (atoms with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus) the atomic ...
Chapter 5 Review Game Questions
... 14) Where are the p block elements on the periodic table? (right) 15) Where is the d-block on the periodic table? (middle) 16) Where is the s block on the periodic table? (left) 17) Half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together? (atomic radius) 18) Elements on the ...
... 14) Where are the p block elements on the periodic table? (right) 15) Where is the d-block on the periodic table? (middle) 16) Where is the s block on the periodic table? (left) 17) Half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together? (atomic radius) 18) Elements on the ...
Sample Questions Sample Questions Standard Atomic Notation
... • Mendeleev began arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic mass and noticed that many elements shared common properties. These elements typically belonged to the same vertical column of his table. • Mendeleev’s arrangement showed a regular pattern. Mendeleev’s periodic law states: ...
... • Mendeleev began arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic mass and noticed that many elements shared common properties. These elements typically belonged to the same vertical column of his table. • Mendeleev’s arrangement showed a regular pattern. Mendeleev’s periodic law states: ...
(periods) to
... particular subshell fall into the same columns (e.g. oxygen and selenium are in the same column because they both have four electrons in the outermost p-subshell ) ...
... particular subshell fall into the same columns (e.g. oxygen and selenium are in the same column because they both have four electrons in the outermost p-subshell ) ...
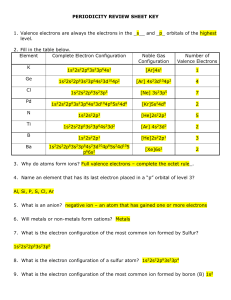
periodicity review sheet key
... Using the graphs from your notes, period table or text book, answer the following with: increases(I), decreases (D), or remains the same (R). __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of ...
... Using the graphs from your notes, period table or text book, answer the following with: increases(I), decreases (D), or remains the same (R). __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of ...
Introduction The Periodic Law
... There is a progression from metals to nonmetals across each period of elements in the periodic table. The diagonal line at the right side of the table shown below separates the elements into two groups: the metals and the nonmetals. The elements that are on the left of this line tend to be metals, w ...
... There is a progression from metals to nonmetals across each period of elements in the periodic table. The diagonal line at the right side of the table shown below separates the elements into two groups: the metals and the nonmetals. The elements that are on the left of this line tend to be metals, w ...
- Catalyst
... in mass number, but not in chemical behavior (much). A sample of the element is treated as though its atoms have an average mass. 4. Compounds are formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in specific ratios, as originally stated by Dalton. ...
... in mass number, but not in chemical behavior (much). A sample of the element is treated as though its atoms have an average mass. 4. Compounds are formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in specific ratios, as originally stated by Dalton. ...
Chapter 4
... • Group 1 • These elements are soft and can be cut with a knife. • They are highly reactive. The will react with both air and water. • They form alkaline/basic solutions (the opposite of acidic solutions). • Their electron configurations all end s1. ...
... • Group 1 • These elements are soft and can be cut with a knife. • They are highly reactive. The will react with both air and water. • They form alkaline/basic solutions (the opposite of acidic solutions). • Their electron configurations all end s1. ...
The Periodic Table
... *As you move across the period, the number of electrons in the outermost orbital increases by one. *In a group, the outermost orbital has the same number of electrons. *Because electrons are the outermost particles in an atom, they are the ones that give an atom it’s properties, so elements with sim ...
... *As you move across the period, the number of electrons in the outermost orbital increases by one. *In a group, the outermost orbital has the same number of electrons. *Because electrons are the outermost particles in an atom, they are the ones that give an atom it’s properties, so elements with sim ...
How Atoms Differ (Section 4.3) part 1
... nuclear charge, so the atom is neutral? • So how many electrons • Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons • How many electons are in an atom of: – Hydrogen? – Lead? – Chlorine? ...
... nuclear charge, so the atom is neutral? • So how many electrons • Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons • How many electons are in an atom of: – Hydrogen? – Lead? – Chlorine? ...
answers
... Remember when we put Mentos in soda and played with oobleck 1. Describe the difference between physical and chemical changes to matter based on the atoms/molecules in the matter. In physical changes to matter, the type of matter does not change. The chemical formula remains the same. However in a ch ...
... Remember when we put Mentos in soda and played with oobleck 1. Describe the difference between physical and chemical changes to matter based on the atoms/molecules in the matter. In physical changes to matter, the type of matter does not change. The chemical formula remains the same. However in a ch ...
Chemistry Terms
... electron By far the lightest of the 3 particles that make up atoms. They orbit the nucleus and have an electric charge of -1.6 × 10-19 Coulombs. electron affinity The tendency of an atom to aquire extra electrons. Elements toward the right side of the periodic table have greater "affinity" for elect ...
... electron By far the lightest of the 3 particles that make up atoms. They orbit the nucleus and have an electric charge of -1.6 × 10-19 Coulombs. electron affinity The tendency of an atom to aquire extra electrons. Elements toward the right side of the periodic table have greater "affinity" for elect ...
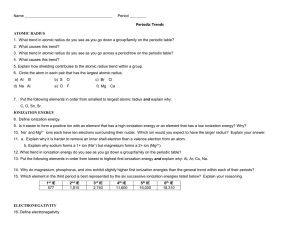
Periodic Trends Worksheet
... a. Which element has the highest first ionization energy? ____________________________ b. Which element has the lowest electronegativity? _________________________________ c. Which element has the least metallic character? _________________________________ d. Which element is the largest atom? _____ ...
... a. Which element has the highest first ionization energy? ____________________________ b. Which element has the lowest electronegativity? _________________________________ c. Which element has the least metallic character? _________________________________ d. Which element is the largest atom? _____ ...
Periodic Trends Review Sheet
... 9. Is it easier to form a positive ion with an element that has a high ionization energy or an element that has a low ionization energy? Why? 10. Na+ and Mg2+ ions each have ten electrons surrounding their nuclei. Which ion would you expect to have the larger radius? Explain your answer. 11. a. Expl ...
... 9. Is it easier to form a positive ion with an element that has a high ionization energy or an element that has a low ionization energy? Why? 10. Na+ and Mg2+ ions each have ten electrons surrounding their nuclei. Which ion would you expect to have the larger radius? Explain your answer. 11. a. Expl ...
Atom and periodic table review
... High ionization energy, do not want to form cations. High electron affinity, want to form anions when bonded to metals. Mostly gases, except for bromine (liquid), and carbon, phosphorus, selenium, and iodine which are solids. Metalloids— zig zag line between the metals and nonmetals on periodic tabl ...
... High ionization energy, do not want to form cations. High electron affinity, want to form anions when bonded to metals. Mostly gases, except for bromine (liquid), and carbon, phosphorus, selenium, and iodine which are solids. Metalloids— zig zag line between the metals and nonmetals on periodic tabl ...
elements and compounds - Hicksville Public Schools
... 8. Circle the element that does NOT belong to the same period. K ...
... 8. Circle the element that does NOT belong to the same period. K ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... The Transition Metals are in groups #3-12. These include most of the familiar metals such as iron, copper, nickel, silver and gold. Most are hard and shiny and are good conductors of electricity. Shade these in green. In groups 13-15 on the Periodic table, only some elements are metals. Most are ...
... The Transition Metals are in groups #3-12. These include most of the familiar metals such as iron, copper, nickel, silver and gold. Most are hard and shiny and are good conductors of electricity. Shade these in green. In groups 13-15 on the Periodic table, only some elements are metals. Most are ...
Parts of the Periodic Table
... than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. • EX: Calcium ...
... than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. • EX: Calcium ...
Chapter 5 – The Periodic Law
... He insisted that elements with similar characteristics be listed in the same groups (vertical columns)…for this reason, he had to leave several blank spaces in his periodic table ...
... He insisted that elements with similar characteristics be listed in the same groups (vertical columns)…for this reason, he had to leave several blank spaces in his periodic table ...